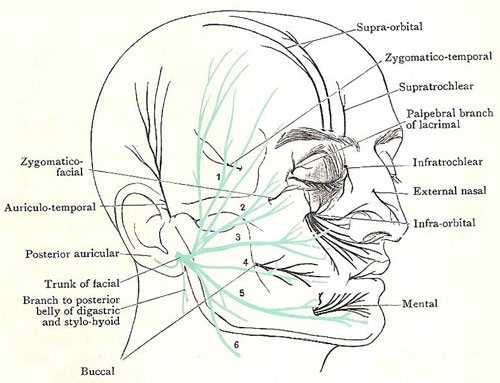
What are the five major branches of the facial nerve?
Within the parotid gland, the nerve terminates by splitting into five branches:
- Temporal branch
- Zygomatic branch
- Buccal branch
- Marginal mandibular branch
- Cervical branch
What nerve serves the face?
- Facial nerve (CN VII), which provides motor innervation to the muscles of the face
- Trigeminal nerve (CN V), which provides sensory innervation to the face via its ophthalmic division (CN V1), maxillary division (CN V2) and mandibular division (CN V3)
- The cervical plexus, which provides innervation to the scalp
Does the facial nerve innervate the skin of the face?
There are close functional and anatomical relationships between cranial nerves V and VII in both their sensory and motor divisions. Sensation on the face is innervated by the trigeminal nerves (V) as are the muscles of mastication, but the muscles of facial expression are innervated mainly by the facial nerve (VII) as is the sensation of taste.
What are the symptoms of facial nerve damage?
Trigeminal neuralgia symptoms may include one or more of these patterns:
- Episodes of severe, shooting or jabbing pain that may feel like an electric shock
- Spontaneous attacks of pain or attacks triggered by things such as touching the face, chewing, speaking or brushing teeth
- Attacks of pain lasting from a few seconds to several minutes
- Pain that occurs with facial spasms

Is facial nerve sensory or motor?
The facial nerve carries both motor and sensory fibers. Motor axons innervate the muscles of facial expression and the stapedius muscle. Parasympathetic fibers go to the ganglia that supply glands in the oral cavity and the lacrimal gland.
Is facial nerve autonomic or somatic?
General visceral efferent fibers in the facial nerve are involved in parasympathetic component of the autonomic nervous system and play an important role in the innervation of the lacrimal gland, nasal and palatine glands as well as the submandibular and sublingual glands.
Is facial nerve central or peripheral?
The facial muscles are innervated peripherally (infranuclear innervation) by the ipsilateral 7th cranial nerve and centrally (supranuclear innervation) by the contralateral cerebral cortex. Central innervation tends to be bilateral for the upper face (eg, forehead muscles) and unilateral for the lower face.
What is the facial nerve known as?
the seventh cranial nerveThe facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue.
Which cranial nerves are somatic?
Cranial nerve III, IV, and VI (oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens nerves, respectively) are general somatic efferent (GSE) nerves responsible for innervating the extraocular muscles within the orbit.
Are any cranial nerves somatic?
In fact, three cranial nerves carry purely sensory information and four cranial nerves carry almost entirely somatic motor information. The remaining cranial nerves carry some combination of sensory, somatic motor and parasympathetic information.
Is Bell's palsy CNS or PNS?
Mechanism of Injury: Bell's Palsy is an acute facial paralysis caused by inflammation of the seventh cranial nerve (facial nerve). This disorder is an idiopathic peripheral nervous system (PNS) impairment, and the prognosis is favorable.
What is the difference between peripheral and central facial palsy?
In a central lesion, the forehead should lift symmetrically, due to bilateral cortical innervation of the frontalis muscle. However, in a peripheral lesion, the patient will be unable to wrinkle their forehead on one side, or have fewer wrinkles on that side.
What are the types of cranial nerves?
What are the types of cranial nerves?Olfactory nerve: Sense of smell.Optic nerve: Ability to see.Oculomotor nerve: Ability to move and blink your eyes.Trochlear nerve: Ability to move your eyes up and down or back and forth.Trigeminal nerve: Sensations in your face and cheeks, taste and jaw movements.More items...•
Is cranial nerve 5 sensory or motor?
Excerpt. The trigeminal nerve is the fifth cranial nerve (CN V). Its primary function is to provide sensory and motor innervation to the face. The trigeminal nerve consists of three branches on either side that extend to different territories of the face.
Is the mandibular nerve sensory or motor?
The mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve, also referred to as the mandibular nerve, is a mixed sensory and branchial motor nerve. It is also the largest of the three branches of the trigeminal nerve. The sensory root arises from the lateral aspect of the ganglion, with the motor division lying deeper.
Where is the facial nerve?
The facial nerve exits the base of the skull at the stylomastoid foramen, which is an opening in the bone located near the base of the ear.
What is an example of somatic nervous system?
Your sense of touch below your neck uses your somatic nervous system to reach your spinal cord, which then relays signals to your brain. Movement control. Your body's muscles rely on signals that give them instructions to help you move around.
