Why is vision the most important sense in our body?
The Senses: Vision All of our senses give us vital information about our surroundings, but the one we rely on most is vision. Accordingly, the physical apparatus for gathering visual information—the eye—and the brain circuits that process this information are more complex than corresponding systems for the other senses.
What is the difference between vision hearing and vision vision?
Vision. Sight or vision is the capability of the eye(s) to focus and detect images of visible light on photoreceptors in the retina of each eye that generates electrical nerve impulses for varying colors, hues, and brightness. Hearing. Hearing or audition is the sense of sound perception. Taste.
What are the different types of vision?
The process of vision can be broken down into three general categories; 1) visual acuity and visual field, 2) visual motor abilities and 3) visual perception. Visual Acuity - This refers to the clarity of sight.
What is the difference between sight and vision?
More than just sight is measured in terms of visual acuity; vision is the process of deriving meaning from what is seen. It is a complex, learned and developed a set of functions that involve a multitude of skills.
What are the senses?
How does visual perception affect the brain?
How many rods and cones are there in the retina?
Why do colors appear washed out in peripheral vision?
How big is the eye?
Where are the cones located in the retina?
What is visual art?
See 4 more
About this website

What sense is vision?
The sense organ for vision is an exquisitely evolved biological instrument for turning light into the brain's language of electrical signals. world onto the retina in the back of the eye. The lens changes shape to allow us to see both near and far objects clearly.
What type of sensory is vision?
Vision. Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding environment using light in the visible spectrum reflected by the objects in the environment. The resulting perception is also known as visual perception, eyesight, sight, or vision (adjectival form: visual, optical, or ocular).
Is vision a mechanical sense?
There are four main modalities: the light senses (photoreception; i.e., vision), the mechanical senses (mechanoreception; i.e., touch, balance, and hearing), the chemical senses (chemoreception; i.e., taste and smell), and the electric sense (electroreception) of certain fish.
Is vision a somatic or special sense?
special sensesHearing, balance and vision belong to the special senses. Both hearing and balance depend on hair cells within the inner ear.
Is vision a special sense?
Special and General Senses Special senses have specialized sense organs that gather sensory information and change it into nerve impulses. Special senses include vision (for which the eyes are the specialized sense organs), hearing (ears), balance (ears), taste (tongue), and smell (nasal passages).
Why is vision our primary sense?
We perceive up to 80% of all impressions by means of our sight. And if other senses such as taste or smell stop working, it's the eyes that best protect us from danger.
What is a mechanical sense?
Senses that detect mechanical stimuli (e.g. touch, hearing (detecting air vibration), and balance).
What are the internal senses?
The classical list of five internal senses was provided by Avicenna: common sense, retentive imagination, compositive imagination, estimative power, and memory. He also localized these faculties in the three ventricles of the brain.
What is considered a chemical sense?
Smell = Olfaction - olfactory system Taste = Gustation - gustatory system - called “chemical” senses because their function is to monitor the chemical content of the environment.
Which is a somatic sense?
Definitions of somatic sense. the faculty of bodily perception; sensory systems associated with the body; includes skin senses and proprioception and the internal organs.
What is somatic sensory?
The somatic sensory system is one of the phylogenetically oldest sensory systems, evolving before the specialized senses of vision and hearing. This complex system provides information on the spatial limits of the organism by communicating information about the body to the brain through distinct receptors and pathways.
What is somatic sensation?
Somatic Sensation: bodily sensations of touch, pain, temperature, vibration, and proprioception. ( Blumenfeld, 276) The process by which the nature and meaning of tactile stimuli are recognized and interpreted by the brain, such as realizing the characteristics or name of an object being touched. (
What are the sensory receptors for vision?
the rods and cones in the retina are the sensory receptors for vision. They convert light into electrical impulses that are ultimately transmitted to the brain.
What is visual in sensory images?
Visual imagery engages the sense of sight. This is what you can see, and includes visual descriptions. Physical attributes including color, size, shape, lightness and darkness, shadows, and shade are all part of visual imagery. 2.
Which is an example of sensory adaptation?
Examples of Sensory Adaptation Sight: When you go into a dark room or outside at night, your eyes eventually adjust to the darkness because your pupils enlarge to let in more light. Likewise, when you are in bright light, your eyes adjust to the narrowing of your pupils. This is another form of sensory adaptation.
