The components involved in translation are
- mRNA
- ribosomes,
- tRNA and
- aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases.
Full Answer
What is the role of RNA in transcription and translation?
May 22, 2020 · There are 4 types of RNA, each encoded by its own type of gene: mRNA - Messenger RNA: Encodes amino acid sequence of a polypeptide. tRNA - Transfer RNA: Brings amino acids to ribosomes during translation. rRNA - Ribosomal RNA: With ribosomal proteins, makes up the ribosomes, the organelles that translate the mRNA.
What is the role of tRNA and rRNA in translation?
Translation is when mRNA molecules from transcription are converted into a series of amino acids that will make a new protein. This is done with …
What are the roles of RNA and DNA?
What types of RNA are involved in translation? a-mRNA: involved in... Image transcription text What types of RNA are involved in translation? a-mRNA: involved in transcription. Brings information from DNA in nucleus to cytoplasm where other RNA are located a-tRNA: matched anticodons with the codons on the mRNA and release... Show more ... Show more
What role does transfer RNA have in translation?
Nov 25, 1996 · Translation is the process that takes the information passed from DNA as messenger RNA and turns it into a series of amino acids bound together with peptide bonds. It is essentially a translation from one code (nucleotide sequence) to …

What type of RNA is used in translation?
transfer RNA (tRNA)transfer RNA (tRNA) – a type of RNA that is folded into a three-dimensional structure. tRNA carries and transfers an amino acid to the polypeptide chain being assembled during translation.
What types of RNA are involved in transcription?
Messenger RNA (or mRNA) has the main role in transcription, or the first step in making a protein from a DNA blueprint. The mRNA is made up of nucleotides found in the nucleus that come together to make a complementary sequence to the DNA found there.Dec 8, 2017
What are the three types of RNA molecules involved in translation What roles do each of them play in this process?
Three RNAsmRNA (messenger RNA): Produced during transcription. ... rRNA (ribosomal RNA): Together with proteins, composes the ribosome, the organelles that are the site of protein synthesis.tRNA (transfer RNA): Brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome during translation.Dec 5, 2014
What are the 4 types of RNA?
On the basis of molecular size and function, the four types RNA are : (i) Messenger RNA (mRNA) (ii) Transfer RNA (tRNA) (iii) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) (iv) Heterogenous nuclear RNA (hn RNA).
What happens when a ribosome reaches a stop code?
When the ribosome reaches one of the "stop" codes, the ribosome releases both the polypeptide and the mRNA. This polypeptide will twist into its native conformation and begin to act as a protein in the cells metabolism. The ribosome binds to mRNA at a specific area.
