Candida albicans
The Health Benefits of Catalase
- Powerful Antioxidant Support Catalases are perhaps the single most efficient enzymes found in the cells of the human body. ...
- Possible Anti-Aging & Anti-Degenerative Effects Catalase is currently being studied for its applications on extending life span and vitality. ...
- Catalase May Increase Lifespan Dr. ...
Enterobacteriaceae
Uses of Catalase Test
- Catalase test is essential for differentiating catalase-positive Micrococcaceae and Staphylococcaceae from catalase-negative Streptococcaceae.
- The test also allows differentiating aerobic and obligate anaerobic organisms.
- The value of the test has been found in the presumptive differentiation among certain Enterobacteriaceae.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
So it looks like a little pink rod under the microscope. Also, E. Coli is a catalase positive bacteria, and that means it produces an enzyme called catalase. This can be tested by adding a few drops of hydrogen peroxide to a colony of bacteria, and catalase makes hydrogen peroxide dissociate into water and oxygen, making the mixture foam.
Gardnerella vaginalis
Staphylococcus species are catalase positive and facultatively anaerobic, except for S. aureus subsp. anaerobius and S. saccharolyticus, which are catalase negative and anaerobic. What does it mean to be catalase positive?
Pseudomonas cepacia
What are the benefits of catalase?
What does a catalase positive test mean?
Is Escherichia coli catalase positive?
Is Staphylococcus catalase positive?

Which Gram-positive bacteria is catalase positive?
StaphylococcusGram-positive cocci include Staphylococcus (catalase-positive), which grows clusters, and Streptococcus (catalase-negative), which grows in chains. The staphylococci further subdivide into coagulase-positive (S.
Can gram negative bacteria be catalase positive?
All of the organisms are Gram-negative cocci or coccobacilli and all are oxidase positive with the exception of Acinetobacter. Moraxella and Neisseria are catalase positive and Kingella are catalase negative. The division of this family is illustrated in Figure 5.1.
Which staphylococci are catalase positive?
Staphylococcus aureus is a gram positive, catalase and coagulase positive coccus and by far the most important pathogen among the staphylococci. It produces enzymes such as catalase which are considered to be virulence determinants.
Is bacillus catalase positive or negative?
Bacillus species are Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria; they can be either obligate or facultative aerobes and show positive reaction in the catalase test. Members of the genus Bacillus are known to form spores under stressful conditions.
Does E coli produce catalase?
Escherichia coli has 2 catalase enzymes, hydroperoxidase I (HPI) and HPII, which catalyze the dismutation of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen1.
Is E coli positive for catalase test?
Escherichia coli and Streptococcus pneumoniae have been used as model catalase-positive and catalase-negative bacteria, respectively.
Does S epidermidis have catalase?
Staphylococcus epidermidis is a coagulase-negative, gram-positive cocci bacteria that form clusters. It is also a catalase-positive and facultative anaerobe.
Does Streptococcus have catalase?
Staphylococcus and Micrococcus spp. are catalase positive, whereas Streptococcus and Enterococcus spp. are catalase negative.
Is Streptococcus pyogenes catalase positive?
pyogenes is a gram-positive, β-hemolytic streptococcus that is catalase negative.
What type of bacteria are catalase negative?
If no bubbles appear, the bacteria are catalase negative. Staphylococcus and Micrococcus spp. are catalase positive, whereas Streptococcus and Enterococcus spp. are catalase negative.
Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa catalase positive?
The Pathogens. P. aeruginosa is a gram-negative, lactose nonfermenting, straight or slightly curved rod with a length ranging from 1.5 to 7 µm and a width of 0.5 to 1.0 µm. It is catalase positive, oxidase positive, and motile with one or more polar flagella.
Is E coli coagulase positive or negative?
Biochemical Test of Escherichia coli (E. coli)Basic CharacteristicsProperties (E. coli)CitrateNegative (-ve)CoagulaseNegative (-ve)FlagellaFlagellatedGasPositive (+ve)57 more rows•Apr 28, 2021
What is the pH of catalase?