What are visual receptors?
Visual receptor: The layer of rods and cones that are the visual cells of the retina.
The 12 senses - Sense of sight - AntroVista
Sense of sight . Your eyes are your most important sensory organ. They are the only organs located visibly on your body's surface. “Seeing” is often used synonymously for “observing” or “understanding”.
Why Vision Is the Most Important Sense Organ - Medium
Out of all the five senses, your vision seems the most important. Humans are fairly unique in their reliance on sight as the dominant sense and this is reflected in how complicated our eyes are…
Why Is the Sense of Sight Important? - Reference.com
The sense of sight is important as it helps compensate for a loss of other senses, enables the differences between good and bad food to be distinguished, helps create impressions and find partners and helps ensure safety by perceiving signs of danger. People without the sense of sight find it difficult to interact with their environment as compared to those who have it.
What is considered to be the most important sense?
What is the most important sense? Humans have five senses: the eyes to see, the tongue to taste, the nose to smell, the ears to hear, and the skin to touch. By far the most important organs of sense are our eyes. We perceive up to 80% of all impressions by means of this human camera. Find out more.
What is vision in science?
More than just sight is measured in terms of visual acuity; vision is the process of deriving meaning from what is seen. It is a complex, learned and developed a set of functions that involve a multitude of skills. Research estimates that eighty to eighty-five percent of our perception, learning, cognition, and activities are mediated ...
What are the three categories of vision?
William Padula, O.D. The process of vision can be broken down into three general categories; 1) visual acuity and visual field , 2) visual motor abilities and 3) visual perception.
What is the term for a condition where the eye turns down?
Exotropia is a form of strabismus where an eye turns out, esotropia is where an eye turns in, hypertropia is where an eye turns up, and hypotropia is where an eye turns down. These can also occur in combination, such as hyper- exotropia, or hypo-esotropia.
What is visual acuity?
Visual Acuity - This refers to the clarity of sight. It is commonly measured using the Snellen chart and noted, for example, as 20/20, 20/50, 20/200 etc. Visual acuity becomes blurred in various refractive conditions, for example, myopia (nearsighted), hyperopia (far-sighted), astigmatism (mixed), and presbyopia (age-related loss of focusing).
What is the term for the ability to steadily and accurately gaze at an object of regard?
Fixation: The ability to steadily and accurately gaze at an object of regard. This is most dysfunctional in nystagmus which is an uncontrollable shaking of the eyes.
What is visual auditory integration?
Visual-Auditory Integration: The ability to relate and associate what is seen and heard.
What is the ability to accurately aim the eyes at an object of regard and to track an object as it moves towards and?
Convergence: The ability to accurately aim the eyes at an object of regard and to track an object as it moves towards and away from the person.
What is the visual system?
Visual System. The visual system is responsible for seeing. The primary visual area of the brain is the occipital lobe (see figure). Projections are received from the retina (through the thalamus) where different types of information are encoded. Types of visual information include: color, shape, orientation, and motion.
What are the types of visual information?
Types of visual information include: color, shape, orientation, and motion. From the ventral stream in the occipital lobe information projects to the temporal lobe to process what objects are. From the dorsal stream, information goes to the parietal lobes to process where objects are located. 2. Auditory System.
Why do we not notice out proprioception?
Generally speaking we do not notice out proprioceptive sense because we disregard through habituation , desensitization, or adaptation sensory stimuli that is continuously present. In essence, the habituation makes the proprioceptive sensory impressions disappear. One practical advantage of this is that unnoticed sensation continue in the background while an individual’s attention can move to another concern.
What does sweet taste mean?
Sweet taste signals that carbohydrates are present. Carbohydrates have a high calorie count and are desirable (humans in the distant past did not know when their next meal would occur, so they evolved to want/need to eat sweet tastes.)
Which system is responsible for hearing?
Auditory System. The auditory system is responsible for hearing. The primary auditory cortex is located in the superior temporal gyrus of the brain (see figure). Specific sound frequencies can be mapped precisely onto the primary auditory cortex. Particular areas in the auditory cortex process changes in sound frequency or amplitude, ...
