What is DNA polymerase and what does it do?
- Family A includes polymerases involved in DNA string copying or repair. ...
- Family B components process DNA replication during the actual cell division process, providing synthesis of DNA strands during the DNA copying activity. ...
- Family C is the active replicative polymerases for bacteria. ...
What are the 3 main functions of DNA polymerase?
What are the 3 functions of DNA polymerase? These include mismatch repair, nucleotide excision repair, base excision repair, double-strand break repair and inter-strand cross-link repair. The biochemical difference that exists between these polymerases allows them to fulfill distinct roles under these specific conditions of repair. What is the function of DNA polymerase 1 quizlet?
What is the difference between DNA polymerase 1 and 3?
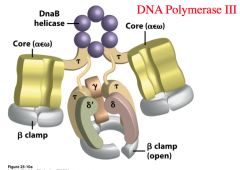
What You Need To Know About DNA Polymerase III
- DNA polymerase III holoenzyme (Pol III HE) is an enzyme that catalyzes elongation of DNA chains during bacterial chromosomal DNA replication.
- It was discovered by Thomas Kornberg and Malcolm Gefter in 1970.
- DNA polymerase 3 is encoded by dnaE, dnaQ and hole genes.
- It belongs to the DNA polymerase family C.
Does DNA polymerase always go the same direction?
Since DNA polymerase requires a free 3′ OH group for initiation of synthesis, it can synthesize in only one direction by extending the 3′ end of the preexisting nucleotide chain. Hence, DNA polymerase moves along the template strand in a 3′-5′ direction, and the daughter strand is formed in a 5′-3′ direction.
See more
What is the type of DNA polymerase?
Classification. On the basis of sequence similarities, DNA polymerases can fall into three groups: type A, type B and type C, which have homology to polA (pol I), polB (pol II) and polC (pol III) from Escherichia coli, respectively [1,2].
Is DNA polymerase is a protein?
DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the three prime (3')-end of a DNA strand, one nucleotide at a time. Every time a cell divides, DNA polymerases are required to duplicate the cell's DNA, so that a copy of the original DNA molecule can be passed to each daughter cell....DNA polymerase.SearchNCBIproteins2 more rows
What type of protein is polymerase?
enzymeA polymerase is an enzyme (EC 2.7. 7.6/7/19/48/49) that synthesizes long chains of polymers or nucleic acids.
What protein structure is DNA polymerase?
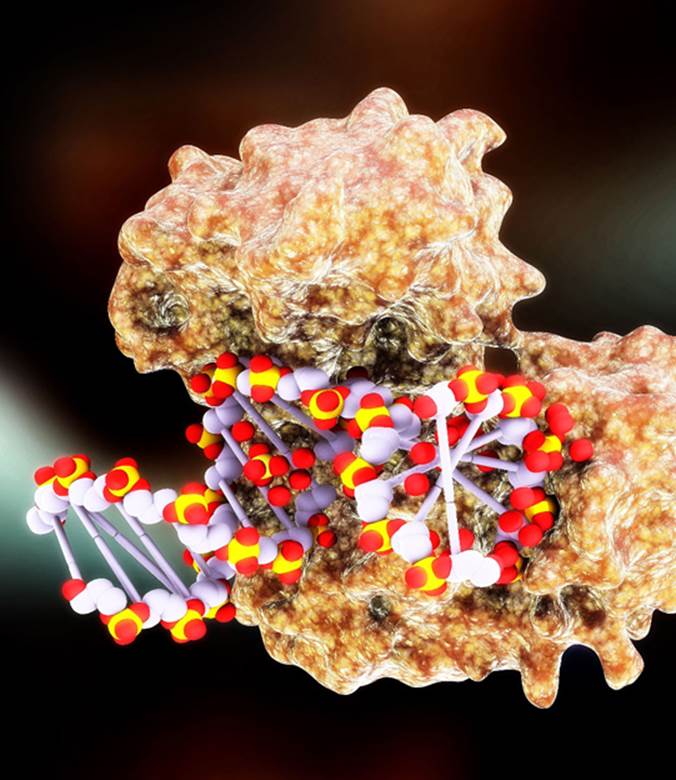
The basic structure of all DNA polymerases consists of subdomains referred to as the palm, fingers, and thumb and resemble an open right hand. The palm contains catalytically essential amino acids in it's active sites. The fingers are essential for nucleotide recognition and binding.