The optimum pH for human catalase is approximately 7 , and has a fairly broad maximum: the rate of reaction does not change appreciably between pH 6.8 and 7.5. The pH optimum for other catalases varies between 4 and 11 depending on the species. The optimum temperature also varies by species.
Where does catalase occur?
Catalase is also universal among plants and occurs in most fungi. One unique use of catalase occurs in the bombardier beetle. This beetle has two sets of liquids that are stored separately in two paired glands.
What is catalase used for?
Catalase is used in the food industry for removing hydrogen peroxide from milk prior to cheese production. Another use is in food wrappers where it prevents food from oxidizing. Catalase is also used in the textile industry, removing hydrogen peroxide from fabrics to make sure the material is peroxide-free.
What is the reaction of catalase?
It does so according to the following reaction: H 2 O 2 + H 2 R → 2H 2 O + R. The exact mechanism of this reaction is not known.
How does peroxide kill bacteria?
Neutrophils and other phagocytes use peroxide to kill bacteria. The enzyme NADPH oxidase generates superoxide within the phagosome, which is converted via hydrogen peroxide to other oxidising substances like hypochlorous acid which kill phagocytosed pathogens. In individuals with chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) there is a defect in producing peroxide via mutations in phagocyte oxidases such as myeloperoxidase. Normal cellular metabolism will still produce a small amount of peroxide and this peroxide can be used to produce hypochlorous acid to eradicate the bacterial infection. However, if individuals with CGD are infected with catalase-positive bacteria, the bacterial catalase can destroy the excess peroxide before it can be used to produce other oxidising substances. In these individuals the pathogen survives and becomes a chronic infection. This chronic infection is typically surrounded by macrophages in an attempt to isolate the infection. This wall of macrophages surrounding a pathogen is called a granuloma. Many bacteria are catalase positive, but some are better catalase-producers than others. The mnemonic "cats Need PLACESS to Belch their Hairballs" can be used to memorise the catalase-positive bacteria (and Candida and Aspergillus, which are fungi): nocardia, pseudomonas, listeria, aspergillus, candida, E. coli, staphylococcus, serratia, B. cepacia and H. pylori.
How many subunits are in catalase?
Human catalase forms a tetramer composed of four subunits, each of which can be conceptually divided into four domains. The extensive core of each subunit is generated by an eight-stranded antiparallel b-barrel (b1-8), with nearest neighbor connectivity capped by b-barrel loops on one side and a9 loops on the other. A helical domain at one face of the b-barrel is composed of four C-terminal helices (a16, a17, a18, and a19) and four helices derived from residues between b4 and b5 (a4, a5, a6, and a7). Alternative splicing may result in different protein variants.
What is the enzyme that catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals) which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen.
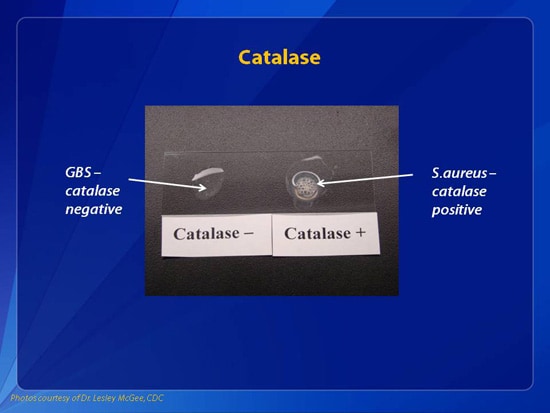
What is a catalase positive reaction?
Catalase positive reaction: Evident by immediate effervescence (bubble formation) Catalase negative reaction: No bubble formation (no catalase enzyme to hydrolyze the hydrogen peroxide) or a few bubbles after 20 seconds. You can perform Catalase Test online here. *Note: Some bacteria possess enzymes other than catalase that can decompose peroxide, ...
What is catalase test?
Catalase test is used to differentiate aerotolerant strains of Clostridium (catalase-negative) from Bacillus species (catalase-positive). A semiquantitative catalase test is used for the identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Catalase test is useful to separate among the fastidious Gram-negative rods.
