The adrenal glands are composed of two heterogenous types of tissue. In the center is the adrenal medulla, which produces adrenaline and noradrenaline and releases them into the bloodstream, as part of the sympathetic nervous system. Surrounding the medulla is the cortex, which produces a variety of steroid hormones.
What stimulates adrenal glands?
- Eat several (4-6) smaller meals or snacks throughout the day, rather than two or three large meals. ...
- Snacks and meals should consist of foods higher in protein. ...
- Avoid sugars and refined carbohydrates.
- Support the adrenals nutritionally with a good multivitamin and/or vitamin B-complex.
What are the functions of adrenal glands?
Primary Functions of Adrenal Glands
- Hormones Produced by the Adrenal Glands. Part of the primary functions of adrenal glands is to produce over 150 hormones. ...
- Symptoms of Poor Adrenal Functioning. ...
- Overactive and Underactive Adrenal Glands. ...
- Contact Dr. ...
What are the adrenal glands responsible for in my body?
The adrenal cortex produces three hormones:
- Mineralocorticoids: the most important of which is aldosterone. This hormone helps to maintain the body’s salt and water levels which, in turn, regulates blood pressure. ...
- Glucocorticoids: predominantly cortisol. ...
- Adrenal androgens: male sex hormones mainly dehydroepiandrosterone ( DHEA) and testosterone. ...
What is the role of the adrenal gland in the body?
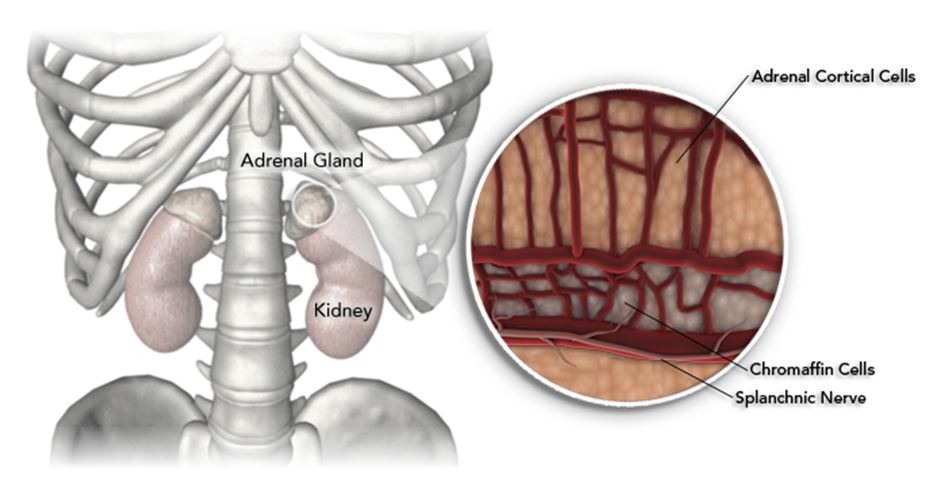
The adrenal glands are tiny organs that rest on top of each kidney. Despite their small size, the adrenal glands play an important role in the body, producing numerous hormones that impact our development and growth, affect our ability to deal with stress, and help to regulate kidney function.

Is the adrenal gland is epithelial tissue?
The adrenocortical tissue is also classically categorized as an epithelial tissue. Studies on the adrenal cortex place its origins in the intermediate mesoderm (mesenchymal) [24], but it is considered to have undergone MET to an epithelial tissue [25].
What is adrenal tissue?
What You Need to Know. Adrenal glands, also known as suprarenal glands, are small, triangular-shaped glands located on top of both kidneys. Adrenal glands produce hormones that help regulate your metabolism, immune system, blood pressure, response to stress and other essential functions.
What type of gland is the adrenal gland?
Your adrenal glands are endocrine glands located on top of your kidneys. They produce many important hormones, including cortisol, aldosterone and adrenaline. The adrenal hormones help regulate several bodily functions including metabolism, blood pressure and your body's response to stress.