Is polymerase a protein?
As complex molecule composed of protein subunits, RNA polymerase controls the process of transcription, during which the information stored in a molecule of DNA is copied into a new molecule of messenger RNA.
What is a DNA polymerase quizlet?
DNA polymerase - An enzyme that assembles new DNA by copying an existing strand. DNA is double stranded and uses Thymine as a base.
What type of enzyme is polymerase?
DNA polymerase (DNAP) is a type of enzyme that is responsible for forming new copies of DNA, in the form of nucleic acid molecules. Nucleic acids are polymers, which are large molecules made up of smaller, repeating units that are chemically connected to one another.
What is polymerase made of?
The RNA polymerase enzyme is a large complex made up of multiple subunits1. The prokaryotic form of RNA polymerase has four subunits capable of transcribing all types of RNA. In eukaryotes, these enzymes have eight or more subunits that facilitate the attachment and processing of DNA throughout transcription.
What is polymerase and types?
DNA polymerase III – is the main enzyme responsible for replication. Other DNA polymerases take part in repair, removing, primer, proofreading, translesion synthesis. Eukaryotes also contain many different types of DNA polymerase. DNA polymerase 𝝳 and 𝜶 – The main DNA polymerases for nuclear replication.
Which statement about DNA polymerase is correct?
So the correct option is 'it remains active at high temperature'.
What is the function DNA polymerase?
The primary role of DNA polymerases is to accurately and efficiently replicate the genome in order to ensure the maintenance of the genetic information and its faithful transmission through generations.
What is DNA polymerase do?
DNA polymerases are enzymes that create DNA molecules by assembling nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. These enzymes are essential to DNA replication and usually work in pairs to create two identical DNA strands from one original DNA molecule.
Is DNA primer a protein?
A number of DNA viruses, RNA viruses and linear plasmids use small proteins as primers for DNA or RNA synthesis (Salas, 1991). These proteins are covalently attached to the 5′ end of the DNA or RNA genomes.
Is primase a protein?
Archaeal and eukaryote primases are heterodimeric proteins with one large regulatory and one minuscule catalytic subunit. The RNA segments are first synthesized by primase and then elongated by DNA polymerase.
Are enzyme and protein the same?
Enzymes are essentially proteins which increase the rate of a chemical reaction in the body. Proteins are complex macromolecules that are composed of amino acids residues linked together by peptide bonds. Antibodies, hormones and even enzymes are proteins.
Is helicase a protein?
Helicases are motor proteins that couple the hydrolysis of nucleoside triphosphate (NTPase) to nucleic acid unwinding.
How does DNA polymerase work?
To replicate the DNA, DNA polymerase reads sequential bases on a template strand before attaching complimentary bases to the 3' end of a growing ne...
What does DNA polymerase do?
DNA Polymerase is the enzyme responsible for replicating DNA . It "reads" the nucleotide sequence of a template strand and constructs a compliment...
How many types of polymerase are there?
There are three main prokaryotic DNA polymerases: DNA pol I — replaces the RNA primer with DNA DNA pol II — DNA proofreading DNA pol III —...
What is the main DNA polymerase?
In eukaryotes, the main DNA polymerase is DNA Pol III . This enzyme is responsible for the bulk on DNA replication on both the leading and laggin...
What Is DNA Polymerase?
Our body is composed of millions of cells that contain their own copy of our DNA. The amazing thing is that we all started out as one cell with the original copy of our DNA. From that one cell, other cells were produced, and each received a copy of the DNA. So, how did this amazing thing happen? Well, just before a cell splits into two cells, the DNA is copied in a process known as DNA replication. There is replication machinery which includes the enzyme DNA polymerase. DNA polymerase has the responsibility of creating new copies of our DNA. Let's take a closer look at how this happens.
How does DNA polymerase work?
Before DNA polymerase can start copying the DNA, it has to have access to the nucleotide bases that compose the DNA. Our DNA is made of two strands of DNA that are connected to each other by hydrogen bonds. As you may recall, our DNA is normally in the double-helix formation, which looks a lot like a winding staircase. In order for the nucleotides to be exposed, DNA helicase comes in and unwinds the DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds that hold the two strands together.
What happens when RNA primers are used?
The next thing that has to happen is that an RNA primer attaches complementary nucleotide bases, which starts the process of replication on both strands.
How does DNA helicase unwind?
