
What is the principle behind Gram staining technique?
The four basic steps of the Gram Stain are:
- Application of the primary stain Crystal Violet (CV) to a heat-fixed smear of bacterial culture. CV dissociates in aqueous solutions into CV+ and Cl – ions. ...
- Addition of Gram’s Iodine. Iodine (I – or I3 –) acts as a mordant and as a trapping agent. ...
- Decolorization with 95% ethyl alcohol. ...
- Counterstain with Safranin
What is the most critical step in Gram staining?
The most critical step in the Gram stain is the decolorizer step with acetone alcohol. If the decolorizer is left on too long Gram positive bacteria will come out pink and if it is not left on long enough the Gram negatives will come out purple.
What is the advantage of the Gram stain over simple stain?
What is the advantage of the Gram stain over a simple stain such as methylene blue? Gram staining highlights different bacteria types through the use of special dyes. It aids in the diagnosis of a specific organism and tells the difference between gram negative and gram positive bacteria. Simple staining is unable to highlight the exact organism.
What is the most important reagent in Gram staining?
What is the most important reagent in the Gram stain method? The primary stain of the Gram’s method is crystal violet. Crystal violet is sometimes substituted with methylene blue, which is equally effective. The microorganisms that retain the crystal violet-iodine complex appear purple brown under microscopic examination.

What is Gram staining?
The Gram staining is one of the most crucial staining techniques in microbiology. It gets its name from the Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram who first introduced it in 1882, mainly to identify organisms causing pneumonia.[1] .
What is the primary color of gram stain?
Often the first test performed, gram staining involves the use of crystal violet or methylene blue as the primary color.[2] . The term for organisms that retain the primary color and appear purple-brown under a microscope is Gram-positive organisms.
What is the term for organisms that retain the primary color and appear purple-brown under a microscope?
The term for organisms that retain the primary color and appear purple-brown under a microscope is Gram-positive organisms. The organisms that do not take up primary stain appear red under a microscope and are Gram-negative organisms. The Gram staining is one of the most crucial staining techniques in microbiology.
When was Gram staining first used?
Last Update: February 23, 2021. Introduction. The Gram staining is one of the most crucial staining techniques in microbiology. It gets its name from the Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram who first introduced it in 1882, mainly to identify organisms causing pneumonia.[1] . Often the first test performed, ...
How long to counterstain a smear?
The smear is counterstained with basic fuchsin solution for 40 to 60 seconds. The fuchsin solution is washed off with water, and excess water is blotted with the bibulous paper. The slide can also be air-dried after shaking off excess water. 3.
Which cocci are Gram positive?
Gram-positive cocci in clusters: Usually characteristic of Staphy lococcusspecies such as S. aureus.
How thick should a smear be?
The smear should be one cell thick with no overlapping of cells
What is the most common gram stain?
A Gram stain of mixed Staphylococcus aureus ( S. aureus ATCC 25923, gram-positive cocci, in purple) and Escherichia coli ( E. coli ATCC 11775, gram-negative bacilli, in red), the most common Gram stain reference bacteria. Gram stain or Gram staining, also called Gram's method, is a method of staining used to distinguish ...
When to use Gram stain?
Gram stains are performed on body fluid or biopsy when infection is suspected. Gram stains yield results much more quickly than culturing, and are especially important when infection would make an important difference in the patient's treatment and prognosis; examples are cerebrospinal fluid for meningitis and synovial fluid for septic arthritis.
How does gram staining work?
Gram staining differentiates bacteria by the chemical and physical properties of their cell walls. Gram-positive cells have a thick layer of peptidoglycan in the cell wall that retains the primary stain, crystal violet. Gram-negative cells have a thinner peptidoglycan layer that allows the crystal violet to wash out on addition of ethanol. They are stained pink or red by the counterstain, commonly safranin or fuchsine. Lugol's iodine solution is always added after addition of crystal violet to strengthen the bonds of the stain with the cell membrane. Gram staining is almost always the first step in the preliminary identification of a bacterial organism. While Gram staining is a valuable diagnostic tool in both clinical and research settings, not all bacteria can be definitively classified by this technique. This gives rise to gram-variable and gram-indeterminate groups.
Why is Lugol's iodine added to the gram stain?
Lugol's iodine solution is always added after addition of crystal violet to strengthen the bonds of the stain with the cell membrane. Gram staining is almost always the first step in the preliminary identification of a bacterial organism.
What is the size of a Gram stain of Candida albicans?
