
Full Answer
What is another name for the central sulcus?
Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy. The central sulcus is a sulcus, or fold, in the cerebral cortex in the brains of vertebrates. Also called the central fissure, or the fissure of Rolando or the Rolandic fissure, after Luigi Rolando.
Does the central sulcus join the lateral fissure?
Near the lateral fissure, the central sulcus is bounded by two short sulci, the anterior subcentral sulcus (ascs) and the posterior subcentral sulcus (pscs), forming the subcentral gyrus (ScG) ( Fig. 10 ). The subcentral gyrus may lie within the lateral fissure, giving the impression that the central sulcus joins the lateral fissure.
What is the difference between the Central and posterior sulcus?
The central sulcus is the next posterior sulcus. L sign: the superior frontal gyrus intersects precentral gyrus in an "L" junction. The central sulcus is immediately posterior. lower T sign: the inferior frontal sulcus terminates posteriorly in the precentral sulcus in a "T" junction. The central sulcus is the next posterior sulcus.
What is the central sulcus of the mid midline?
midline sulcus sign: the central sulcus is the longest sulcus in a roughly coronal plane intersecting the interhemispheric fissure upper T sign : the superior frontal sulcus intersects the precentral sulcus in a "T" junction. The central sulcus is the next posterior sulcus.
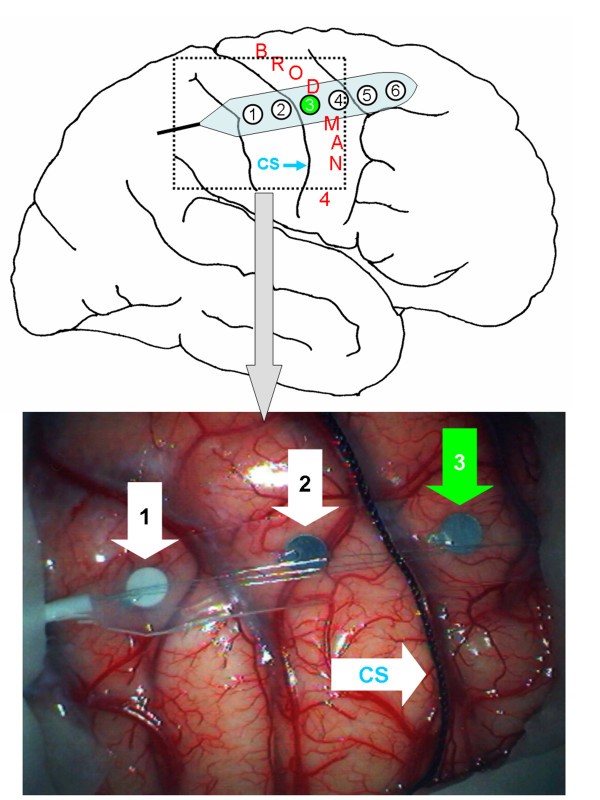
How far apart are the injections in the precentral gyrus?
In this method, two injections are made 4 mm apart in the precentral gyrus and two injections in the postcentral gyrus, paralleling each other. A 27-gauge needle is used for the injection, which is placed into the cortex to a depth of approximately 4 mm.
What is the inferior precentral sulcus?
The inferior precentral sulcus (iprs) separates the ventral orofacial part of the precentral gyrus from the pars opercularis of the inferior frontal gyrus. It continues dorsally for a considerable distance so that its superior ramus (iprs-s) forms the posterior margin of the middle frontal gyrus. A horizontally directed protrusion ...
What is the central sulcus?
The central sulcus (the sulcus of Rolando) forms the boundary between the frontal and the parietal lobes on the lateral and medial surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres (Figs. 10 and 11). Near the lateral fissure, the central sulcus is bounded by two short sulci, the anterior subcentral sulcus (ascs) and the posterior subcentral sulcus (pscs), forming the subcentral gyrus (ScG) (Fig. 10). The subcentral gyrus may lie within the lateral fissure, giving the impression that the central sulcus joins the lateral fissure. The precentral motor region of the brain extends from the anterior bank of the central sulcus to the superior and inferior precentral sulci, which form the anterior limit of the precentral gyrus (Fig. 10). The inferior precentral sulcus (iprs) separates the ventral orofacial part of the precentral gyrus from the pars opercularis of the inferior frontal gyrus. It continues dorsally for a considerable distance so that its superior ramus (iprs-s) forms the posterior margin of the middle frontal gyrus. A horizontally directed protrusion of the inferior precentral sulcus, the horizontal extension (he), projects into the middle frontal gyrus, but this short sulcus is often submerged and cannot be observed on the surface of the brain (dotted line in Fig. 10 ). A short sulcus close to the inferior precentral sulcus frequently projects towards the central sulcus, the posterior ramus of the inferior precentral sulcus (iprs-p) ( Fig. 10 ).
