Precautions
Is TWINRIX a recombinant vaccine?
TWINRIX [Hepatitis A & Hepatitis B (Recombinant) Vaccine] is a bivalent vaccine containing the antigenic components used in producing HAVRIX® (Hepatitis A Vaccine) and ENGERIX-B® [Hepatitis B Vaccine (Recombinant)].
What type of vaccine is hepatitis vaccine?
Hepatitis B vaccineVaccine descriptionTargetHepatitis B virusVaccine typeSubunitClinical dataTrade namesRecombivax HB, Engerix-B, Heplisav-B, others17 more rows
How many years is the Twinrix vaccine good for?
When you complete the Twinrix® series,your protection will likely last for at least 20 years for hepatitis A and lifelong for hepatitis B.
What is TWINRIX made of?
Twinrix Junior The liquid suspension is made isotonic with sodium chloride in water for injection. Nonmedicinal ingredients: aluminum hydroxide, aluminum phosphate, sodium chloride, and water for injection. Residues: amino acids for injection, formaldehyde, neomycin sulphate, and polysorbate 20.
What are the 4 types of vaccines?
What are the Different Types of Vaccines?Live-attenuated vaccines.Inactivated vaccines.Subunit, recombinant, conjugate, and polysaccharide vaccines.Toxoid vaccines.mRNA vaccines.Viral vector vaccines.
Which vaccines are live vaccines?
Live vaccines are used to protect against:Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR combined vaccine)Rotavirus.Smallpox.Chickenpox.Yellow fever.
Can you get TWINRIX twice?
Yes. The standard children's TWINRIX schedule for adolescents, children, and infants ages 1-18 years uses the TWINRIX Junior vaccine and requires 3 doses over a span of 6 months. You choose the date for the first dose. The second dose is 1 month after the first and the last dose is 6 months after the first.
Can TWINRIX be used as a booster?
In situations where a booster dose of both hepatitis A and hepatitis B are desired, Twinrix Adult can be given. Alternatively, subjects primed with Twinrix Adult may be administered a booster dose of either of the monovalent vaccines.
What are the side effects of Twinrix vaccine?
Very common adverse events (>10% of doses) reported in adults, were pain or discomfort, redness at the infection site, headache, and tiredness. Common adverse events (1% to 10% of doses) were swelling at the injection site, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, and generally feeling unwell. Allergic reactions may also occur.
Is TWINRIX a live virus vaccine?
What is Twinrix Adult? Twinrix Adult is a vaccine, which is available as a suspension for injection. It contains inactivated (killed) hepatitis A viruses and parts of the hepatitis B virus as active substances.
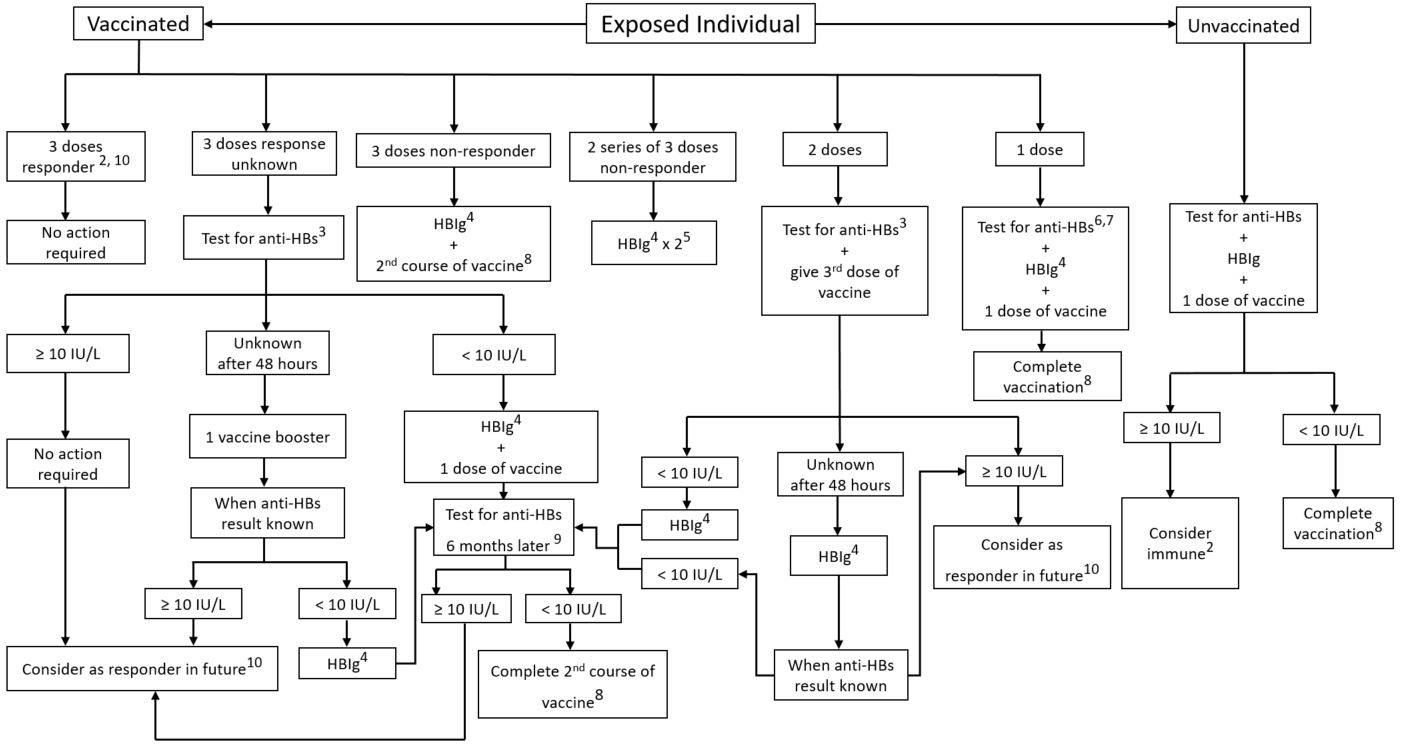
Are 2 doses of TWINRIX enough?