What is the histology of the adrenal gland?
The adrenal gland is encased in a connective tissue capsule that extends septae into the substance of the gland....Overview of Adrenal Histology.Cortexzona glomerulosamineralocorticoids (aldosterone)zona fasiculataglucocorticoids (cortisol)zona reticularissex steroids (androgens)Medullacatecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine)
What is adrenal gland and its function?
The adrenal glands have two parts: the cortex and the medulla. The cortex is the outer part of the gland. It produces the hormones cortisol and aldosterone. The medulla, meanwhile, is the inner part of the gland. It produces the hormones adrenaline and noradrenaline.
What do adrenal glands make?
The adrenal glands make the hormones cortisol, aldosterone, adrenaline, and noradrenaline. They also make hormones that your body uses to make sex hormones (estrogen and testosterone). All of these hormones do many important jobs, including: Turning food into energy and managing blood sugar levels.
What is the name of a tissue that has receptor sites for a particular hormone?
A target tissue is a tissue that has receptor sites for a particular hormone. Endocrine glands have ducts that empty their secretions onto a surface.
What does the adrenal gland produce quizlet?
What do they produce? One produces epinephrine (adrenaline) and the other produces norepinephrine (noradrenaline).
What are 3 diseases that affect the adrenal glands?
Some of the most common include:Addison's disease, also called adrenal insufficiency. In this disorder, you don't produce enough cortisol and/or aldosterone.Cushing's syndrome. ... Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. ... Adrenal gland suppression. ... Hyperaldosteronism. ... Virilization.
What are signs of adrenal gland problems?
Adrenal Disorders: What You Need to Know Symptoms of hormone underproduction, the cause of Addison's disease, can include: weakness, fatigue, dizziness, dark skin, weight loss, dehydration, lack of appetite, muscle aches, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, low blood pressure and low sugar levels.
Can you live without adrenal glands?
Humans cannot live without adrenal glands, so if both adrenal glands are removed (very rarely necessary), then the patient needs to take medications and supplements to provide the necessary hormones.
What causes adrenal gland problems?
Adrenal gland disorders are caused by problems with one or both adrenal glands or by problems with other glands, such as the pituitary gland. Specific disorders can develop when the adrenal glands produce too few or too many hormones, or when too many hormones are introduced from an outside source.
Overview
Your adrenal glands, also known as suprarenal glands, are small, triangle-shaped glands that are located on top of each of your two kidneys. They’re a part of your endocrine system and produce certain hormones that help regulate several important bodily functions, including:
Function
Your adrenal glands are responsible for producing and releasing the following essential hormones:
Anatomy
You have two adrenal glands that are located on top of each of your kidneys. Your kidneys are located underneath your ribcage on each side of your spine.
Conditions and Disorders
There are several different adrenal gland disorders. They happen when your adrenal glands make too much or not enough of one or more hormones. Some adrenal conditions are temporary, whereas others are chronic (lifelong).
Care
If you have concerning symptoms such as high or low blood pressure and unexplained weight loss or weight gain, reach out to your healthcare provider. While many conditions could cause these symptoms, it could be an issue with your adrenal glands.
What are the adrenal glands?
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla.
Where are the adrenal glands located?
The adrenal glands are located on both sides of the body in the retroperitoneum, above and slightly medial to the kidneys. In humans, the right adrenal gland is pyramidal in shape, whereas the left is semilunar or crescent shaped and somewhat larger.
What are the three main types of steroid hormones produced by the adrenal cortex?
The adrenal cortex produces three main types of steroid hormones: mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens. Mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone) produced in the zona glomerulosa help in the regulation ...
How many people have adrenal insufficiency?
Adrenal insufficiency (the deficiency of glucocorticoids) occurs in about 5 in 10,000 in the general population. Diseases classified as primary adrenal insufficiency (including Addison's disease and genetic causes) directly affect the adrenal cortex. If a problem that affects the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis arises outside the gland, it is a secondary adrenal insufficiency .