How is the central sulcus exposed?
The central sulcus of either adult or adolescent monkeys is exposed through a frontal craniotomy under general anesthetic, taking great care not to damage the cortex. After opening the dura, the hand-face region of the sensorimotor cortex is identified with cortical stimulation and injected with alumina gel.
Which sulcus is located on the superior aspect of the posterior horizontal ramus?
Of greater importance in locating the central sulcus are the two sulci on the superior aspect of the posterior horizontal ramus: the anterior and posterior subcentral sulci. The small protrusion of the brain between those sulci is the subcentral gyrus, and the central sulcus approaches (but does not contact) the cortex of the gyrus.
Which sulcus can be localized with MEG?
The central sulcus can be localized with MEG by two independent measurements, by localizing the primary sensory cortex, S1, and the primary motor cortex, M1. Stimulation of sensory nerves elicits somatosensory evoked fields (SEFs) generated at S1.
How long does it take for a sharp wave to show up?
In general within 2 to 4 weeks sharp waves can be detected over the injection site. Within 1 to 2 months, epileptiform activity and clinical seizures will begin to be observed. These are initially focal and frequently progress to Jacksonian-type marches. Secondary generalized seizures are not uncommon.
What is the sign of a sigmoidal hook?
sigmoidal hook (handknob, omega) sign: the precentral gyrus bulges posteriorly at the hand motor area. bifid postcentral gyrus sign: the postcentral gyrus is split medially by the pars marginalis of the cingulate sulcus.
What are the signs of a sulcus?
The most well-known signs include the following: upper T sign : the superior frontal sulcus intersects the precentral sulcus in a "T" junction. The central sulcus is the next posterior sulcus. L sign: the superior frontal gyrus intersects precentral gyrus in an "L" junction. The central sulcus is immediately posterior.
Which sulcus terminates posteriorly in the precentral sulcus?
The central sulcus is immediately posterior. lower T sign: the inferior frontal sulcus terminates posteriorly in the precentral sulcus in a "T" junction. The central sulcus is the next posterior sulcus. M sign: the inferior frontal gyrus has a characteristic "M" configuration and terminates posteriorly in the precentral gyrus.
What is the central sulcus?
Central sulcus. The central sulcus ( of Rolando) is a very important landmark in both anatomical and functional neuroanatomy.
What is the purpose of functional MRI?
In cases where anatomy is uncertain, or it is of critical importance to confirm the anatomy, then functional MRI can be performed, particularly aimed at identifying the hand motor cortex.
Which lobe of the brain separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe
The central sulcus separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe, and more specifically separates the primary motor cortex anteriorly from the primary somatosensory cortex posteriorly 1.
Is the central sulcus posterior?
The central sulcus is immediately posterior. bracket sign: the marginal sulcus is visible immediately posterior to the central sulcus, and is easily identifiable of sagittal paramedian images as the continuation of the cingulate sulcus.
Overview
All the functions performed by the body are a result of many coordinated actions that take place and lead to the execution of single or multiple tasks. There are numerous kinds of data that is received by the body’s sensory organs and tissues which is sent to the relevant centres of the brain for it to process and interpret that information.
Summary
The cerebral cortex’s numerous creases and ridges have an added benefit in that they provide a larger surface area for an increased number of nerve cells to survive, allowing for the processing of large amounts of data
Gyrus
The cerebral cortex has a somewhat creased appearance with numerous grooves and perforations. A gyrus (plural called gyri) is the word used to describe the ridges and grooves on the cerebral cortex, which is the layer that is present in the outer boundary of the brain.
Sulcus
A sulcus (plural called sulci) is also another word for a furrow present on the cerebral cortex. Every gyrus is encircled by sulci, which work with each other to contribute to increasing the surface area of the cortex and establish distinctions in the brain surface to understand its divisions.
Sulci present in the brain
A few sulci that are located on the brain’s surface are briefly described below (Figure 2).
Central sulcus
The central sulcus connects the frontal lobe and the parietal lobe. It is also recognized as the Rolando sulcus. This is an important sulcus because it separates the primary motor cortex from the primary somatosensory cortex, and also the frontal and parietal lobes.
Development of Central Sulcus
The central sulcus starts to develop roughly around thirteen weeks of gestational age and grows at its quickest between thirteen and fifteen weeks of gestational age. Nevertheless, the most energetic developmental stage occurs between eighteen and nineteen weeks of gestation.
What is the central sulcus?