Which is an example of an autonomic reflex?
Everyday examples include breathing, swallowing, and sexual arousal, and in some cases functions such as heart rate.
What is the difference between autonomic and somatic nerves?
The somatic nervous system consists of nerves that go to the skin and muscles and is involved in conscious activities. The autonomic nervous system consists of nerves that connect the CNS to the visceral organs such as the heart, stomach, and intestines.
Can a nerve be both somatic and autonomic?
The peripheral nervous system carries both somatic and autonomic signals, innervating the entire periphery (not just skeletal muscle). The sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the nervous system are both autonomic.
What is the facial nerve?
The facial nerve is one of a group of nerves called the cranial nerves (CN), twelve pairs of nerves that , with the exception of the spinal accessory nerve (CN XI), originate in the brain and contribute to the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
What is the function of the facial nerve?
While it is indeed responsible for innervating the muscles of facial expression, the facial nerve is a complex structure containing many fiber types with a variety of functions, including motor, sensory, and autonomic. The following article will discuss the importance and versatility facial nerve.
Where do facial nerve fibers travel?
The fibers travel towards the floor of IV ventricle and go around the abducens nucleus and descend. The facial nerve emerges from the lateral surface of brainstem at the pontine-medullary junction between the VI and VIII nerves.
What is the vascular damage of the facial nerve?
Vascular damage to the facial nerve usually occurs at the supranuclear, pontine, and (rarely) cerebellopontine angle. Upper motor neuron (UMN) lesions occur in strokes and can easily be differentiated with lower motor neuron (LMN) lesions by their presentation. A LMN lesion causes paralysis of the whole side of face, ...
What are the components of the facial nerve?
The facial nerve contains many different types of fibers, including general sensory (afferent) fibers, special sensory fibers, visceral/autonomic motor (efferent) fibers, and somatic motor fibers. General sensory fibers in the facial nerve are responsible for transmitting signals to the brain from ...
Which nerve is responsible for innervating the lacrimal gland, submandibular gland, sublingual?
Visceral/autonomic motor fibers in the facial nerve are responsible for innervating the lacrimal gland, submandibular gland, sublingual gland, and the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity and hard and soft palates, allowing for production of tears, saliva, etc., from these locations.
Which nerve contains motor fibers?
the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) Some of these contain motor fibers, some contain autonomic fibers, some contain somatic sensory fibers, some contain special sensory fibers, and some contain combinations of a number of these aforementioned fiber types.
Where is the facial nerve located?
It is one of the longest cranial nerves, extending from the brainstem to the terminal (end) branches, which are located throughout the face. Several structures of the facial nerve—described as nuclei, segments, and branches—produce the four components of facial nerve function. 1
What are the branches of the facial nerve?
Most of the branches of the facial nerve are motor branches that stimulate the movement of the facial muscles. These muscles include: 1 the stapedius muscle in the ear, which controls the vibration of a bone in the ear to help moderate hearing 2 the stylohyoid muscle in the neck, which is involved with swallowing 3 the posterior belly of the digastric muscle, which is involved with movements of chewing, swallowing, talking, and breathing 4 the muscles of facial expression are controlled by the facial nerve 5 the frontalis muscle moves the forehead and eyebrows 6 the orbiculus oculi, which controls the muscles of the eyelids 7 the buccinator muscle, which moves the mouth and cheek 8 the orbicularis oris, which controls movements of the mouth and lips 9 the platysma, which is a large muscle in the neck that controls movements of the neck and jaw 10 the occipitalis muscle, which is located in the back of the head and moves the scalp skin posteriorly.
How many sections does the facial nerve have?
The facial nerve has: six major sections (described as segments) along the pathway from the brainstem to the terminal branches in the face. divisions and subdivisions (also called branches), which are small nerves in and around the face that merge along the segments into the main facial nerve.
How to recover from facial nerve damage?
If you have had any type of facial nerve disease or injury, recovery includes physical therapy , which can help your face and mouth muscles regain at least some of their strength. 10 The extent of recovery depends on the type and severity of the damage, how much of the nerve was involved, and the type of disease.
Why does the forehead move?
The fascinating thing about this redundancy is that if the facial nerve can’t function properly due to a problem in the brain, the muscles of the forehead can still move. When the area of the brain that controls the face becomes damaged, only the lower two-thirds of the face becomes weak.
What neurotransmitter is released by the facial nerve?
The motor branches of the facial nerve activate muscles to move by releasing acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that binds to the surface of muscle cells. Activated muscles respond by contracting (becoming shorter in length), pulling or twisting nearby joints and bones, and ultimately producing movement of the face.
What nerves regulate the mouth and face?
Associated Conditions. Rehabilitation. The facial nerve and its branches regulate a number of functions of the mouth and face. Most of its divisions stimulate muscles that allow eyelids to open and close, as well as facial movements.
What is the name of the facial nerve?
The facial and intermediate nerves can be collectively referred to as the nervus intermediofacialis.
Where is the facial nerve located?