Why do adrenal glands shrink?
The size of the glands decreases relatively after birth, mainly because of shrinkage of the cortex.
Which gland produces cortisol?
Adrenal gland. The adrenal glands lie above the kidneys. The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys.
Where are hormones produced?
Different hormones are produced in different zones of the cortex and medulla of the gland . Light microscopy at magnification × 204. The adrenal gland secretes a number of different hormones which are metabolised by enzymes either within the gland or in other parts of the body.
Sex Hormones and Their Impact on Cardiovascular Health
Sasha De Jesus, ... Stacey E. Rosen, in Sex Differences in Cardiac Diseases, 2021
Leptin
Krzysztof W. Nowak, ... Mathias Z. Strowski, in Handbook of Biologically Active Peptides (Second Edition), 2013
The Human Hypothalamus
Virginie Tolle, ... Jacques Epelbaum, in Handbook of Clinical Neurology, 2021
Renal Modulation: Arginine Vasopressin and Atrial Natriuretic Peptide
Marco Zaffanello MD, PhD, ... Francesco Emma MD, in Nephrology and Fluid/Electrolyte Physiology: Neonatology Questions and Controversies, 2008
Transplantation for Primary Hepatic Malignancy
Nicholas Onaca, ... Göran B.G. Klintmalm, in Transplantation of the Liver (Third Edition), 2015
Volume 2
Maria Luisa S. Sequeira Lopez, Roberto Ariel Gomez, in Fetal and Neonatal Physiology (Fourth Edition), 2011
What are the adrenal glands?
Summary. The adrenal glands are small glands that sit above the kidneys in the upper abdomen. They produce and release several hormones in the body. A range of medical conditions can affect the adrenal glands. These include Addison’s disease, Cushing’s syndrome, and adrenal cancer, as well as high blood pressure due to the overproduction ...
What is it called when you have adrenal gland problems?
Sometimes, the adrenal glands produce too much or not enough of their hormones. When this happens, it is known as an adrenal gland disorder. The following sections discuss the most common adrenal gland disorders.
What is secondary adrenal insufficiency?
Secondary adrenal insufficiency. This occurs when the pituitary gland does not make enough of a hormone called adrenocorticotropin (ACTH). Without ACTH, the adrenals do not receive a signal to make cortisol.
What is it called when the adrenal glands do not produce enough cortisol?
When the adrenal glands do not make enough cortisol, it is known as adrenal insufficiency . There are three types of adrenal insufficiency : Primary adrenal insufficiency , or Addison’s disease. This condition develops when the adrenal gland itself does not function well and cannot make enough cortisol.
Why do tumors in the adrenal glands not start?
The ACS say that most tumors in the adrenals do not start there. Instead, they often arise because other cancers, such as breast cancer or lung cancer, spread to the adrenals.
How many people get adrenal cancer each year?
Adrenal cancer is rare, affecting as few as 200 people in the United States each year, according to the American Cancer Society (ACS). Benign, or noncancerous, tumors are much more common.
What causes Addison's disease?
autoimmune disease, which is the most common cause of Addison’s disease, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. being born with damaged adrenal glands. tumors on the adrenal glands or those that communicate with the adrenal glands. infections, such as tuberculosis.
How many parts does the adrenal gland have?
Each adrenal gland has two parts external adrenal cortex and internal adrenal medulla. The cortex is surrounded by a fibrous capsule. Both adrenal cortex and medulla have different embryonic origin, structure and functions.
What is the structure of the adrenal medulla?
Structure: The adrenal medulla consists of rounded groups of relatively large and granular cells. These cells are modified postganglionic cells of sympathetic nervous system which have lost normal processes and have acquired a glandular function. These cells are called chromaffin cells or phaeochromocytes.
What is the role of aldosterone in the body?
