
What is the viscosity of a volcanic eruption?
They are typified by their high ferromagnesian content, and generally erupt at temperatures of 1,100 to 1,200 °C (2,010 to 2,190 °F). Viscosities can be relatively low, around 10 4 to 10 5 cP, although this is still many orders of magnitude higher than water. This viscosity is similar to that of ketchup.
Does ultramafic lava have a high viscosity?
Mafic and ultramafic lava, which have progressively lower viscosities, also contain progressively lower quantities of silica and aluminum, which form macromolecules. Instead, they are rich in magnesium oxide, which does not form large molecular structures in liquid state.
How viscous is rhyolite magma?
With such a high silica content, these magmas are extremely viscous, ranging from 10 8 cP for hot rhyolite magma at 1,200 °C (2,190 °F) to 10 11 cP for cool rhyolite magma at 800 °C (1,470 °F). For comparison, water has a viscosity of about 1 cP.
What is the viscosity of felsic lava?
Whereas temperatures in common silicate lavas range from about 800 °C (1,470 °F) for felsic lavas to 1,200 °C (2,190 °F) for mafic lavas, the viscosity of the same lavas ranges over seven orders of magnitude, from 10 4 cP for mafic lava to 10 11 cP for felsic magmas.
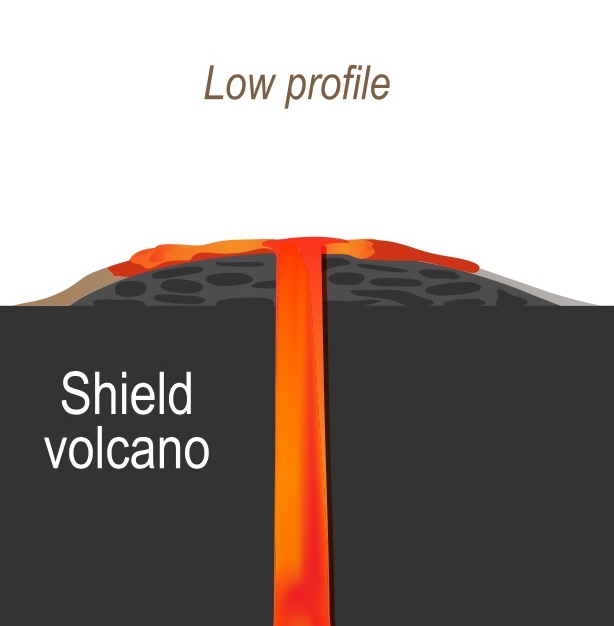
What type of volcano has lava with high viscosity?
Stratovolcano. Stratovolcanoes have relatively steep sides and are more cone-shaped than shield volcanoes. They are formed from viscous, sticky lava that does not flow easily.
Which volcanic rock has the highest viscosity?
The magma that has the highest viscosity is rhyolitic magma.
What type of volcano has low viscosity?
shield volcanoesAnd over time, volcanoes made from low lava viscosity are wide and have a shallow slope; these are known as shield volcanoes. Classic examples of shield volcanoes are Mauna Kea and Mauna Loa in Hawaii, as well as Olympus Mons on Mars.
Do explosive volcanoes have high or low viscosity?
Explosive eruptions are favored by high gas content and high viscosity (andesitic to rhyolitic magmas). Explosive bursting of bubbles will fragment the magma into clots of liquid that will cool as they fall through the air.
Do stratovolcanoes have high viscosity?
The lava flowing from stratovolcanoes typically cools and hardens before spreading far, due to high viscosity.
Do composite volcanoes have high viscosity?
There are two types of volcanoes. Composite volcanoes have steep slopes consisting of layers of lava and ash, and often have very explosive eruptions. This type of volcano is found along convergent boundaries and has a very high viscosity. The gas content is high, but the temperature is low.
Do cinder cone volcanoes have high viscosity?
Spheroidal and spindle-shaped bombs are common at cinder cones. Unlike the violently explosive eruptions that create large stratovolcanoes, cinder cones form when low-viscosity lava with lots of gas erupts, often as liquid fountains.
What is an example of high viscosity?
Liquids which flow very slowly, like glycerin or honey, have high viscosities. Those like ether or gasoline which flow very readily have low viscosities. Viscosity is governed by the strength of intermolecular forces and especially by the shapes of the molecules of a liquid.
What is high viscosity?
A fluid that is highly viscous has a high resistance (like having more friction) and flows slower than a low-viscosity fluid. To think of viscosity in everyday terms, the easier a fluid moves, the lower the viscosity.
