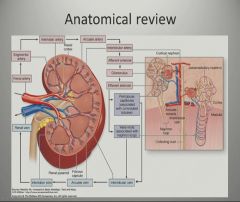
What organs are in the kidney?
There are three main sections:
- The mouth cavity, pharynx, oesophagus and stomach
- The Small Intestine
- The Large Intestine
Are there nervous tissues in the kidney?
The parenchyma of the kidney is epithelial tissue (renal tubules and corpuscles). The blood vessels, nerves, and supporting connective tissue of the kidney comprise the stroma. The parenchyma of the spleen is connective tissue (mostly lymphocytes and other blood cells). The supporting fibrous connective tissue of the spleen comprises the stroma.
What type of tissues are kidneys made up of?
The kidneys are surrounded by three layers of tissue: The renal fascia is a thin, outer layer of fibrous connective tissue that surrounds each kidney (and the attached adrenal gland) and fastens it to surrounding structures. The adipose capsule is a middle layer of adipose (fat) tissue that cushions the kidneys.
What is the tissue called that covers the kidneys?
The renal fascia is a thin, outer layer of fibrous connective tissue that surrounds each kidney (and the attached adrenal gland) and fastens it to surrounding structures. The adipose capsule is a middle layer of adipose (fat) tissue that cushions the kidneys.

What is the function of the kidney?
The main function of the kidney is to eliminate excess bodily fluid, salts and byproducts of metabolism – this makes kidneys key in the regulation of acid-base balance, blood pressure, and many other homeostatic parameters. Key facts about the kidney. Functions.
Which kidney is more medially pointed towards the spine?
This is because the liver and the stomach offset the symmetry of the abdomen, with the liver forcing the right kidney a bit down, and the stomach forcing the left kidney a bit up. The superior poles (extremities) ( T12) of both kidneys are more medially pointed towards the spine than the inferior poles (extremities) (L3).
How many renal pyramids are there in the kidney?
Internal anatomy of the kidney (overview) The main unit of the medulla is the renal pyramid. There are 8-18 renal pyramids in each kidney, that on the coronal section look like triangles lined next to each other with their bases directed toward the cortex and apex to the hilum.
How long does it take to read a kidney?
Reading time: 22 minutes. The kidneys are bilateral organs placed retroperitoneally in the upper left and right abdominal quadrants and are part of the urinary system. Their shape resembles a bean, where we can describe the superior and inferior poles, as well as the major convexity pointed laterally, and the minor concavity pointed medially.
Why does kidney failure cause a sudden fall in blood pressure?
It can be caused by a variety of factors, but most often arises because of the ischemia of the kidney and the toxic effect of some medications, resulting in the failure of all kidney functions. We’ve mentioned that the most important functions of the kidney are the regulation of the blood homeostasis and blood pressure, so acute kidney failure can lead to a quick fall of blood pressure which presents as a state of shock.
What is the role of the kidney in homeostasis?
The kidney is a very important organ in regards to body homeostasis. It participates in vital processes such as regulation of blood osmolarity and pH, regulation of blood volume and blood pressure, production of hormones, and filtration of foreign substances.
Where to find kidneys with ultrasound?
If we wanted to examine someone’s kidneys with ultrasound, we definitely must know where to find them. Since they are located deep retroperitoneally, the easiest way to examine them is from the patient’s back.
What is the thick layer of adipose tissue that surrounds the kidneys called?
Each kidney is held in place by connective tissue, called renal fascia, and is surrounded by a thick layer of adipose tissue, called perirenal fat, which helps to protect it. A tough, fibrous, connective tissue renal capsule closely envelopes each kidney and provides support for the soft tissue that is inside.
What is the outer part of the kidney?
The outer, reddish region, next to the capsule, is the renal cortex. This surrounds a darker reddish-brown region called the renal medulla. The renal medulla consists of a series of renal pyramids, which appear striated because they contain straight tubular structures and blood vessels. The wide bases of the pyramids are adjacent to the cortex and the pointed ends, called renal papillae, are directed toward the center of the kidney. Portions of the renal cortex extend into the spaces between adjacent pyramids to form renal columns. The cortex and medulla make up the parenchyma, or functional tissue, of the kidney.
What is the kidney shaped indentation?
It is roughly bean-shaped with an indentation, called the hilum, on the medial side. The hilum leads to a large cavity, called the renal sinus, within the kidney. The ureter and renal vein leave the kidney, and the renal artery enters the kidney at the hilum.
What are the two parts of the nephron?
A nephron has two parts: a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule .The renal corpuscle consists of a cluster of capillaries, called the glomerulus, surrounded by a double-layered epithelial cup, called the glomerular capsule.
How big is a kidney?