As the name indicates, they are responsible for the regulation of mineral metabolism. Aldosterone (salt-retaining hormone) is the principal mineralocorticoid (90 to 95%) in humans. Like all other hormones of the adrenal cortex, aldosterone is a steroid. Its main function is to regulate the sodium content of the body.
What are the three hormones that make up the adrenal cortex?
Corticosteroids (corticoids—hormones of adrenal cortex) are grouped into three categories : mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids and gonad corticoids.
Where does the adrenal cortex come from?
The adrenal cortex is derived from the mesoderm of the embryo. Structure (Fig, 22. 12).
Which zone of the gland is arranged in branching cords?
This is the inner zone that constitutes about 7% of the gland. The cells are arranged in branching cords which secrete gonado-corticoids (e.g., androgens that have masculinizing effects).
Which zone of the thyroid gland is the widest?
This is the middle zone which is widest of the three zones. It constitutes about 50% of the gland. It consists of the cells arranged in long, straight columns. The cells of this zone secrete mainly glucocorticoids, which are named because they affect glucose homeostasis.
Where are Adrenal Glands Located?
Adrenal glands are orange-colored glands located on the top of both kidneys. Adrenal glands are about the size of a fortune cookie and are triangular shaped, sitting on top of the kidneys like hats. Everyone has two adrenal glands that make several important hormones required for healthy life. Although some adrenal conditions are treated with hormones, most adrenal diseases are treated with surgery to remove the adrenal gland or the adrenal tumor that is causing a very specific hormone problem. Adrenal.com has hundreds of pages of information about the adrenal gland organized in easy-to-navigate groups.
How do adrenal glands form?
Inside the Adrenal Gland: The Medulla and Cortex. The adrenal glands are paired (you have two of them) flat glands with a triangular shape, each weighing about 5 grams (about half of a lime). When we cut the adrenal gland in half, we can see with our eyes two distinct regions that are different shades of orange. These two major sections of the adrenal are called the adrenal medulla (inner layer), and the adrenal cortex (outer layer).
What are the two parts of the adrenal gland that are cut in half?
These two major sections of the adrenal are called the adrenal medulla (inner layer), and the adrenal cortex (outer layer).
What is the color of the adrenal gland?
The adrenal glands are shaped like a triangular fortune cookie. And they really are orange in color!
How many adrenal glands are there?
Everyone has two adrenal glands that make several important hormones required for healthy life. Although some adrenal conditions are treated with hormones, most adrenal diseases are treated with surgery to remove the adrenal gland or the adrenal tumor that is causing a very specific hormone problem.
What organs are involved in adrenal surgery?
The kidney, IVC and liver are incredibly important structures and it is absolutely crucial that the adrenal surgeon is experienced in dealing with them. If the surgeon is off by just millimeters, the operation can very rapidly end with a tremendously bad outcome. The Left Adrenal Gland: The left adrenal gland is located on top of the left kidney.
What is the adrenal cortex?
The Adrenal Cortex: The adrenal cortex is of mesodermal origin and is derived from the adrenogenital ridge (sorry folks for the technical stuff). The adrenal cortex is organized into three layers, each with a different function: Transection of a portion of normal adrenal tissue displaying the adrenal cortex (yellow), medulla (brownish), ...
Where are the adrenal glands located?
They are located right on top of the kidneys and are enveloped by a fibrous capsule surrounded by adipose tissue. Each gland has two parts, the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla. The adrenal gland has a rich blood supply and nervous innervation, for the rapid release of hormones into the bloodstream.
What are the two parts of the adrenal gland?
Each gland is divided into two distinct parts, a centrally located adrenal medulla and an outer adrenal cortex. These two different parts are derived from different embryological layers, the medulla from the ectoderm and the cortex from the mesoderm.
What are the hormones released from the adrenal cortex?
The hormones released from the adrenal cortex are vital to life. Glucocorticoids regulate the body's metabolic processes and stress response. Mineralocorticoids are involved in the control of electrolyte balance and blood pressure.