The central sulcus (the sulcus of Rolando) forms the boundary between the frontal and the parietal lobes on the lateral and medial surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres (Figs. 10 and 11 ). Near the lateral fissure, the central sulcus is bounded by two short sulci, the anterior subcentral sulcus (ascs) and the posterior subcentral sulcus (pscs), forming the subcentral gyrus (ScG) ( Fig. 10 ). The subcentral gyrus may lie within the lateral fissure, giving the impression that the central sulcus joins the lateral fissure. The precentral motor region of the brain extends from the anterior bank of the central sulcus to the superior and inferior precentral sulci, which form the anterior limit of the precentral gyrus ( Fig. 10 ). The inferior precentral sulcus (iprs) separates the ventral orofacial part of the precentral gyrus from the pars opercularis of the inferior frontal gyrus. It continues dorsally for a considerable distance so that its superior ramus (iprs-s) forms the posterior margin of the middle frontal gyrus. A horizontally directed protrusion of the inferior precentral sulcus, the horizontal extension (he), projects into the middle frontal gyrus, but this short sulcus is often submerged and cannot be observed on the surface of the brain (dotted line in Fig. 10 ). A short sulcus close to the inferior precentral sulcus frequently projects towards the central sulcus, the posterior ramus of the inferior precentral sulcus (iprs-p) ( Fig. 10 ).
Where is the frontal lobe?
The frontal lobe extends from the central sulcus to the frontal pole. This large cortical expanse includes about half of the entire cortex in primates. The prefrontal cortex occupies roughly the anterior half of the frontal lobe in macaque monkeys, and about two thirds in humans. The primary motor cortex, also known as M1 (or area 4 of Brodmann) marks the posterior extent of the frontal lobe, and the premotor cortex (also known as area 6) is interposed between the primary motor and prefrontal cortices (Figures 1 and 2 ). Other species besides primates have a prefrontal cortex, and at least in mammals it's found in front of the premotor cortex.
What is the central sulcus?
The central sulcus is a fold in the cerebral cortex in the brains of vertebrates. Also called the central fissure, it was originally called the fissure of Rolando or the Rolandic fissure, after Luigi Rolando. It is sometimes confused with the medial longitudinal fissure . The central sulcus is a prominent landmark of the brain, ...
Which hemispheres did the central sulcus not reach?
In 68/82 hemispheres, the central sulcus did not reach the posterior ramus of the lateral sulcus. A knob on the second curve of the precentral gyrus was reliably identified in only 64/82 hemispheres 1) .
Which lobe of the brain is the central sulcus?
The central sulcus is a prominent landmark of the brain, separating the parietal lobe from the frontal lobe and the primary motor cortex from the primary somatosensory cortex . The central sulcus joins the Sylvian fissure in only 2 % of cases (i.e., in 98% of cases there is a subcentral gyrus )

Overview
The central sulcus is a sulcus, or groove, in the cerebral cortex in the brains of vertebrates. Also called the central fissure, or the fissure of Rolando or the Rolandic fissure, after Luigi Rolando. It is sometimes confused with the longitudinal fissure.
The central sulcus is a prominent landmark of the brain, separating the parietal lobe from the frontal lobe and the primary motor cortex from the primary somatosensory cortex.
Evolution of the central sulcus
The evolution of the central sulcus is theorized to have occurred in mammals when the complete dissociation of the original somatosensory cortex from its mirror duplicate developed in placental mammals such as primates, though the development did not stop there as time progressed the distinction between the two cortices grew.
The central sulcus is more prominent in apes as a result of fine-tuning of the motor system in ap…
Development in humans
The central sulcus begins developing around 13 weeks of gestational age undergoes the fastest period of growth between 13 and 15 weeks of gestational age. However, the most active period of development is at approximately 18 to 19 weeks of gestational age. This is determined by when there is the greatest amount of migration of neurons and fibers occurring. It begins as a point or groove in the parasagittal region of the brain. It then becomes a distinct invagination that length…
Clinical significance
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) has been associated with sensorimotor deficits and the central sulcus divides both somatosensory and primary motor areas prompting research into how the shape of the central sulcus and ADHD may alter brain development in these individuals. The cortical thickness and average and maximum depth of the central sulcus has been shown to be larger for ADHD individuals when compared to neurotypical individuals. Additi…
Gallery
• Position of central sulcus (shown in red).
• Human brain dissection video. Demonstrating position of the central sulcus of the left cerebral hemisphere
See also
• Primary motor cortex
• Primary somatosensory cortex
• Luigi Rolando
• List of human anatomical parts named after people
External links
• "Anatomy diagram: 13048.000-3". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2012-07-22.