What are arrector pili muscles?
The arrector pili muscles are small muscles attached to hair follicles in mammals. Contraction of these muscles causes the hairs to stand on end, known colloquially as goose bumps .
What type of tissue is involved in muscle contraction?
Muscle tissue that activates arrector pili muscles to stand hairs on end Smooth muscle tissue Performs very slow, sometimes rhythmic, contractions Skeletal muscle tissue
What causes goose bumps on the arrector pili?
[edit on Wikidata] The arrector pili muscles are small muscles attached to hair follicles in mammals. Contraction of these muscles causes the hairs to stand on end, known colloquially as goose bumps.
What causes the arrector pili to contract?
Contraction of the arrector pili is involuntary. Stresses such as cold and fear may stimulate the autonomic nervous system and cause contraction — making the hair stand on end. In humans, the result is called goose bumps.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3158/XNQJt48ZgGFD38ZH1uXGg_Muscle_Bundle.png)
Is arrector pili muscle skeletal muscle?
The arrector pili consists of smooth muscle tissue.
What kind of muscle is Arrector?
The arrector pili muscles, also known as hair erector muscles, are small muscles attached to hair follicles in mammals. Contraction of these muscles causes the hairs to stand on end, known colloquially as goose bumps (piloerection).
Where is the origin of the arrector pili muscle?
Conclusion: At the isthmus level, above their follicular attachments, the arrector pili muscles that originate from their respective follicles join together, forming a single muscular structure that extends upward to its superior attachment zone.
Is the arrector pili muscle voluntary or involuntary?
the standing of hair happens without us commanding. Therefore, arrector pili muscles are involuntary. Thus, this is the correct option.
What is the arrector pili muscle quizlet?
Arrector Pili muscle. The arrector pili muscles are small muscles attached to hair follicles in mammals. Contraction of these muscles causes the hairs to stand on end, known colloquially as goose bumps.
What describes the arrector pili muscle Milady?
arrector pili muscles. small, involuntary muscles in the base of the hair follicle that cause goose flesh, sometimes called goose bumps, and papillae.
Which fibers stimulate the arrector pili muscle?
CardsTerm The largest organ of the body is:Definition SkinTerm Identify the slender outgrowth of the scalp.Definition HairTerm Which fibers stimulate the arrector pili muscles?Definition Motor NervesTerm Which cells in the basal layer produce pigment granules?Definition melanocytes98 more rows•Apr 28, 2010
How do arrector pili muscles contract?
Arrector pili muscles attach to the bulge region of hair follicles where hair follicle stem cells (HFSCs) reside. Arrector pili muscles are enwrapped by sympathetic pilomotor nerves, which release the neurotransmitter norepinephrine (NE) to trigger muscle contraction and cause hairs to become erect in response to cold.
What causes arrector pili muscles to contract?
Under physiological or emotional stress, such as cold or fright, autonomic nerve endings stimulate the arrector pili muscles to contract, which pulls the hair shafts perpendicular to the skin surface. This action causes “goose bumps” or “gooseflesh” because the skin around the shaft forms slight elevations.
Is smooth muscle voluntary?
Smooth muscle fibers are located in walls of hollow visceral organs (such as the liver, pancreas, and intestines), except the heart, appear spindle-shaped, and are also under involuntary control.
What muscle tissue causes goosebumps?
arrector pili musclesGoosebumps occur when tiny muscles in our skin's hair follicles, called arrector pili muscles, pull hair upright. For animals with thick fur, this response helps keep them warm. But it doesn't do so for people.
What is it called when you give yourself goosebumps?
Autonomic nervous systems in the human body are named for their operation outside of conscious control. One rare exception is voluntarily generated piloerection (VGP)—the conscious ability to induce goosebumps—whose physiological study, to our knowledge, is confined to three single-individual case studies.
What is smooth muscle made of?
Smooth muscle consists of thick and thin filaments that are not arranged into sarcomeres giving it a non-striated pattern. On microscopic examination, it will appear homogenous. Smooth muscle cytoplasm contains a large amount of actin and myosin. Actin and myosin act as the main proteins involved in muscle contraction.
What does Arrector mean?
[ah-rek´tor] (pl. arrecto´res) (L.) raising, or that which raises; an erector muscle.
What are smooth muscle cells?
A smooth muscle cell is a spindle-shaped myocyte with a wide middle and tapering ends, and a single nucleus. Like striated muscle, smooth muscle can tense and relax. In the relaxed state, each cell is 30–200 micrometers in length, some thousands of times shorter than a skeletal muscle cell.
What are the functions of smooth muscle?
Smooth muscles move food through the digestive tract. Folds in the stomach and small intestine, which are made of smooth muscle, help the body better absorb nutrients. Smooth muscle composes all sphincters in the digestive system. In the bladder, smooth muscle helps to push out urine.