What is the specificity of the transcriptome of the adrenal gland?
Specificity illustrates the number of genes with elevated or non-elevated expression in the adrenal gland compared to other tissues. Elevated expression includes three subcategory types of elevated expression:
What is the function of the adrenal gland?
The main function of the adrenal gland is to supply the body with two different sets of hormones, steroid hormones from the adrenal cortex and catecholamines from the adrenal medulla. The cortical steroid hormones are involved in metabolic function, electrolyte balance and have androgenic effects. Catecholamines are released in response ...
What is the adrenal medulla?
The adrenal medulla is stimulated by preganglionic sympathetic neurons to release adrenalin and noradrenalin and has a rapid response to external and internal stress. The release of adrenalin and noradrenalin leads to increased heart rate increased blood pressure and increased blood flow to the muscles.
How many genes are in the adrenal gland?
There are 84 group enriched genes expressed in adrenal gland. Group enriched genes are defined as genes showing a 4-fold higher average level of mRNA expression in a group of 2-5 tissues, including adrenal gland, compared to all other tissues.
Which gland is responsible for releasing hormones?
The adrenal glands , located on the top of each kidney, are responsible for releasing different hormones. Adrenal gland disorders occur when the adrenal glands produce too much or too little of these hormones.
Is congenital adrenal hyperplasia serious?
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) Symptoms of CAH range from mild to serious. Some people with mild CAH are never diagnosed because their symptoms do not cause them any problems. Symptoms of the mild form of CAH, which can be diagnosed in children or adults, may include 1: Shorter than average final height.

Overview
Structure
The adrenal glands are located on both sides of the body in the retroperitoneum, above and slightly medial to the kidneys. In humans, the right adrenal gland is pyramidal in shape, whereas the left is semilunar or crescent shaped and somewhat larger. The adrenal glands measure approximately 5 cm in length, 3 cm in width, and up to 1 cm in thickness. Their combined weight in an adult human ranges from 7 to 10 grams. The glands are yellowish in colour.
Function
The adrenal gland secretes a number of different hormones which are metabolised by enzymes either within the gland or in other parts of the body. These hormones are involved in a number of essential biological functions.
Corticosteroids are a group of steroid hormones produced from the cortex of the adrenal gland, from which they are named.
Gene and protein expression
The human genome includes approximately 20,000 protein coding genes and 70% of these genes are expressed in the normal adult adrenal glands. Only some 250 genes are more specifically expressed in the adrenal glands compared to other organs and tissues. The adrenal-gland-specific genes with the highest level of expression include members of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes. Corresponding proteins are expressed in the different compartments o…
Development
The adrenal glands are composed of two heterogenous types of tissue. In the center is the adrenal medulla, which produces adrenaline and noradrenaline and releases them into the bloodstream, as part of the sympathetic nervous system. Surrounding the medulla is the cortex, which produces a variety of steroid hormones. These tissues come from different embryological precursors and have distinct prenatal development paths. The cortex of the adrenal gland is derived from mesoderm, …
Clinical significance
The normal function of the adrenal gland may be impaired by conditions such as infections, tumors, genetic disorders and autoimmune diseases, or as a side effect of medical therapy. These disorders affect the gland either directly (as with infections or autoimmune diseases) or as a result of the dysregulation of hormone production (as in some types of Cushing's syndrome) leading to an excess or insufficiency of adrenal hormones and the related symptoms.
History
Bartolomeo Eustachi, an Italian anatomist, is credited with the first description of the adrenal glands in 1563–4. However, these publications were part of the papal library and did not receive public attention, which was first received with Caspar Bartholin the Elder's illustrations in 1611.
The adrenal glands are named for their location relative to the kidneys. The term "adrenal" comes from Latin ad, "near", and ren, "kidney". Similarly, "suprarenal", as termed by Jean Riolan the Younger in …
See also
• Adrenopause