Which part of the brain receives top down information?
The olfactory bulb does receive “top-down” information from areas such as the amygdala, neocortex, hippocampus, and others. It has four functions:
What is the ability of the eye to perceive images of visible light?
Sight, or vision, is the ability of the eyes to perceive images of visible light. The structure of the eye is key in how the eye works. Light enters the eye through the pupil and is focused through the lens onto the retina on the back of the eye.
Which part of the brain receives sensory information?
Sensory information is transmitted from the peripheral nervous system to the central nervous system. A structure of the brain called the thalamus receives most sensory signals and passes them along to the appropriate area of the cerebral cortex to be processed.
Which part of the brain receives signals from the olfactory bulb?
The olfactory cortex receives signals from the olfactory bulb for processing and identifying odors. In all, limbic system structures take information perceived from the five senses, as well as other sensory information (temperature, balance, pain, etc.) to make sense of the world around us.
How many receptors are there in smell?
There are over 300 different receptors that each bind a specific molecule feature. Each odor contains combinations of these features and binds to different receptors with varying strengths. The totality of these signals is what is recognized as a particular smell.
What are the receptors that sense pressure?
There are also receptors for pain, known as nociceptors, and for temperature, called thermoreceptors.
What is the ability to detect chemicals in food, minerals, and dangerous substances such as poisons?
Taste, also known as gustation, is the ability to detect chemicals in food, minerals and dangerous substances such as poisons. This detection is performed by sensory organs on the tongue called taste buds. There are five basic tastes that these organs relay to the brain: sweet, bitter, salty, sour and umami.
What is the flavor of food?
The flavor of a particular food is actually a combination of the taste and smell as well as the texture and temperature.
When does vision change?
This can occur around age 40 and later. There are many visual changes between ages 40-60, but after age 60 they become more severe. Macular Degeneration - This is a deterioration of the center part of your retina or the area in the back of the eye that receives the images and sends information to the brain.
How many tests are there to measure your eyesight?
Did you know we have over 100 tests to measure your eyes with? Some of those include eye coordination, depth perception, color blindness, peripheral vision or awareness, focusing ability and more. With conditions such as glaucoma, a comprehensive exam can literally save your vision, as it can detect subtle changes in eyesight that you may not even be aware of.
What is 20/200 vision?
20/200 - This is the level at which you are considered to be legally blind. That means a person with 20/200 vision has to be 20 feet away from an object to see clearly , whereas a person with normal eyesight can see clearly at 200 feet away.
What causes a double vision in one eye?
Cataracts - The clouding of the lens in your eye that can affect only one eye or both eyes. The lens sits behind the colored part of your eye (the iris) and will cloud over, causing light to scatter and blur. You may also see a double vision with objects. This condition generally is caused by age or injury but sometimes can be caused by genetics, past eye conditions, surgeries, chronic illnesses, and medications.
How far away can you see at 20/100?
20/100 - This is just an example, but those who have a vision type that is 20/100 would have to be 20 feet away from an object that most people can see at 100 feet. The same goes for 20/80, 20/60 and so on when it comes to distance.
Can you see objects clearly?
A person can see objects clearly when they are close to them, but objects at a distance will appear blurred. Nearsightedness affects about 30% of the population and is easily treated with contacts or glasses. Farsightedness - This is also known as hyperopia and is the opposite of nearsightedness. A person can see objects clearly ...
Can you see blurry objects?
A person can see objects clearly that are far away, but objects close to them are blurry. This is also easily treatable just like myopia. Astigmatism - The surface of the cornea or lens is not spherical, causing your eyes to focus at two separate points instead of one.
What is the sense of space?
This sense is called proprioception . Proprioception includes the sense of movement and position of our limbs and muscles.