Why is catalase test used?
Catalase test is useful to separate among the fastidious Gram-negative rods. Catalase test can be used as an aid to the identification of Enterobacteriaceae. Members of the Enterobacteriaceae family are catalase positive.
What is the function of catalase?
Catalase is an enzyme, which is produced by microorganisms that live in oxygenated environments to neutralize toxic forms of oxygen metabolites; H 2 O 2. The catalase enzyme neutralizes the bactericidal effects of hydrogen peroxide and protects them. Anaerobes generally lack the catalase enzyme.
Can you use platinum loops to test for catalase?
Instead, use a platinum loop or wooden stick to perform this test. If using colonies from a blood agar plate, be very careful not to scrape up any of the blood agar as blood cells are catalase-positive and any contaminating agar (carryover of red blood cells) could give a false positive.
Do catalase bacteria use oxygen?
They all have the ability to respire using oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor. Catalase-negative bacteria may be anaerobes, or they may be facultative anaerobes that only ferment and do not respire using oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor (ie. Streptococci).
Which microorganisms do not produce catalase?
Most microorganisms that are aerobic and facultative anaerobic produce the enzyme catalase except Streptococcus spp, lactobacillus spp, Leuconostoc spp, Clostridium spp, Mycoplasma. Other bacteria that do not produce catalase enzyme are Obligate anaerobes or microaerophiles.
What is the purpose of catalase test?
The enzyme catalase, is produced by bacteria that respire using oxygen and protects them from the toxic by-product of oxygen metabolism . Catalase-positive bacteria include strict aerobes as well as facultative anaerobes, although they all have ability to respire using oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor. Catalase-negative bacteria may be anaerobes or they may be facultative anaerobes that only ferment and do not respire using oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor (i.e Streptococci).
What are the objectives of catalase?
Objectives. To detect the ability of organisms to produce the catalase enzyme. To differentiate catalase-positive organisms like micrococci and staphylococci from catalase-negative organisms like streptococci.
What is a semiquantitative catalase test?
Semiquantitative catalase test is used for the identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Catalase test can be used as an aid to the identification of Enterobacteriaceae. Members of Enterobacteriaceae family are catalase positive.
Can you mix reagents with S. aureus?
The reagent and the colony should not be mixed. Some strains of S. aureus may appear catalase-negative by drop method so the test should be repeated with the tube method. 30% H 2 O 2 is extremely caustic to the skin. If contact occurs, wash immediately with 70% ethyl alcohol, not water.
What is the most pathogenic organism in the genus Staphylococcus?
Bacteria in the genus Staphylococcus are pathogens of man and other mammals. Traditionally they were divided into two groups on the basis of their ability to clot blood plasma (the coagulase reaction). The coagulase-positive staphylococci constitute the most pathogenic species S aureus.
Which is the most pathogenic species?
The coagulase-positive staphylococci constitute the most pathogenic species S aureus. The coagulase-negative staphylococci (CNS) are now known to comprise over 30 other species. The CNS are common commensals of skin, although some species can cause infections.
Is coagulase a virulence factor?
Coagulase is a marker for S aureus but there is no direct evidence that it is a virulence factor. Also, some natural isolates of S aureus are defective in coagulase. Nevertheless, the term is still in widespread use among clinical microbiologists.

Overview
Clinical significance and application
Catalase is used in the food industry for removing hydrogen peroxide from milk prior to cheese production. Another use is in food wrappers, where it prevents food from oxidizing. Catalase is also used in the textile industry, removing hydrogen peroxide from fabrics to make sure the material is peroxide-free.