In order for the nucleotides to be exposed, DNA helicase comes in and unwinds the DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds that hold the two strands together.
What is the result of DNA polymerase function?
The result of DNA polymerase function is two copies of DNA that contain one original and one newly synthesized strand of DNA. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account.
What direction does DNA polymerase work?
DNA polymerase will synthesize the DNA in the 5' to 3' direction. This will continue down the length of both of the single strands of DNA. Once the process is complete, DNA polymerase will have made a copy of the DNA.
What is the meaning of each copy of DNA?
Each copy of DNA will be semiconservative, meaning that it will contain one of the template strands as well as one of the newly synthesized strands of DNA. In summary, we have covered what DNA polymerase is and what it does. DNA polymerase is an enzyme that synthesizes new copies of DNA.
What is DNA Polymerase?
A number of molecular biologists originally believed that the first DNA molecule is the reason for life on earth. That sentiment changed after many years of research and experimental work.
DNA Polymerase Structures
More complex cells possess more DNA polymerases; viruses have only 1 DNA pol, prokaryotes have 5 DNA pol (DNA polymerase I, II, III, IV, and V), and eukaryotes have 15 DNA pol, designated with greek letters as DNA pol α, 𝛃, 𝛄, ẟ, ε, ζ, η, θ, ι, 𝛋, λ. 𝛍, and v.
The 2 Main DNA Polymerase Functions
DNA polymerases perform two central functions in organisms: DNA replication and DNA repair. Both activities are essential to the proper development and function of an organism.
Procure High-Caliber Lab Equipment and Consumables with Excedr
DNA polymerases are one of the essential catalytic enzymes involved in DNA replication in different organisms. These enzymes have very different structural and functional properties in different organisms. They are topics of massive interest in many life science laboratories, including biochemistry, molecular biology, and biotechnology labs.
What is DNA polymerase?
DNA polymerase definition. DNA polymerases are a group of enzymes that are used to make copies of DNA templates, essentially used in DNA replication mechanisms. These enzymes make new copies of DNA from existing templates and also function by repairing the synthesized DNA to prevent mutations. DNA polymerase catalyzes the formation ...
What is the structure of DNA polymerase?
Structure of DNA polymerase. The DNA polymerases generally have a conserved structure , and therefore, defining its vital role in the cell function which can not be replaced. DNA polymerases are made up of subdomains resembling an open right hand as palm, fingers, and thumb.
What type of enzyme is used to replicate DNA?
Polymerase α, Polymerase δ, and Polymerase ε. These are the type B Polymerase enzymes and they are the main polymerases applied in DNA replication. Pol α works by binding to the primase enzyme, forming a complex, where they both play a role in initiating replication.
How does DNA polymerase correct mismatches?
They also correct post-replication mismatches by monitoring and repairing the errors, by distinguishing mismatches of the new strand from the template strand sequences.
How does DNA polymerase work?
DNA polymerase acts by synthesizing the new DNA strand by adding new nucleotides that match those of the template, extending the 3′ end of the template chain. Each nucleotide is linked with a phosphodiester bond.
What are the different types of DNA polymerase?
DNA polymerase types. Basically, the types of DNA polymerase are also divided depending on the organism that posses them i.e. eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA polymerases. These types of DNA polymerase are classified based on their characteristics including structural sequences, and functions.
Where is DNA polymerase II located?
The DNA polymerase II is found in the replication fork, to help in directing the activities of other polymerases.
What is the name of the PDB file that contains the viral DNA polymerase?
At upper right is human DNA polymerase, from the PDB file 1zqa . At bottom is a viral DNA polymerase, from the PDB file 1clq . They are quite different in size and shape, but notice how all wrap around the DNA, and enclosing the end of the DNA in a pocket in which the synthetic reaction is performed. These illustrations were created with RasMol.
What color is the DNA strand?
The space between the "fingers" and the "thumb" is just the right size for a DNA helix. But surprisingly, DNA actually fits into the palm when the enzyme is at work. In these pictures, the template strand is colored purple and the new strand is colored green. The enzyme contains three separate active sites.
What happens after repeating the same DNA strand?
After repeating this many times, many identical DNA strands are produced. Our own DNA polymerases, and those from most organisms, would be destroyed by the heating step in this process. But today, DNA polymerase from Thermus aquaticus, a bacterium that lives in hot springs, is used.
How many copies of DNA are made in a test tube?