Gram stain of Candida albicans from a vaginal swab. The small oval chlamydospores are 2–4 µm in diameter.
What did Gram do to make bacteria more visible?
Gram devised his technique not for the purpose of distinguishing one type of bacterium from another but to make bacteria more visible in stained sections of lung tissue. He published his method in 1884, and included in his short report the observation that the typhus bacillus did not retain the stain.
What is the difference between a purple and a pink gram positive?
Purple-stained gram-positive (left) and pink-stained gram-negative (right) Gram-positive bacteria have a thick mesh-like cell wall made of peptidoglycan (50–90% of cell envelope), and as a result are stained purple by crystal violet, whereas gram-negative bacteria have a thinner layer (10% of cell envelope), so do not retain ...
What is a Gram stain?
A Gram stain is a test that checks for bacteria at the site of a suspected infection or in certain body fluids, such as blood or urine. These sites include the throat, lungs, and genitals, and in skin wounds. There are two main categories of bacterial infections: Gram-positive and Gram-negative. The categories are diagnosed based on the how ...
What happens during a Gram stain?
Your health care provider will need to take a sample from the site of a suspected infection or from certain body fluids, depending on what type of infection you may have . The most common types of Gram stain tests are listed below.
What happens when a stain is a Gram positive?
When the stain combines with bacteria in a sample, the bacteria will either stay purple or turn pink or red. If the bacteria stays purple, they are Gram-positive. If the bacteria turns pink or red, they are Gram-negative. The two categories cause different types of infections: Gram-positive infections include methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus ...
What are the two types of bacteria?
There are two main categories of bacterial infections: Gram-positive and Gram-negative. The categories are diagnosed based on the how the bacteria reacts to the Gram stain. A Gram stain is colored purple. When the stain combines with bacteria in a sample, the bacteria will either stay purple or turn pink or red. If the bacteria stays purple, they are Gram-positive. If the bacteria turns pink or red, they are Gram-negative. The two categories cause different types of infections:
What does it mean when a bacterial infection is pink?
If the bacteria was colored pink or red, it means you likely have a Gram-negative infection.
Do you need special preparations for Gram stain?
You don't need any special preparations for a Gram stain.
Is there anything else I need to know about a Gram stain?
If you are diagnosed with a bacterial infection, you will probably be prescribed antibiotics. It's important to take your medicine as prescribed, even if your symptoms are mild. This can prevent your infection from getting worse and causing serious complications.
What is a Gram Stain?
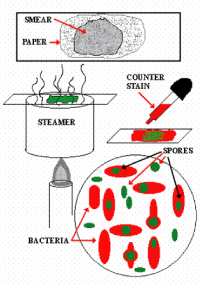
Gram stain is the differential stain, which makes the use of four reagents that are given below:
What is the purpose of Gram staining?
Gram stain is used to differentiate the bacterial cells by staining the cell wall and distinguish two major groups of bacteria that are gram-positive and gram-negative . Gram-positive bacteria appear violet in colour, and gram-negative bacteria appear pink in colour, as a result of Gram staining.
What is the name of the antibacterial that stains the decolourized bacterial cell?
Safranin: It acts as a “ Counterstain ” that stains the decolourized bacterial cell by giving it a pink colour.
Why do Gram stainings help?
It stains the bacterial cell wall differently, by giving violet colour to the gram-positive bacteria and pink colour to the negative bacteria. Therefore, it adds colour to the cell wall of bacteria, which increases the visibility under the light microscope. Besides, gram staining also helps in the study of the morphology and arrangement ...
How to prepare a bacterial smear?
Prepare bacterial smear by taking little inoculum from the bacterial culture by the help of the inoculating loop.
What is the most common method of staining?
Gram staining is used widely and the most popular method in laboratories. It is the type of differential staining , which makes the use of more than one stains to differentiate the bacteria. The gram staining method was first given in 1884 by the Danish scientist and Physician Han’s Christian Gram. The Gram stain is the differential stain ...
What color does a Gram positive stain?
Gram-Positive: If the bacteria cell gives a positive result for the gram reaction, it will stain Violet. Gram-negative: If the bacterial cell gives a negative result for the gram reaction, it will stain Pink.
How Does Gram Staining Work?