Where does the term "arrector pili" come from?
The term "arrector pili" comes from Latin. It translates to "hair erector".
What is the muscle that holds hair on end called?
Contraction of these muscles causes the hairs to stand on end, known colloquially as goose bumps (piloerection).
What is the name of the muscle that makes hair stand on end?
Contraction of these muscles causes the hairs to stand on end, known colloquially as goose bumps (piloerection).
What causes muscle contraction?
The contraction of the muscle is involuntary. Stresses such as cold, fear etc. may stimulate the sympathetic nervous system, and thus cause muscle contraction.
Which division of the nervous system innervates the follicle?
Each is innervated by the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. The muscle attaches to the follicular stem cell niche in the follicular bulge, splitting at their deep end to encircle the follicle.
Which muscle tissue has the same filaments as the muscle fiber?
However, smooth muscle tissue does consist of the same thin (actin) filaments and thick (myosin) filaments found in both skeletal and cardiac muscle tissue, which work to contract the muscle fiber via a sliding filament mechanism.
Which muscle type is responsible for contraction?
Cardiac Muscle Contraction Mechanism. Cardiac muscle also contains myofibrils and sarcomeres, which not only enable contraction, but they also create the striations (striped pattern) that characterize both cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue.
Why does smooth muscle not have striations?
Because smooth muscle lacks myofibrils and sarcomeres, it does not contain the striations (or striped pattern) that characterizes both skeletal and cardiac muscle tissue. And that’s an important point to remember for exams: smooth muscle is the only muscle tissue type that does not contain striations, and that’s why it’s called “smooth.”
What is the structure of skeletal muscle?
Skeletal Muscle Structure. Each skeletal muscle is considered an organ, and it’s made up of connective tissue layers, muscle fibers, blood vessels, and nerves. Skeletal muscles attach to the bones through tendons or through a direct attachment. As you look at this muscle diagram, you’ll notice an outer layer of connective tissue called epimysium.
What type of muscle tissue is most commonly attached to bones?
Skeletal Muscle Tissue. Skeletal muscles most commonly attach to bones, and they help you move your body. Unlike the other two types of muscle tissue, skeletal muscles contract on a voluntary basis via the somatic nervous system, allowing you to move your body at will. Skeletal muscles also serve important functions, ...
How many nuclei are in skeletal muscle?
Another difference is that skeletal muscle contains multiple nuclei that are scattered around the peripheral portion of the muscle cells, whereas cardiac muscle contains only 1-2 nuclei, which are located near the center of the cell.
How does smooth muscle work?
For example, in most of the digestive tract, smooth muscle cells are formed in two layers with different orientations, which work together to propel food down the digestive tract, a process known as peristalsis.