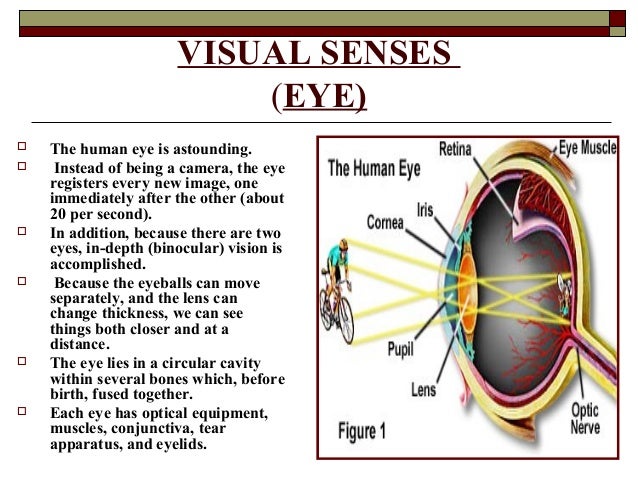
How does the eye work?
First, light reflects off an object to the eye. The transparent outer layer of the eye called the cornea bends the light that passes through the hole of the pupil. The iris (which is the colored part of the eye) works like the shutter of a camera, retracting to shut out light or opening wider to let in more light.
Why is balance important in the middle ear?
People retain their sense of balance because the Eustachian tube, or pharyngotympanic tube, in the middle ear equalizes the air pressure in the middle ear with the air pressure in the atmosphere. The vestibular complex, in the inner ear, is also important for balance, because it contains receptors that regulate a sense of equilibrium. The inner ear is connected to the vestibulocochlear nerve, which carries sound and equilibrium information to the brain.
What does texture mean in psychology?
Texture can be associated with abstract concepts, and touching something with a texture can influence the decisions a person makes, according to six studies by psychologists at Harvard University and Yale University, published in the June 24, 2010, issue of the journal Science.
What are the four tastes of the gustatory sense?
There is also a fifth taste, defined as umami or savory. There may be many other flavors that have not yet been discovered. Also, spicy is not a taste. It is actually a pain signal, according to the National Library of Medicine (NLM).
Why is touch important?
Touch isn't just a sense used to interact with the world; it also seems to be very important to a human's well-being. For example, touch has been found to convey compassion from one human to another .
How does sound work?
This sense works via the complex labyrinth that is the human ear. Sound is funneled through the external ear and piped into the external auditory canal. Then, sound waves reach the tympanic membrane, or eardrum. This is a thin sheet of connective tissue that vibrates when sound waves strike it.
What is the sense of sound perception?
Hearing. Hearing or audition is the sense of sound perception. Taste.
What are the four senses that are interpreted by the nervous system?
People are responsive creatures; hold freshly baked bread before us, and our mouths water; a sudden clap of thunder makes us jump; these “irritants” and many others are the stimuli that continually greet us and are interpreted by our nervous system; the four “traditional” senses—smell, taste, sight, and hearing- are called special senses.
What is the ability to detect the taste of substances such as food, certain minerals, and poisons?
Taste. Taste refers to the capability to detect the taste of substances such as food, certain minerals, and poisons, etc.
What are the receptors in the vestibule called?
Within the membrane sacs of the vestibule are receptors called maculae that are essential to our sense of static equilibrium.
Which layer of the eye is the white?
Fibrous layer. The outermost layer, called the fibrous layer, consists of the protective sclera and the transparent cornea. Sclera. The sclera, thick, glistening, white connective tissue, is seen anteriorly as the “white of the eye”. Cornea.
Where are the eyelids located?
Eyelids. Anteriorly, the eyes are protected by the eyelids, which meet at the medial and lateral corners of the eye, the medial and lateral commissure (canthus), respectively.
Which muscles are attached to the outer surface of the eye?
Six extrinsic, or external, eye muscles are attached to the outer surface of the eye; these muscles produce gross eye movements and make it possible for the eyes to follow a moving object; these are the lateral rectus, m edial rectus, superior rectus, inferior rectus, inferior oblique, and superior oblique.
How to check visual acuity?
Generally, visual acuity is checked on the eye chart with numbers and letters. A regular eye exam can save you from any severity. In case of a new prescription, you can order by Online Prescription Eyewear from any store.
How far can you see with 20/20 vision?
In this vision, a person can see clearly at a distance of 100 feet. He/she can see as clear as a person of normal 20/20 vision can see at 20 feet.
What is the opposite of nearsightedness?
This is also called as hyperopia or opposite of nearsightedness. In these conditions, a person can see the far away objects. But close objects give a blurred view. Farsightedness can be treated like myopia. Nearsightedness: This is called as myopia. A person can see close objects but find blur view at distance objects.