The tiny sample is placed in a test tube, and DNA polymerase is added to make a copy. Then the sample is heated up momentarily, and the two strands of DNA separate. Then DNA polymerase builds a new double helix from each strand. These two copies are then heated, and duplicated, yielding four copies.
What is the most accurate enzyme?
DNA polymerase is the most accurate enzyme. It creates an exact copy of your DNA each time a cell divides, making less than one mistake in a billion bases. This is far better than information in our own world: imagine reading a thousand novels, and finding only one mistake. The excellent match of cytosine to guanine and adenine to thymine, the language of DNA, provides much of the specificity needed for this high accuracy. But DNA polymerase adds an extra step. After it copies each base, it proofreads it and cuts it out if the base is wrong.
What is the function of a ring-shaped protein?
Some even have a ring-shaped protein that clamps the polymerase to the DNA strand. A single cell often has several different polymerases: complex ones that do the major DNA replication when the cell divides, and simpler ones that help in day-to-day repair and maintenance of the DNA.
What makes a copy of the cell's genome?
DNA Polymerase. DNA polymerase makes an accurate copy of the cell's genome. Taq DNA polymerase, with a short piece of DNA in magenta and green. Download high quality TIFF image.
Prokaryotes
Prokaryotic organisms (organisms without a true nucleus, bounded by a membrane) possess three main DNA polymerases, commonly abbreviated as pol I, II, and III.
Eukaryotes
Eukaryotes (organisms with a true nucleus, delimited by a membrane) have five DNA polymerases, named with letters of the Greek alphabet: α, β, γ, δ and ε.
Arches
New sequencing methods have succeeded in identifying a huge variety of DNA polymerase families. In archaea, specifically, a family of enzymes, called the D family, has been identified that are unique to this group of organisms.
What is DNA replication?
DNA is the molecule that carries all the genetic information of an organism. It is made up of a sugar, a nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine) and a phosphate group.
Reaction
For DNA synthesis to occur, the substrates necessary for the process are required: deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate (dNTP)
Properties of DNA polymerases
All known DNA polymerases share two essential properties associated with the replication process.
Fragments of Okazaki
The first property of DNA polymerases mentioned in the previous section represents a complication for semi-conservative replication. As the two DNA strands run antiparallel, one of them is synthesized discontinuously (the one that would need to be synthesized in the 3'-5 'sense).
Overview
Variation across species
Based on sequence homology, DNA polymerases can be further subdivided into seven different families: A, B, C, D, X, Y, and RT.
Some viruses also encode special DNA polymerases, such as Hepatitis B virus DNA polymerase. These may selectively replicate viral DNA through a variety of mechanisms. Retroviruses encode an unusual DNA polymerase called reverse transcriptase, which is an RNA-dependent DNA poly…
History
In 1956, Arthur Kornberg and colleagues discovered DNA polymerase I (Pol I), in Escherichia coli. They described the DNA replication process by which DNA polymerase copies the base sequence of a template DNA strand. Kornberg was later awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1959 for this work. DNA polymerase II was discovered by Thomas Kornberg (the son of Arthur Kornberg) and Malcolm E. Gefter in 1970 while further elucidating the role of Pol I in E. coli DNA …
Function
The main function of DNA polymerase is to synthesize DNA from deoxyribonucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. The DNA copies are created by the pairing of nucleotides to bases present on each strand of the original DNA molecule. This pairing always occurs in specific combinations, with cytosine along with guanine, and thymine along with adenine, forming two sepa…
See also
• Biological machines
• DNA sequencing
• Enzyme catalysis
• Genetic recombination
• Molecular cloning
Further reading
• Burgers PM, Koonin EV, Bruford E, Blanco L, Burtis KC, Christman MF, Copeland WC, Friedberg EC, Hanaoka F, Hinkle DC, Lawrence CW, Nakanishi M, Ohmori H, Prakash L, Prakash S, Reynaud CA, Sugino A, Todo T, Wang Z, Weill JC, Woodgate R (November 2001). "Eukaryotic DNA polymerases: proposal for a revised nomenclature". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (47): 43487–90. doi:10.1074/jbc.R100056200. PMID 11579108.
External links
• DNA+polymerases at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
• PDB Molecule of the Month DNA polymerase
• Unusual repair mechanism in DNA polymerase lambda, Ohio State University, July 25, 2006.