
Testing and Screening for Fragile X
- Reproductive carrier screening. Genetic carrier screening helps people find out whether they have a chance of having a child with a genetic condition, such as Ffragile X syndrome.
- Preimplantation Genetic Testing. ...
- Testing during pregnancy. ...
- Testing after birth. ...
What type of screening is done for Fragile X?
What type of screening is done for Fragile X? Tests for fragile X in pregnancy include: Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) — this test is usually done between weeks 10 and 12 of the pregnancy. It checks cells from the placenta for the FMR1 gene.
What type of screening is done for Fragile X syndrome?
The test that is required is called DNA studies for fragile X syndrome. This is generally a blood test, although some laboratories offer testing via a cheek swab or saliva sample. A general practitioner, paediatrician or any medical doctor can order the test for a patient. The blood sample can be collected by the doctor or a pathology centre.
How much does fragile X test cost?
Test results are usually available approximately 4 to 8 weeks after the sample is taken, but the time taken can vary. The cost of the genetic test for Fragile X alone is approx. $150-$200. Where there is a family history of Fragile X-associated disorders or where a Fragile X-associated disorder is suspected testing may be covered under Medicare.
What is the life expectancy of Fragile X syndrome?
Life expectancy for people with fragile X syndrome is generally normal. Many affected people participate in an active lifestyle and have good health. Some people are more prone to a number of medical problems, such as ear infections and/or seizures. Regular medical checkups and awareness of increased health risks may improve the outlook for affected people.
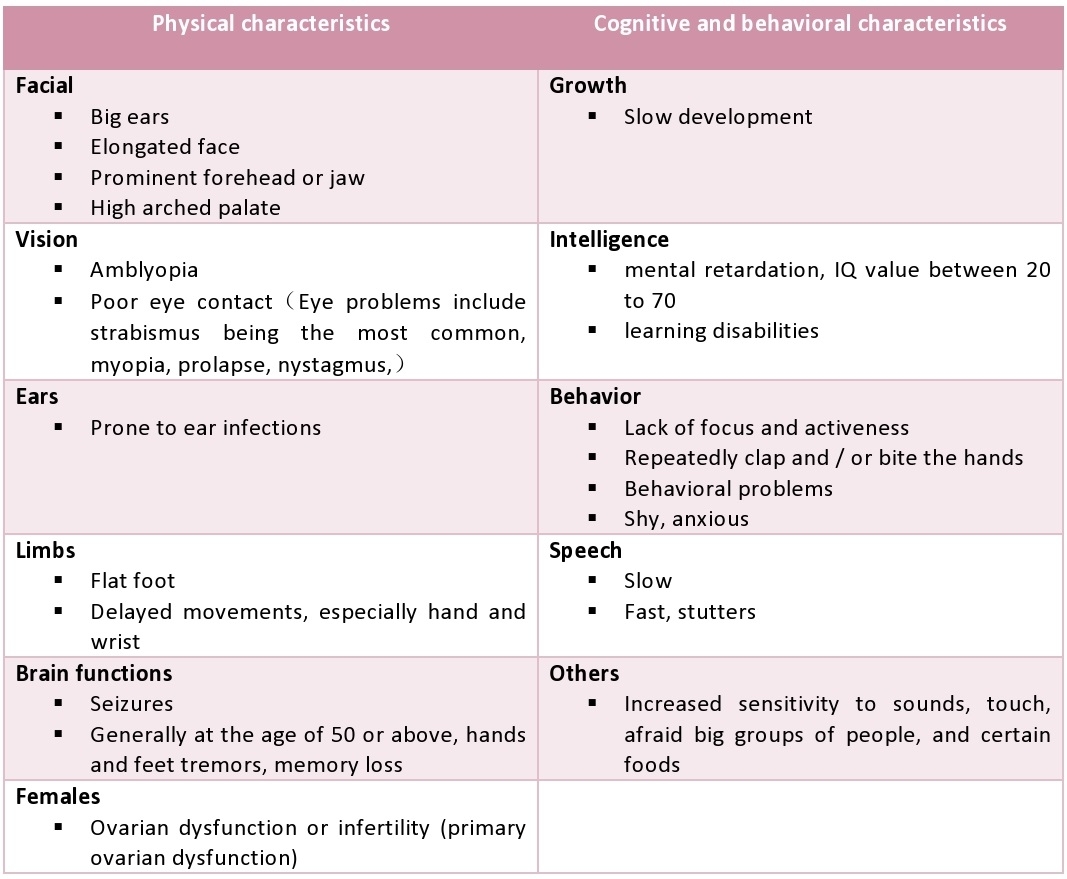
What tests are done to diagnose fragile X syndrome?
FXS can be diagnosed by testing a person's DNA from a blood test. A doctor or genetic counselor can order the test. Testing also can be done to find changes in the FMR1 gene that can lead to fragile X-associated disorders.
Can fragile X syndrome be screened?
Fragile X-associated disorders, including Fragile X syndrome, are diagnosed by DNA testing. The test that is required is called DNA studies for fragile X syndrome. This is generally a blood test, although some laboratories offer testing via a cheek swab or saliva sample.
How do you get tested for fragile X carrier?
Carrier screening for fragile X syndrome can be performed using a blood sample, saliva sample, or buccal (cheek) swab and results are typically available in two to three weeks. Fragile X carrier screening analyzes a specific part of a gene called FMR1. The FMR1 gene is located on the X chromosome.
Do they test for fragile X at birth?
Can you find out if your baby has fragile X syndrome before birth? Yes. If you or your partner is a carrier, you can talk to your health care provider about prenatal tests called amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling (also called CVS). These tests can help you find out the chances of having a baby with fragile X.
