(38).jpg)
What is synovial membrane made up of?
The synovial membrane is the inner layer of the joint capsule made up of intima and subintima (an outer layer of connective tissue). The intima is the inner layer of the synovial membrane consisting of two types of cells: fibroblast-like (type B) synovial cells and macrophage-like (type A) synovial cells.
Is synovium epithelial tissue or connective tissue?
connective tissueSynovial membranes are connective tissue membranes that line the cavities of the freely movable joints such as the shoulder, elbow, and knee. Like serous membranes, they line cavities that do not open to the outside. Unlike serous membranes, they do not have a layer of epithelium.
Are synovial membrane cells epithelial cells?
Slide 1. Synovial Membrane (or Synovium) The surface of the synovium is characterized by a discontinuous layer of cells up to 4 cells deep. These synovial cells are not connected by junctional complexes and do not rest on a basal lamina, therefore they do not constitute an epithelium.
Is synovial fluid a connective tissue?
Normal synovial fluid is a hypocellular, avascular connective tissue.
Is synovium cartilage?
Synovium (also called the synovial membrane) is a specialized connective soft-tissue membrane that lines the inner surface of synovial joint capsules. Together with bone, articular cartilage, tendon, ligament, and fibrous capsule, it is an important component of the tissues that form an integrated joint.
What are the 3 types of epithelial membranes?
Epithelium, endothelium and mesothelium are three types of epithelial cell layers that line your internal organs, body cavities and form the outer layer of your skin.
What type of joint is a synovial?
A synovial joint is the type of joint found between bones that move against each other, such as the joints of the limbs (e.g. shoulder, hip, elbow and knee). Characteristically it has a joint cavity filled with fluid.
Where is synovium located?
Synovium Anatomy The synovium is a special type of connective tissue located in articulated joints like the knees and elbows. The synovium lines the entire inner surface of the joint, except where the joint is lined with cartilage.
What is the synovial membrane?
The synovial membrane (also known as the synovial stratum, synovium or stratum synoviale) is a specialized connective tissue that lines the inner surface of capsules of synovial joints and tendon sheath. It makes direct contact with the fibrous membrane on the outside surface and with the synovial fluid lubricant on ...
How many layers does the synovial membrane have?
The synovial membrane is variable but often has two layers. The outer layer, or subintima, can be of almost any type of connective tissue – fibrous (dense collagenous type), adipose (fatty; e.g. in intra-articular fat pads) or areolar (loose collagenous type). The inner layer (in contact with synovial fluid), or intima, ...
What is the name of the polymer that makes synovial fluid?
The fibroblast-like synoviocytes (derived from mesenchyme) manufacture a long-chain sugar polymer called hyaluronan (hence rich in endoplasmic reticulum ); which makes the synovial fluid "ropy"-like egg-white, together with a molecule called lubricin, which lubricates the joint surfaces.
What is the cell that makes contact with the synovial fluid?
In contact with the synovial fluid at the tissue surface are many rounded macrophage -like synovial cells (type A) and also type B cells, which are also known as fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS).
What type of cells are in the intimal cell?
The intimal cells are of two types, fibroblast-like synoviocytes or type B cells and macrophage - like synovial cells. Surface cells have no basement membrane or junctional complexes denoting an epithelium despite superficial resemblance.
What is the meaning of the word "synovium"?
The word synovium is related to the word synovia in its sense meaning " synovial fluid ". The latter was coined by Paracelsus. More information is given at Synovial fluid § Etymology and pronunciation .
What holds the synovium together?
More often the surfaces are held together by cord-like ligaments. Virtually all the space between muscles, ligaments, bones, and cartilage is filled with pliable solid tissue. The fluid-filled gap is at most only a twentieth of a millimetre thick. This means that synovium has certain rather unexpected jobs to do.
What is the membrane of connective tissue?
Connective Tissue Membranes. The connective tissue membrane is formed solely from connective tissue. These membranes encapsulate organs, such as the kidneys, and line our movable joints. A synovial membrane is a type of connective tissue membrane that lines the cavity of a freely movable joint.
What are the two types of tissue membranes?
Tissue Membranes. The two broad categories of tissue membranes in the body are (1) connective tissue membranes, which include synovial membranes, and (2) epithelial membranes, which include mucous membranes, serous membranes, and the cutaneous membrane, in other words, the skin.
What is the epithelial membrane?
The epithelial membrane is composed of epithelium attached to a layer of connective tissue, for example, your skin. The mucous membrane is also a composite of connective and epithelial tissues. Sometimes called mucosae, these epithelial membranes line the body cavities and hollow passageways that open to the external environment, and include the digestive, respiratory, excretory, and reproductive tracts. Mucous, produced by the epithelial exocrine glands, covers the epithelial layer. The underlying connective tissue, called the lamina propria (literally “own layer”), help support the fragile epithelial layer.