A minor use is in contact lens hygiene – a few lens-cleaning products disinfect t…
Structure
Human catalase forms a tetramer composed of four subunits, each of which can be conceptually divided into four domains. The extensive core of each subunit is generated by an eight-stranded antiparallel β-barrel (β1-8), with nearest neighbor connectivity capped by β-barrel loops on one side and α9 loops on the other. A helical domain at one face of the β-barrel is composed of four C-terminal helices (α16, α17, α18, and α19) and four helices derived from residues between β4 an…
History
Catalase was first noticed in 1818 by Louis Jacques Thénard, who discovered hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Thénard suggested its breakdown was caused by an unknown substance. In 1900, Oscar Loew was the first to give it the name catalase, and found it in many plants and animals. In 1937 catalase from beef liver was crystallized by James B. Sumner and Alexander Dounce and the molecular weight was measured in 1938.
Function
While the complete mechanism of catalase is not currently known, the reaction is believed to occur in two stages:
H2O2 + Fe(III)-E → H2O + O=Fe(IV)-E(.+)
H2O2 + O=Fe(IV)-E(.+) → H2O + Fe(III)-E + O2
Here Fe()-E represents the iron center of the heme group attached to the enzyme. Fe(IV)-E(.+) is a …
Distribution among organisms
The large majority of known organisms use catalase in every organ, with particularly high concentrations occurring in the liver in mammals. Catalase is found primarily in peroxisomes and the cytosol of erythrocytes (and sometimes in mitochondria )
Almost all aerobic microorganisms use catalase. It is also present in some anaerobic microorganisms, such as Methanosarcina barkeri. Catalase is also universal among plants and o…
Interactions
Catalase has been shown to interact with the ABL2 and Abl genes. Infection with the murine leukemia virus causes catalase activity to decline in the lungs, heart and kidneys of mice. Conversely, dietary fish oil increased catalase activity in the heart, and kidneys of mice.
Methods for determining catalase activity
In 1870, Schoenn discovered a formation of yellow color from the interaction of hydrogen peroxide with molybdate; then, from the middle of the 20th century, this reaction began to be used for colorimetric determination of unreacted hydrogen peroxide in the catalase activity assay. The reaction became widely used after publications by Korolyuk et al. (1988) and Goth (1991).
Direct UV measurement of the decrease in the concentration of hydrogen peroxide is also widel…
Introduction
- The Catalase test is used to differentiate staphylococci (catalase-positive) from streptococci (catalase-negative). The enzyme catalase, is produced by bacteria that respire using oxygen and protects them from the toxic by-product of oxygen metabolism. Catalase-positive bacteria include strict aerobes as well as facultative anaerobes, although they...
Objectives
- To detect the ability of organisms to produce the catalase enzyme.
- To differentiate catalase-positive organisms like micrococci and staphylococci from catalase-negative organisms like streptococci.
Principle
- Catalase is an enzyme that breaks Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a toxic metabolic byproducts of aerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria into non toxic products water (H2O) and Oxygen (O2). H2O2 is toxic to cells. It is highly reactive molecule that damage cell components. So the bacteria living in presence of Oxygen produces enzyme catalase that breakdown H2O2 into H2O and O2 …
Experiment
- Reagent And Materials Required
1. Slides 2. Bibulous paper 3. Inoculating loop 4. Bunsen burner 5. Laminar flow chamber 6. Hydrogen peroxide (3%), isolated colonies or pure cultures of bacteria. - Procedure
1. Take a clean, dry and grease free microscopic glass slide and place a drop of 3% H2O2 onto the slide. 2. At one time you can easily perform Catalase test of 2 or 3 specimens on a single slide so divide the space accordingly and Place the H2O2 drop in the center of the divided portions of th…
Limitations of Catalase Test
- The reagent and the colony should not be mixed.
- Some strains of S. aureus may appear catalase-negative by drop method so the test should be repeated with the tube method.
- 30% H2O2 is extremely caustic to the skin. If contact occurs, wash immediately with 70% ethyl alcohol, not water.
- The reagent and the colony should not be mixed.
- Some strains of S. aureus may appear catalase-negative by drop method so the test should be repeated with the tube method.
- 30% H2O2 is extremely caustic to the skin. If contact occurs, wash immediately with 70% ethyl alcohol, not water.
- RBCs contain catalase, and thus, in order to avoid false-positive results, blood agar should not be picked up with the colony. If a colony is difficult to pick up or doesn’t grow well, the test can...