In the adult, each kidney is approximately 3 cm thick, 6 cm wide, and 12 cm long. It is roughly bean-shaped with an indentation, called the hilum, on the medialside. The hilum leads to a large cavity, called the renal sinus, within the kidney. The ureterand renal vein leave the kidney, and the renal arteryenters the kidney at the hilum.
What are the organs that filter blood and remove wastes?
The kidneys are the primary organs of the urinary system. The kidneys are the organs that filter the blood, remove the wastes, and excrete the wastes in the urine. They are the organs that perform the functions of the urinary system. The other components are accessory structures to eliminate the urine from the body.
Where is the renal pelvis located?
The central region of the kidney contains the renal pelvis, which is located in the renal sinus, and is continuous with the ureter. The renal pelvis is a large cavity that collects the urine as it is produced. The periphery of the renal pelvis is interrupted by cuplike projections called calyces.
What is the function of the kidney?
The kidney’s functions in filtration, ion homeostasis, and blood pressure control rely on multiple cell types and anatomical structures. Blood and urine are separated by the filtration barrier that consists of the glomerular basement membrane sandwiched between glomerular endothelial cells contacting the blood and podocytes contacting ...
Which cell controls ionic composition and concentration of urine?
Ionic composition and concentration of the urine are regulated by tubule epithelial cells. The macula densa is a region of the tubule epithelium which contacts the glomerular tuft capillaries. This arrangement provides tubule-glomerular feedback and enables the renal corpuscle to fine tune ion homeostasis, acid-base balance, and blood pressure.
Which propels materials along the surface of an epithelial cell?
C. Cilia propel materials along the surface of an epithelial cell.
What is the shape of secretory epithelial cells?
A. Secretory epithelial cells are usually cuboidal or columnar in shape.
What is the most common benign renal mass?
The most common benign renal mass is called an oncocytoma. Oncocytomas have a typical appearance when large, but when small look similar to malignancy. Another common benign renal mass, more common in fertile women, is called an Angiomyolipoma.
What is the most common type of kidney cancer?
The most common cell type found in kidney cancer is called clear cell renal cell carcinoma, but variants such as papillary, sarcomatoid, medullary and others are seen. Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) is not uncommon, is typically found in smokers, and arises from the lining of the kidney rather than the functioning kidney tissue itself. TCC of the renal pelvis is more similar to bladder cancer than kidney cancer, carries a higher metastasis risk, and if found, typically necessitates removal of not only the entire kidney but also the entire ureter as well. Thus, if TCC of the renal pelvis or collecting system is found, a patient is offer a “nephro-ureterectomy”, also performed laparoscopically by Dr. Engel.
How to treat renal mass?
Treatment for renal masses is predominately surgical. Radiation and/ or chemotherapy play almost no role in the initial management of a kidney mass unless proof of metastasis exists. In certain cases, a patient may be a candidate for percutaneous management such as freezing the tumor (cryotherapy) or heating the tumor (microwave or ultrasound). Such a patient would be an elderly patient or a patient with co-morbidities precluding surgery, and a tumor location and size that is amenable to such an approach. Cryotherapy is sometimes offered laparascopically by Dr. Engel, but only in cases where laparoscopic partial nephrectomy is precluded due to the location of the tumor.
What are the risks of laparoscopic kidney surgery?
The risks present for all laparoscopic kidney surgeries include of course pain, infection and bleeding. But, since we are in the abdomen when performing laparoscopy, there is always the risk of inadvertent bowel injury that will require repair.
How long does it take to recover from laparoscopic kidney surgery?
The bowels will take some days to be regular, but typically patients are back to work within 10 days to 2 week.
How to remove a kidney mass?
The contemporary mainstay of surgery for renal masses is laparoscopy, the act of performing abdominal surgery by inflating the abdomen with carbon dioxide, inserting a camera and several instruments that allow for surgery through small incisions with a rapid recovery . Once it is determined that treatment of a kidney mass is necessary, the next step is to review the actual films, usually a contrast CT, to determine if removing only the tumor is feasible. This is always the desired approach, and in Dr. Engel’s hands will always be attempted. In cases however where the tumor is in a central location, invades deeply into the center of the kidney, or if negative margins cannot be assured in the operating room, the entire kidney will be removed. One only needs one healthy kidney, so in such a circumstance the patient is not usually adversely affected.
What is the most common imaging method for finding a mass on the kidney?
Kidney Masses. The incidental discovery of a mass on the kidney has become a commonplace occurrence now that imaging modalities such as ultrasound, MRI and particularly CT scanning is so prevalent. It is of course very scary to be told that by accident a mass or lesion has been found on one’s kidney, and almost always in such a circumstance ...