Which type of volcano releases thick or viscous lava that can reach great heights?
In fact, Mount Vesuvius is a composite volcano that is most famous for burying the ancient Roman city of Pompeii in up to 20 feet of volcanic ash in 79 AD. The explosiveness of their eruptions is due to the thick, highly viscous lava that is produced by composite cone volcanoes.
What are the elements in felsic lava?
Though felsic lava contains elements of relatively small size such as sodium and aluminum, these elements form polymers and large crystalline macromolecules such as silica (silicon dioxide), which is known as the minerals feldspar and quartz.
What are some of the most fascinating and deadly natural phenomena in the world?
Volcanoes and Viscosity. Volcanoes are some of the most fascinating and deadly natural phenomena in the world. Immediately, lava flows and avalanches of poisonous gas and dust come to mind; those with which Vesuvius buried Pompeii and those of Kīlauea, Pinatubo, and St. Helens that are in recent memory. While we tend to consider only the shared ...
What are the most deadly natural phenomena?
Volcanoes are some of the most fascinating and deadly natural phenomena in the world. Immediately, lava flows and avalanches of poisonous gas and dust come to mind; those with which Vesuvius buried Pompeii and those of Kīlauea, Pinatubo, and St. Helens that are in recent memory.
Is lava high in magnesium oxide?
Extremely high in magnesium oxide, with almost no polymerization. Low viscosity, relative to that of water. The behavior of lava in terms of viscosity seems to be relative to the size of the molecules that comprise it.
What is the difference between magma and lava?
Lava flow on Hawaii. Lava is the extrusive equivalent of magma. Magma (from Ancient Greek μάγμα ( mágma) meaning "thick unguent ") is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed.
What are the physical properties of magma?
Physical and chemical properties. Magma consists of liquid in which there are usually suspended solid crystals. As magma approaches the surface, and the overburden pressure drops, dissolved gases begin to separate from the liquid as bubbles, so that a magma near the surface consists of both solid, liquid, and gas phases.
How does temperature affect magma formation?
Such temperature increases can occur because of the upward intrusion of magma from the mantle . Temperatures can also exceed the solidus of a crustal rock in continental crust thickened by compression at a plate boundary. The plate boundary between the Indian and Asian continental masses provides a well-studied example, as the Tibetan Plateau just north of the boundary has crust about 80 kilometers thick, roughly twice the thickness of normal continental crust. Studies of electrical resistivity deduced from magnetotelluric data have detected a layer that appears to contain silicate melt and that stretches for at least 1,000 kilometers within the middle crust along the southern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Granite and rhyolite are types of igneous rock commonly interpreted as products of the melting of continental crust because of increases in temperature. Temperature increases also may contribute to the melting of lithosphere dragged down in a subduction zone.
What is the most abundant element in magmatic liquids?
Most magmatic liquids are rich in silica. Rare nonsilicate magmas can form by local melting of nonsilicate mineral deposits or by separation of a magma into separate immiscible silicate and nonsilicate liquid phases. Silicate magmas are molten mixtures dominated by oxygen and silicon, the most abundant chemical elements in the Earth’s crust, ...
How does water affect magma?
The change of rock composition most responsible for the creation of magma is the addition of water. Water lowers the solidus temperature of rocks at a given pressure. For example, at a depth of about 100 kilometers, peridotite begins to melt near 800 °C in the presence of excess water, but near or above about 1,500 °C in the absence of water. Water is driven out of the oceanic lithosphere in subduction zones, and it causes melting in the overlying mantle. Hydrous magmas composed of basalt and andesite are produced directly and indirectly as results of dehydration during the subduction process. Such magmas, and those derived from them, build up island arcs such as those in the Pacific Ring of Fire. These magmas form rocks of the calc-alkaline series, an important part of the continental crust.
How does magma evolve?
While cooling, the magma evolves in composition because different minerals crystallize from the melt. 1: olivine crystallizes; 2: olivine and pyroxene crystallize; 3: pyroxene and plagioclase crystallize; 4: plagioclase crystallizes. At the bottom of the magma reservoir, a cumulate rock forms.
How much of magma is melted before the heat supply is exhausted?
Melt rapidly separates from its source rock once the degree of partial melting exceeds 30%. However, usually much less than 30% of a magma source rock is melted before the heat supply is exhausted. Pegmatite may be produced by low degrees of partial melting of the crust.