Intra operatively the facial nerve is recognized at 3 constant landmarks: At the tip of tragus where the nerve is 1 cm deep and inferior. At the posterior belly of digastric by tracing this backwards to the tympanic plate, the nerve can be found between these two structures.
What is the function of parasympathetic innervation?
Parasympathetic innervation serves to increase the flow of saliva from these glands. It also supplies parasympathetic innervation to the nasal mucosa and the lacrimal gland via the pterygopalatine ganglion. The parasympathetic fibers that travel in the facial nerve originate in the superior salivatory nucleus .
How many segments are there in the facial nerve?
The path of the facial nerve can be divided into six segments: intracranial (cisternal) segment. meatal (canalicular) segment (within the internal auditory canal) labyrinthine segment (internal auditory canal to geniculate ganglion) tympanic segment (from geniculate ganglion to pyramidal eminence)
Which nerve is located in the labyrinthine segment?
The labyrinthine segment is very short, and ends where the facial nerve forms a bend known as the geniculum of the facial nerve ( genu meaning knee), which contains the geniculate ganglion for sensory nerve bodies. The first branch of the facial nerve , the greater petrosal nerve, arises here from the geniculate ganglion. The greater petrosal nerve runs through the pterygoid canal and synapses at the pterygopalatine ganglion. Postsynaptic fibers of the greater petrosal nerve innervate the lacrimal gland .
Which nerve runs through the pterygoid canal?
The greater petrosal nerve runs through the pterygoid canal and synapses at the pterygopalatine ganglion. Postsynaptic fibers of the greater petrosal nerve innervate the lacrimal gland . In the tympanic segment, the facial nerve runs through the tympanic cavity, medial to the incus .
What is the second arch of the facial nerve called?
Development. The facial nerve is developmentally derived from the second pharyngeal arch, or branchial arch. The second arch is called the hyoid arch because it contributes to the formation of the lesser horn and upper body of the hyoid bone (the rest of the hyoid is formed by the third arch).
What is the facial nerve?
The facial nerve is also known as the seventh cranial nerve (CN7). This nerve performs two major functions. It conveys some sensory information from the tongue and the interior of the mouth. Specifically, CN7 serves about two-thirds of the tongue’s tip. The nerve extends from the brain stem, at the pons and the medulla.
What nerve innervates facial muscles?
It conveys some sensory information from the tongue and the interior of the mouth. Specifically, CN7 serves about two-thirds of the tongue’s tip. The nerve extends from the brain stem, at the pons and the medulla. Also, this nerve innervates facial muscles, controlling how to contract and produce facial expressions.
What causes facial nerve paralysis?
This condition, as well as other forms of paralysis, is sometimes triggered by a viral infection or complications of Lyme disease. Last medically reviewed on January 23, 2018.
Which nerves are involved in the CN7?
During its course, CN7 splits into several branches. The greater petrosal nerve serves the lacrimal gland (the gland that produces tears) and the nasal cavity, as well sphenoid, frontal, maxillary, and ethmoid sinuses (cavities in the skull).
Which nerve is located in the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular divisions?
The sensory root of your trigeminal nerve branches into the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular divisions. The motor root of your trigeminal nerve passes below the sensory root and is only distributed into the mandibular division. VI. Abducens nerve.
Which nerve is responsible for vision?
The optic nerve is the sensory nerve that involves vision.
What are the functions of the cranial nerves?
Their functions are usually categorized as being either sensory or motor. Sensory nerves are involved with your senses, such as smell, hearing, and touch. Motor nerves control the movement and function of muscles or glands. Keep reading to learn more about each of the 12 cranial nerves and how they function.
What is the function of the oculomotor nerve?
The oculomotor nerve has two different motor functions: muscle function and pupil response. Muscle function. Your oculomotor nerve provides motor function to four of the six muscles around your eyes. These muscles help your eyes move and focus on objects.
How many cranial nerves are there?
What are cranial nerves? Your cranial nerves are pairs of nerves that connect your brain to different parts of your head, neck, and trunk. There are 12 of them, each named for their function or structure. Each nerve also has a corresponding Roman numeral between I and XII.
How many divisions does the trigeminal nerve have?
The trigeminal nerve has three divisions, which are:
Which nerve transmits sensory information to your brain regarding smells that you encounter?
The olfactory nerve transmits sensory information to your brain regarding smells that you encounter.
Symptoms
Facial nerve disorders can cause weakness on one or both sides of your face. You might lose your facial expressions and find it difficult to eat, drink and speak clearly. It can also become difficult to close your eye and blink, which can lead to damage to your cornea.
Disorders caused by infection
This is the most common cause of facial paralysis - around 80% of all cases. It's also known as idiopathic unilateral facial paralysis and 15% of these patients have partial facial weakness.
Other causes
A traumatic injury to your head or face is one of the most common causes of severe permanent facial paralysis. In particular, fractures through the temporal bone of your skull are commonly associated with injury to the facial nerve, as well as injury to the labyrinth leading to hearing loss and vertigo.