Which organization recommends fragile X carrier testing?
The Fragile X Association of Australia recommends Fragile X carrier testing for:
What is preimplantation genetic testing?
This testing, also referred to as Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD), is an IVF treatment and is available to people who know they have an increased risk of having a child with a genetic condition, such as Fragile X.
Can you test for fragile X syndrome?
Testing for Fragile X syndrome is not currently available as part of the newborn bloodspot screening program. If Fragile X syndrome is suspected, testing can be arranged through a general practitioner, paediatrician or clinical genetics service. Testing can be performed on blood or saliva samples.
Is Fragile X inherited?
As Fragile X is an inherited genetic condition, if a person finds out they have the premutation or full mutation other family members may also be carriers and/or may have a Fragile X associated condition. There is also a risk of passing the Fragile X premutation or full mutation on to children. A number of reproductive options exist ...
What are the results of a fragile X carrier test?
There are four possible results from a fragile X carrier test: Negative You are not a carrier for the most common alteration in the FMR1 gene and your baby is not at increased risk for fragile X syndrome. Intermediate Your results fall in the range between negative and premutation. Your baby is not at increased risk for fragile X syndrome.
How long does it take to get a fragile X test?
The test is performed on a small sample of blood. Results are usually available within two weeks. Testing provides accurate results more than 99 percent of the time. Other causes of mental retardation are not identified through this test.
How is fragile X inherited?
This abnormal gene, which can be passed from generation to generation, is usually inherited through the gene that is carried by women. A fragile X carrier is someone who has an altered FMR1 gene, but does not show any obvious signs or symptoms of fragile X syndrome.
How many women have fragile X syndrome?
Approximately 1 in 250 women in the general population are carriers of the abnormal gene that causes fragile X syndrome. A woman of any age can have a child with fragile X syndrome, whether or not she has had previous children.
When is genetic counseling recommended?
Genetic counseling is recommended and available when someone is shown to be a carrier of fragile X.
Can a fragile X carry on to a son?
Men who are fragile X carriers will pass the altered gene to all of their daughters but none of their sons. Daughters of carrier men are expected to be intellectually normal but are at risk of having children affected with fragile X syndrome. The genetics of fragile X syndrome are complicated.
Fragile X syndrome
Fragile X syndrome is found among a variety of ethnic groups, 2 and can occur in families with no history of inherited intellectual disability. Approximately one in 260 women 3 and one in 800 males 4 in the general population is a fragile X carrier.
Why focus on fragile X screening?
Fragile X is the most common cause of inherited intellectual disability, which affects approximately 1 in 4,000 males and 1 in 8,000 females. 1 Carrier screening for Fragile X will detect approximately 99% of individuals who are carriers of a mutation in the Fragile X gene and at risk of having a child with Fragile X syndrome. 2
Choice in testing for fragile X syndrome
At Labcorp, our focus is offering the right test at the right time to the right patient, which is why we offer two types of testing for fragile X.
What is the test for Fragile X?
Health care providers often use a blood sample to diagnose Fragile X. The health care provider will take a sample of blood and will send it to a laboratory, which will determine what form of the FMR1 gene is present. 1.
What can a healthcare provider do to determine the nature of delays in a child?
A healthcare provider can perform developmental screening to determine the nature of delays in a child. If a healthcare provider suspects the child has Fragile X syndrome, he/she can refer parents to a clinical geneticist, who can perform a genetic test for Fragile X syndrome. 2
What test is done to determine if a child has fragile X syndrome?
If you’re pregnant and concerned that your child has fragile X syndrome, you can see a genetic counselor where you may undergo the following prenatal tests: Amniocentesis: The healthcare provider takes a sample of the amniotic fluid for testing.
Who can order a test for fragile X syndrome?
Your pediatrician or genetic counselor can order a test for fragile X syndrome.
How does fragile X syndrome get passed from parent to child?
Fragile X syndrome gets passed from parent to child. A DNA part called the “CGG triplet repeat” expands within a gene called “FMR1,” producing a mutation that causes fragile X syndrome. A normal part repeats five to 40 times, but in people with fragile X syndrome it repeats more than 200 times. That “silences” the FMR1 gene, stopping it from producing an important protein called “FMRP” (fragile X mental retardation protein). This messes up the nervous system and causes the symptoms of fragile X syndrome.
Why is FXS called FXS?
FXS is named fragile X syndrome because, when looked at through a microscope, part of the X chromosome looks “broken” or “fragile.”. FXS is one of three syndromes in the fragile X family. The other two syndromes are: Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS). Symptoms include balance problems, shaky hands, unstable mood, memory loss, ...
How many times does fragile X syndrome repeat?
A normal part repeats five to 40 times, but in people with fragile X syndrome it repeats more than 200 times .
How many people have fragile X syndrome?
Although the exact number isn’t clear, researchers estimate that, worldwide, about 1 in 8,000 to 11,000 females and 1 in 4,000 to 7,000 males have fragile X syndrome. Experts don’t know for sure how many people carry the fragile X premutation, which can be passed down to their child and cause fragile X. Some studies estimate that, in the United ...
What is fragile X syndrome?
Fragile X syndrome can be a difficult diagnosis for the child’s family and friends. It’s the start of a lot of change and adjustment. Therapy, medications and accommodations at school are now part of your child’s life. While helping your child with their issues, be sure not to neglect your own needs. Remember that if your child has fragile X syndrome, that means you’re more vulnerable to dementia, depression, migraines, chronic pain, premature menopause, high blood pressure, anxiety, hypothyroidism and sleep apnea. Don’t neglect your own care!