It should be noted that two doses of the combined vaccine will protect almost 100% against HA but result in protective anti-HBs antibodies level in 50%–95% of individuals. Higher rates of seroprotection may be achieved when three doses of vaccine or accelerated schedule are given to travelers before travel.
How old is the TWINRIX vaccine?
Children's TWINRIX Vaccination SchedulesAge groupVaccine Dose #2Standard schedule* TWINRIX Junior 0.5 mL1-18 years1 month after the first dose.Alternate schedule* TWINRIX 1.0 mL1-15 years6-12 months after the first dose.
What type of vaccine is the measles vaccine?
MMR is an attenuated (weakened) live virus vaccine. This means that after injection, the viruses cause a harmless infection in the vaccinated person with very few, if any, symptoms before they are eliminated from the body.
What are the types of hepatitis virus?
There are 5 main hepatitis viruses, referred to as types A, B, C, D and E. These 5 types are of greatest concern because of the burden of illness and death they cause and the potential for outbreaks and epidemic spread.
What are the types of hepatitis?
Causes of hepatitisType of hepatitisCommon route of transmissionhepatitis Aexposure to HAV in food or waterhepatitis Bcontact with HBV in body fluids, such as blood, vaginal secretions, or semenhepatitis Ccontact with HCV in body fluids, such as blood, vaginal secretions, or semen2 more rows
What is hepatitis B vaccine series?
The hepatitis B vaccine is given as a series of three shots. The first dose is given within 24 hours of birth. The second dose is given one to two months after the first dose, and the third dose is given between 6 months and 18 months of age.
Indications and Usage For Twinrix
This combination vaccine is used to help prevent infection from the hepatitis A and B viruses.
Status: Discontinued
May Treat: Hepatitis A vaccination · Hepatitis B vaccination
Drug Class: Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B Vaccine Combinations
Availability: Prescription Required
Pregnancy: Consult a doctor before using
Status: Discontinued
May Treat: Hepatitis A vaccination · Hepatitis B vaccination
Drug Class: Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B Vaccine Combinations
Availability: Prescription Required
Pregnancy: Consult a doctor before using
Lactation: Consult a doctor before using
Alcohol: Limit intake while taking this medication
Driving: May cause drowsiness or dizziness. Use caution
Manufacturer: GLAXOSMITHKLINE
Twinrix Dosage and Administration
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Contraindications
Warnings and Precautions
Adverse Reactions
- Preparation for Administration
The vaccine should be re-suspended before use. When re-suspended, the vaccine will have a uniform hazy white appearance. Upon storage, a fine white deposit with a clear colorless layer above may be present. Re-suspend the vaccine following the steps below. 1. Hold the syringe up… - Administration
Twinrix should be administered by intramuscular injection only as a 1-mL dose. Administer in the deltoid region. Do not administer in the gluteal region; such injections may result in a suboptimal response. Do not administer this product intravenously, intradermally, or subcutaneously.
Drug Interactions
- Suspension for injection available in 1-mL prefilled TIP-LOK syringes [see Description (11), How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)].
Use in Specific Populations
- Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose of any hepatitis A-containing or hepatitis B-containing vaccine, or to any component of Twinrix, including yeast and neomycin, is a contraindication to administration of Twinrix [see Description (11)].
Twinrix - Clinical Pharmacology
- Latex
The tip caps of the prefilled syringes contain natural rubber latex which may cause allergic reactions. - Syncope
Syncope (fainting) can occur in association with administration of injectable vaccines, including Twinrix. Syncope can be accompanied by transient neurological signs such as visual disturbance, paresthesia, and tonic-clonic limb movements. Procedures should be in place to avoid falling inj…
Who Should Be Vaccinated with Hepatitis A?
- Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a vaccine cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another vaccine and may not reflect the rates observed in practice. Following any dose … - Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of Twinrix, HAVRIX, or ENGERIX-B. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to th…
Who Should Be Vaccinated with Hepatitis B?
- Concomitant Administration with Vaccines and Immune Globulin
Do not mix Twinrix with any other vaccine or product in the same syringe. When concomitant administration of immunoglobulin is required, it should be given with a different syringe and at a different injection site. There are no data to assess the concomitant use of Twinrix with other va… - Immunosuppressive Therapies
Immunosuppressive therapies, including irradiation, antimetabolites, alkylating agents, cytotoxic drugs, and corticosteroids (used in greater-than-physiologic doses), may reduce the immune response to Twinrix.
Dosage
- Pregnancy
Risk Summary All pregnancies have a risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively. There are no adequa… - Lactation
Risk Summary There is no information regarding the presence of Twinrix in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Twinrix …
Potential Side Effects
- Mechanism of Action
Hepatitis A The course of infection with hepatitis A virus (HAV) is extremely variable, ranging from asymptomatic infection to fulminant hepatitis.3 The presence of antibodies to HAV (anti-HAV) confers protection against hepatitis A disease. However, the lowest titer needed to confer prote…
Who Should Not Get The Vaccine?