How does the ribosome match the mRNA codon?
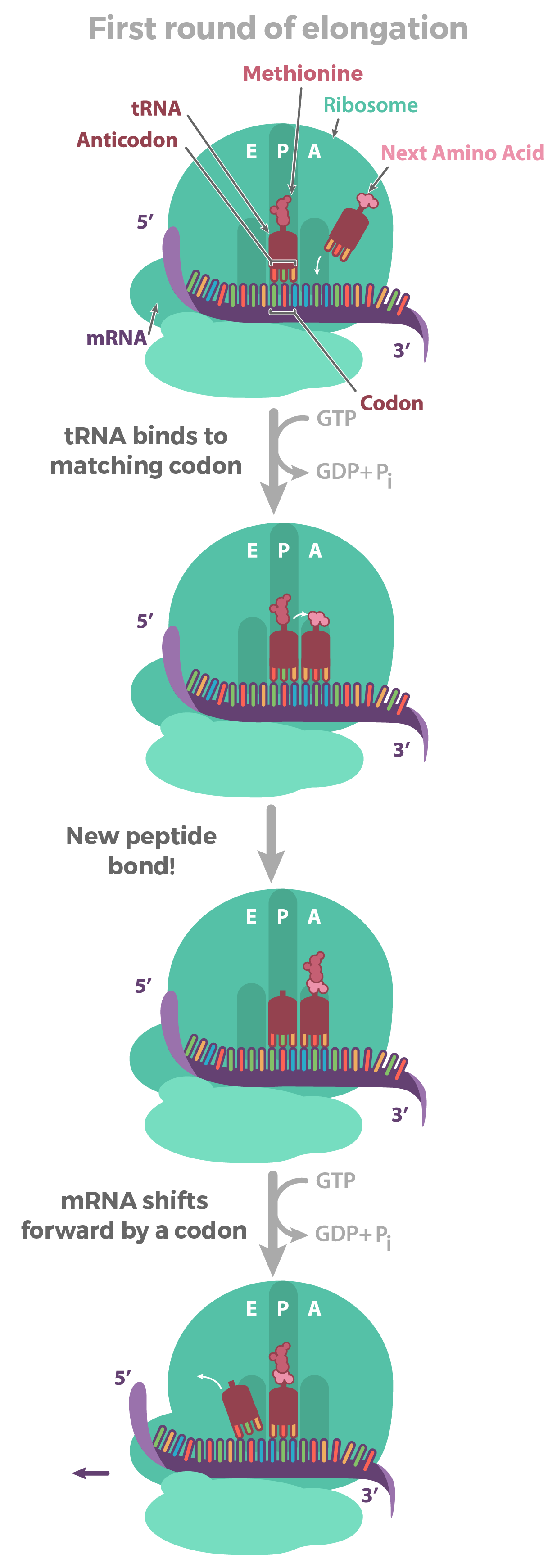
The ribosome starts matching tRNA anticodon sequences to the mRNA codon sequence. Each time a new tRNA comes into the ribosome, the amino acid that it was carrying gets added to the elongating polypeptide chain. The ribosome continues until it hits a stop sequence, then it releases the polypeptide and the mRNA.
How many bases does a ribosome have?
The ribosome matches the base sequence on the mRNA in sets of three bases (called codons) to tRNA molecules that have the three complementary bases in their anticodon regions. Again, the base-pairing rule is important in this recognition (A binds to U and C binds to G).
What happens to the ribosome when it hits a stop sequence?
The ribosome continues until it hits a stop sequence, then it releases the polypeptide and the mRNA. The polypeptide forms into its native shape and starts acting as a functional protein in the cell. (from Biology 101, link http://edtech.clas.pdx.edu/gene_expression_tutorial/translation.html, John Rueter 11/25/96)
What is the process of translating DNA into amino acids?
Translation is the process that takes the information passed from DNA as messenger RNA and turns it into a series of amino acids bound together with peptide bonds. It is essentially a translation from one code (nucleotide sequence) to another code (amino acid sequence). The ribosome is the site of this action, just as RNA polymerase was the site ...
What is messenger RNA?
Translation is the process that takes the information passed from DNA as messenger RNA and turns it into a series of amino acids bound together with peptide bonds.
What is rRNA in a ribosome?
rRNA - ribosomal RNA is one of the structural components of the ribosome. Its sequence is the compliment of regions in the mRNA so that the ribosome can match with and bind to an mRNA it will make a protein from.
What is the function of RNA transfer?
Transfer RNA brings or transfers amino acids to the ribosome that corresponds to each three-nucleotide codon of rRNA. The amino acids then can be joined together and processed to make polypeptides and proteins. Helmenstine, Anne Marie, Ph.D. "The 3 Types of RNA and Their Functions.".
What is the function of mRNA?
mRNA transcribes the genetic code from DNA into a form that can be read and used to make proteins. mRNA carries genetic information from the nucleus to the cytoplasm of a cell .
What are the three types of RNA?
They are messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA. Dr. Helmenstine holds a Ph.D. in biomedical sciences and is a science writer, educator, and consultant. She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels. One common homework and test question asks students to name the three types of RNA and list their functions.