How do zygote cells form?
The zygote, or fertilized egg, is a single cell formed by the fusion of an egg and sperm. After fertilization the zygote gives rise to rapid mitotic cycles, generating many cells to form the embryo. The first embryonic cells generated have the ability to differentiate into any type of cell in the body and, as such, are called totipotent, meaning each has the capacity to divide, differentiate, and develop into a new organism. As cell proliferation progresses, three major cell lineages are established within the embryo. As explained in a later chapter, each of these lineages of embryonic cells forms the distinct germ layers from which all the tissues and organs of the human body eventually form. Each germ layer is identified by its relative position: ectoderm (ecto- = “outer”), mesoderm (meso- = “middle”), and endoderm (endo- = “inner”). [link] shows the types of tissues and organs associated with the each of the three germ layers. Note that epithelial tissue originates in all three layers, whereas nervous tissue derives primarily from the ectoderm and muscle tissue from mesoderm.
What is the membrane of the body?
A tissue membrane is a thin layer or sheet of cells that covers the outside of the body (for example, skin), the organs (for example, pericardium), internal passageways that lead to the exterior of the body (for example, abdominal mesenteries), and the lining of the moveable joint cavities. There are two basic types of tissue membranes : connective tissue and epithelial membranes ( [link] ).
What are the different types of tissue?
The Four Types of Tissues. Epithelial tissue, also referred to as epithelium, refers to the sheets of cells that cover exterior surfaces of the body, lines internal cavities and passageways, and forms certain glands. Connective tissue, as its name implies, binds the cells and organs of the body together and functions in the protection, support, ...
How many types of tissue are there in the human body?
Identify the four types of tissue in the body, and describe the major functions of each tissue.
Which type of membrane contains only connective tissue?
Connective tissue membranes contain only connective tissue. Synovial membranes and meninges belong to this category.
What are the two types of epithelial membranes?
The two main types of epithelial membranes are the mucous membranes and serous membranes.
What is the membrane that covers the organs?
Serous Membranes. Serous membranes line body cavities that do not open directly to the outside, and they cover the organs located in those cavities. Serous membranes are covered by a thin layer of serous fluid that is secreted by the epithelium.
What is the membrane that lines the body cavities?
Mucous membranes are epithelial membranes that consist of epithelial tissue that is attached to an underlying loose connective tissue. These membranes, sometimes called mucosae, line the body cavities that open to the outside. The entire digestive tract is lined with mucous membranes.
What is the membrane of the body?
Membranes. Body membranes are thin sheets of tissue that cover the body, line body cavities, and cover organs within the cavities in hollow organs. They can be categorized into epithelial and connective tissue membrane.
What is the connective tissue covering on the brain and spinal cord, within the dorsal cavity, called?
The connective tissue covering on the brain and spinal cord, within the dorsal cavity, are called meninges. They provide protection for these vital structures.
Do serous membranes have epithelium?
Like serous membranes, they line cavities that do not open to the outside. Unlike serous membranes, they do not have a layer of epithelium. Synovial membranes secrete synovial fluid into the joint cavity, and this lubricates the cartilage on the ends of the bones so that they can move freely and without friction.
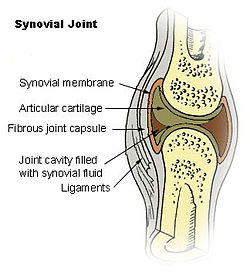
Overview
Structure
The synovial membrane is variable but often has two layers:
• The outer layer, or subintima, can be of almost any type of connective tissue – fibrous (dense collagenous type), adipose (fatty; e.g. in intra-articular fat pads) or areolar (loose collagenous type).
• The inner layer (in contact with synovial fluid), or intima, consists of a sheet of cells thinner than a piece of paper.
Mechanics
Although a biological joint can resemble a man-made joint in being a hinge or a ball and socket, the engineering problems that nature must solve are very different because the joint works within an almost completely solid structure, with no wheels or nuts and bolts.
In general, the bearing surfaces of manmade joints interlock, as in a hinge. This is rare for biological joints (although the badger's jaw interlocks).
Pathology
Synovium can become irritated and thickened (synovitis) in conditions such as osteoarthritis, Ross River virus or rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) play a key role in the pathogenesis of RA, and the aggressive phenotype of FLS in RA and the effect these cells have on the microenvironment in the joint can be summarized into hallmarks that distinguish them from healthy FLS. These hallmark features of FLS in RA are divided into seven cell-intrinsic hallmarks …
Etymology and pronunciation
The word synovium is related to the word synovia in its sense meaning "synovial fluid". The latter was coined by Paracelsus. More information is given at Synovial fluid § Etymology and pronunciation.
See also
• Synovial sheath