Gram staining involves three processes: staining with a water-soluble dye called crystal violet, decolorization, and counterstaining, usually with safanin. Due to differences in the thickness of a peptidoglycan layer in the cell membrane between Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria, Gram positive bacteria (with a thicker peptidoglycan layer) retain crystal violet stain during the decolorization process, while Gram negative bacteria lose the crystal violet stain and are instead stained by the safranin in the final staining process. The process involves three steps:
Why do Gram positive bacteria stain violet?
Gram positive bacteria stain violet due to the presence of a thick layer of peptidoglycan in their cell walls, which retains the crystal violet these cells are stained with. Alternatively, Gram negative bacteria stain red, which is attributed to a thinner peptidoglycan wall, which does not retain the crystal violet during the decoloring process.
How to stain a cell?
How To- Staining Protocol and Concerns: 1 Make a slide of cell sample to be stained. Heat fix the sample to the slide by carefully passing the slide with a drop or small piece of sample on it through a Bunsen burner three times. 2 Add the primary stain (crystal violet) to the sample/slide and incubate for 1 minute. Rinse slide with a gentle stream of water for a maximum of 5 seconds to remove unbound crystal violet. 3 Add Gram's iodine for 1 minute- this is a mordant, or an agent that fixes the crystal violet to the bacterial cell wall. 4 Rinse sample/slide with acetone or alcohol for ~3 seconds and rinse with a gentle stream of water. The alcohol will decolorize the sample if it is Gram negative, removing the crystal violet. However, if the alcohol remains on the sample for too long, it may also decolorize Gram positive cells. 5 Add the secondary stain, safranin, to the slide and incubate for 1 minute. Wash with a gentle stream of water for a maximum of 5 seconds. If the bacteria is Gram positive, it will retain the primary stain (crystal violet) and not take the secondary stain (safranin), causing it to look violet/purple under a microscope. If the bacteria is Gram negative, it will lose the primary stain and take the secondary stain, causing it to appear red when viewed under a microscope.
What is the process of staining cells with crystal violet?
The process involves three steps: Cells are stained with crystal violet dye. Next, a Gram's iodine solution (iodine and potassium iodide) is added to form a complex between the crystal violet and iodine. This complex is a larger molecule than the original crystal violet stain and iodine and is insoluble in water.
Does alcohol decolorize a cell?
However, if the alcohol remains on the sample for too long, it may also decolorize Gram positive cells. Add the secondary stain, safranin, to the slide and incubate for 1 minute.
Overview
Gram stain or Gram staining, also called Gram's method, is a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into two large groups: gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. The name comes from the Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram, who developed the technique in 1884.
Gram staining differentiates bacteria by the chemical and physical properties o…
History
The method is named after its inventor, the Danish scientist Hans Christian Gram (1853–1938), who developed the technique while working with Carl Friedländer in the morgue of the city hospital in Berlin in 1884. Gram devised his technique not for the purpose of distinguishing one type of bacterium from another but to make bacteria more visible in stained sections of lung tissue. He published his method in 1884, and included in his short report the observation that the typhus bac…
Uses
Gram staining is a bacteriological laboratory technique used to differentiate bacterial species into two large groups (gram-positive and gram-negative) based on the physical properties of their cell walls. Gram staining is not used to classify archaea, formerly archaeabacteria, since these microorganisms yield widely varying responses that do not follow their phylogenetic groups.
Staining mechanism
Gram-positive bacteria have a thick mesh-like cell wall made of peptidoglycan (50–90% of cell envelope), and as a result are stained purple by crystal violet, whereas gram-negative bacteria have a thinner layer (10% of cell envelope), so do not retain the purple stain and are counter-stained pink by safranin. There are four basic steps of the Gram stain:
Examples
Gram-positive bacteria generally have a single membrane (monoderm) surrounded by a thick peptidoglycan. This rule is followed by two phyla: Bacillota (except for the classes Mollicutes and Negativicutes) and the Actinomycetota. In contrast, members of the Chloroflexota (green non-sulfur bacteria) are monoderms but possess a thin or absent (class Dehalococcoidetes) peptidoglycan and can stain negative, positive or indeterminate; members of the Deinococcota stain positive bu…
Orthographic note
The term Gram staining is derived from the surname of Hans Christian Gram; the eponym (Gram) is therefore capitalized but not the common noun (stain) as is usual for scientific terms. The initial letters of gram-positive and gram-negative, which are eponymous adjectives, can be either capital G or lowercase g, depending on what style guide (if any) governs the document being written. Lowercase style is used by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other style re…
See also
• Bacterial cell structure
• Ziehl–Neelsen stain
External links
• Gram staining technique video