How far can you see with 3M glasses?
In this vision level a person can see at a distance of 20 feet and a normal vision person can see at a distance of 60, 70, and 80. A person is able to read large headlines of a newspaper. You can wear 3M safety Glasses to read any print material easily.
What is it called when you can see blurry objects?
This is called as myopia. A person can see close objects but find blur view at distance objects. Most people are affected by these conditions. This is easily treated by Prescription Safety Glasses or contact lenses. Presbyopia: This type of condition appears when the eye’s lens becomes more flexible.
What does 20/20 vision mean?
1. 20/20 vision: 20/20 vision is used to define a certain level of visual acuity. It is related to sharpness and precision of vision. 20/20 vision means you can see clearly the object at the distance of 20 feet. It does not mean you have a perfect vision. It means you can see clearly at some specific distance.
How far can a person see if they are legally blind?
In this level of vision, a person is considered to be legally blind. In this vision level, a person can see at a distance of 20 feet away. While a normal vision’s person can see at a distance of 100 feet away.
What is the name of the eye that blurs the sharp central vision needed to see straight ahead?
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) AMD is a disease that blurs the sharp, central vision needed to see straight-ahead. It affects the part of the eye called the macula that is found in the center of the retina. The macula lets a person see fine detail and is needed for things like reading and driving.
What is the difference between nearsightedness and farsightedness?
Blurred vision (refractive errors) Nearsightedness (called myopia) is when you can see clearly up close but blurry in the distance. Farsightedness (called hyperopia) is when you can see clearly in the distance but blurry up close.
Why is glaucoma called the sneak thief of sight?
Glaucoma is called the “sneak thief of sight” because people don’t usually notice a problem until some vision is lost.
What is lazy eye?
Amblyopia — often called lazy eye — is a problem that is common in children. Amblyopia is a result of the brain and the eyes not working together. The brain ignores visual information from one eye, which causes problems with vision development. Treatment for amblyopia works well if the condition is found early.
Why is my vision blurry?
Astigmatism is another condition that causes blurred vision, but it is because of the shape of the cornea. These conditions affect the shape of the eye and, in turn, how the eye sees. They can be corrected by eyeglasses, contact lenses, and in some cases surgery.
Which condition is when one eye turns inward toward the nose?
Esotropia – one or both eyes turn inward toward the nose
Can amblyopia cause permanent vision loss?
Treatment for amblyopia works well if the condition is found early. If untreated, amblyopia causes permanent vision loss.
What are the senses?
The Senses: Vision. All of our senses give us vital information about our surroundings , but the one we rely on most is vision. Barring vision-impairing conditions, we walk (or drive, or ride) safely through the world, recognize friends (and enemies), read, write, and otherwise learn what’s happening by the power of sight.
How does visual perception affect the brain?
As with the other senses, visual perception engages other parts of the brain as well-signals flow back and forth to regions that store memory, govern emotion, make decisions, and initiate action—as we recognize, interpret, and react to what we see. It’s a highly active process.
How many rods and cones are there in the retina?
The retina contains nerve cells as well as a layer of 120 million rods and cones, receptor cells that respond to light. There are three kinds of cones, each “tuned” to different parts of the light spectrum. Some react primarily to red, some to green, some to blue light.
Why do colors appear washed out in peripheral vision?
Similarly, because rods greatly outnumber cones in outer areas of the retina, colors seem washed out in peripheral vision. In both rods and cones, light initiates chemical reactions that activate neurotransmitters to generate nerve signals.
How big is the eye?
The eye is roughly spherical and about an inch in diameter. In the front, the cornea and lens focus light reflected from objects in the. world onto the retina in the back of the eye. The lens changes shape to allow us to see both near and far objects clearly.
Where are the cones located in the retina?
The cones are most concentrated in the very center of the retina —a tiny spot called the fovea, responsible for our most acute vision and the region we use when we “focus” our vision on something. Cones function well only in reasonably bright light.
What is visual art?
The visual arts—drawing, painting, sculpture—showcase the power and complexity of our sense of sight. When we appreciate a great painting, we discriminate subtleties of color and brightness, and we respond to the relationship between forms. The transforming power of perception makes a flat surface seem three-dimensional.