What is muscle tissue composed of?
Muscle tissue composed of branching cells and intercalated discs
Where is muscle tissue found?
Muscle tissue found only in the heart
What ions are responsible for binding myosin heads to actin filaments?
Calcium ions trigger the binding of myosin heads to actin filaments.
Which molecule binds to receptors on the sarcolemma and allows passage of sodium?
Acetylcholine (ACh) binds to receptors on the sarcolemma and allows passage of sodium ions into the cell.
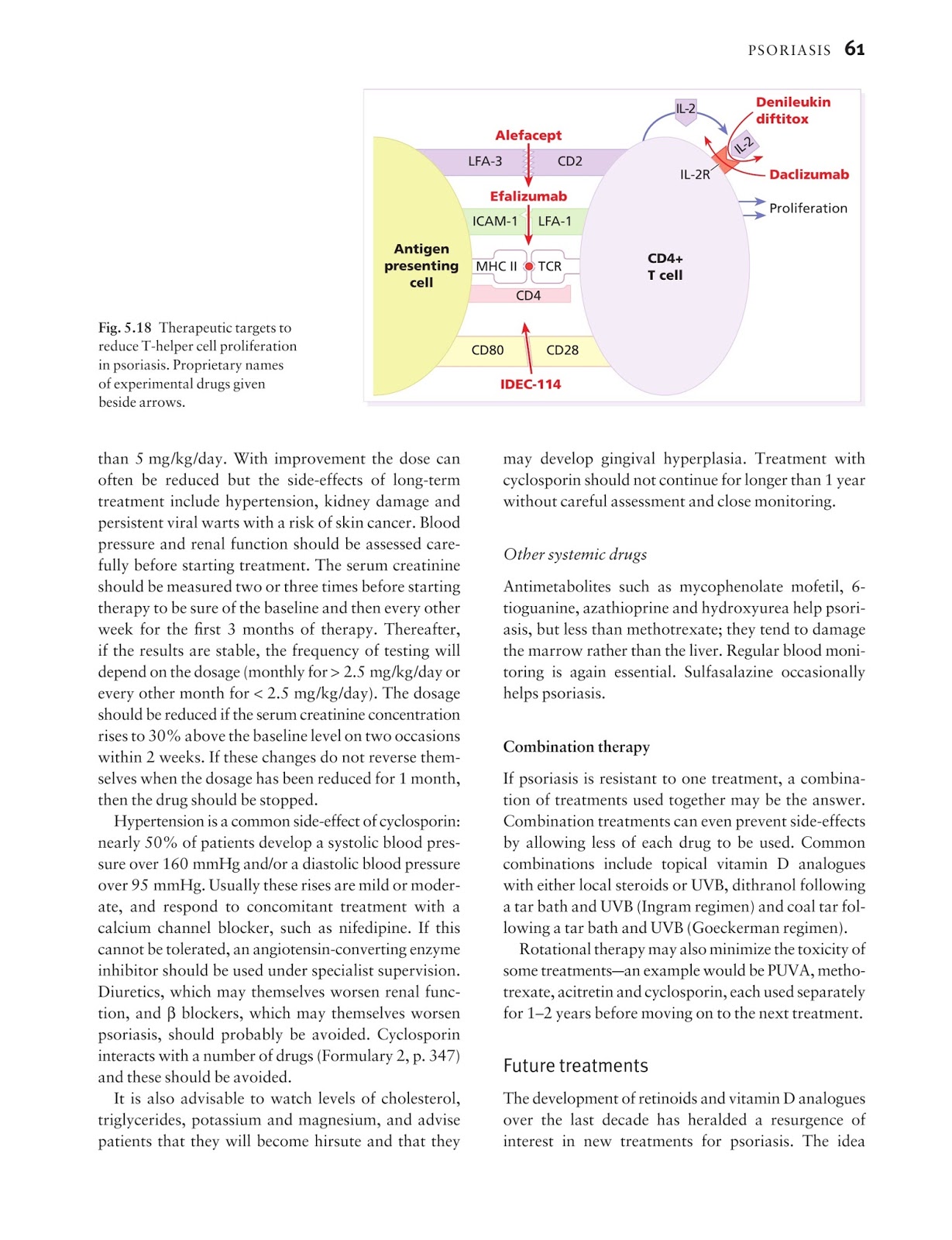
INTRODUCTION
Although many cell types are now known to contain the contractile proteins actin and myosin, some cells are specialized for contraction. These cells are usually derived from mesoderm, although the most primitive muscle cells are thought to have been specialized ectodermal cells, e.g. the dilator pupilae of the eye.
OBJECTIVES OF THE MUSCLE LAB
Describe the characteristics of muscle tissue as compared with the other basic tissues.
LAB GUIDE
In distinguishing the different types of muscle the following characteristics can be compared: cross-striations, position of nucleus in the cells, number of nuclei within a cell, branching of the cells, cell junctions and cross-sectional appearance.
STUDY QUESTIONS
Concerning the distinguishing characteristics of the three types of muscle:- (Check the correct responses.) Unlike striated muscles, smooth muscle uses microtubules and kinesin to generate a contraction force. Calveoli are found on smooth and cardiac muscle cells Intercalated disks are found in any striated muscle that has a high, continuous work load. Skeletal muscles have different myosins depending on the function of the muscle. Cardiac muscles communicate electrically via gap junctions..

Overview
Structure
Each arrector pili is composed of a bundle of smooth muscle fibres which attach to several follicles (a follicular unit). Each is innervated by the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. The muscle attaches to the follicular stem cell niche in the follicular bulge, splitting at their deep end to encircle the follicle.
Function
The contraction of the muscle is involuntary. Stresses such as cold, fear etc. may stimulate the sympathetic nervous system, and thus cause muscle contraction.
Contraction of arrector pili muscles have a principal function in the majority of mammals of providing thermal insulation. Air becomes trapped between the erect hairs, helping the animal retain heat.
History
The term "arrector pili" comes from Latin. It translates to "hair erector".
Additional images
• Insertion of sebaceous glands into hair shaft
• Cross-section of all skin layers
Notes
1. ^ "Anatomy of the Skin | SEER Training". training.seer.cancer.gov. Retrieved 2021-01-21.
2. ^ David H. Cormack (1 June 2001). Essential histology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 1–. ISBN 978-0-7817-1668-0. Retrieved 15 May 2011.
3. ^ Fujiwara, Hironobu; Ferreira, Manuela; Donati, Giacomo; Marciano, Denise K.; Linton, James M.; Sato, Yuya; Hartner, Andrea; Sekiguchi, Kiyotoshi; Reichardt, Louis F.; Watt, Fiona M. (2011-02-18). "The Basement Membrane of Hair Follicle Stem …