Ligases are enzymes that are capable of catalyzing the reaction of joining two large molecules by establishing a new chemical bond, generally with concomitant hydrolysis
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis usually means the cleavage of chemical bonds by the addition of water. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g. sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is termed saccharification. Generally, hydrolysis or …
What types of reaction are catalyzed by lyases?
oxidation–reduction reactions addition of a group to a double bond or removal of a group from a double bond hydrolysis reactions rearrangement This problem has been solved! 1a.)
What is the difference between ligase and hydrolysis?
Single bond formation by eliminating the elements of water. Hydrolases break bonds by adding the elements of water; ligases carry out the converse reaction, removing the elements of water from two functional groups to form a single bond. Synthetases are a subclass of ligases that use the hydrolysis of ATP to drive this formation.
What is a ligase enzyme?
What Are Enzymes? In biochemistry, ligase, also called synthetase, is an enzyme catalyzing the joining of two large molecules through the formation of a new chemical bond such as C-O, C-S, C-N, or the linking together of two compounds, usually accompanied with the hydrolysis of a small attached chemical group to one of the larger molecules.
What is the difference between ligase and phosphorylase?
• Ligases enzymes catalyze reactions in which two molecules join to form one molecule. • Phosphorylases are enzymes that catalyze the addition of a phosphate group from an inorganic phosphate (phosphate+hydrogen) to an acceptor. Hydrolysis: a reaction in which a molecule breakdown when it reacts with water

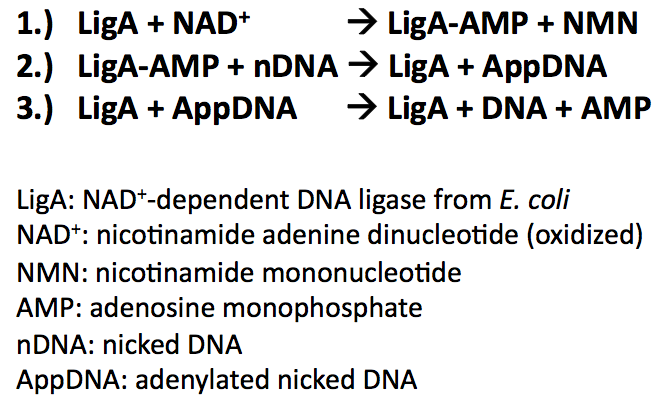
What is catalyzed by DNA ligase?
DNA ligases catalyze the formation of a phosphodiester bond between DNA single strands in the duplex form (Fig. 2.1). The covalent linkage of the 5′-P group of one chain with the adjacent 3′-OH group of another is coupled with the pyrophosphate hydrolysis of the cofactor ATP or NAD.
What reaction in the DNA replication is catalyzed by DNA ligase?
What is the reaction in DNA replication catalyzed by DNA ligase? Explanation: DNA ligase catalyzes the formation of a phosphodiester bond between 3'-OH of one Okazaki fragment and 5'-phosphate of the next.
What process is ligase used in?
DNA cloningIn DNA replication, ligase's job is to join together fragments of newly synthesized DNA to form a seamless strand. The ligases used in DNA cloning do basically the same thing. If two pieces of DNA have matching ends, DNA ligase can join them together to make an unbroken molecule.
Which reaction is catalysed by lyase?
Lyases are the enzymes responsible for catalyzing addition and elimination reactions. Lyase-catalyzed reactions break the bond between a carbon atom and another atom such as oxygen, sulfur, or another carbon atom.
What is ligase chain reaction used for?
It has been widely used for the detection of single base mutations, as in genetic diseases. LCR and PCR may be used to detect gonorrhea and chlamydia, and may be performed on first-catch urine samples, providing easy collection and a large yield of organisms.
What is the reaction in DNA replication catalyzed by DNA ligase quizlet?
DNA Ligase is a linking enzyme essential for DNA replication; catalyzes the covalent bonding of the 3' end of one DNA fragment to the 5' end of another DNA fragment (such as a growing DNA chain).
What is the function of ligase quizlet?
Repairs irregularities or breaks in the backbone of double-stranded DNA molecules. It has important role in the process of DNA replication and DNA repair.
What is the product of ligase?
Ligases catalyze the formation of phosphodiester bond between 3′OH and 5′phosphate on various substrates such as DNA nicks, DNA fragments with various lengths cohesive ends, DNA fragments with blunt ends and some DNA/RNA hybrids.
What type of bond is made by ligase?
covalent phosphodiester bondsDNA ligase works by forming two covalent phosphodiester bonds between the 3′ hydroxyl end of one nucleotide (acceptor) and the 5′ phosphate end of another (donor). Each phosphodiester bond requires the use of two ATP molecules.
How lyases and ligases catalyse a reaction?
Lyases catalyse the removal of groups from their substrate by mechanisms other than hydrolysis, leaving double bond. Whereas, ligases catalyse the linking together of compounds utilizing the energy from ATP.
What are examples of lyases enzymes?
A few examples of lyase include phenylalanine ammonia-lyase, citrate lyase, isocitrate lyase, hydroxynitrile, pectate lyase, argininosuccinate lyase, pyruvate formate lyase, alginate lyase, and pectin lyase.
What do lyases enzymes do?
Lyases are a group of enzymes (EC 4) that catalyze the breakdown of chemical bonds through methods other than hydrolysis or oxidation. They differ from other enzyme classes in that most reactions catalyzed by lyases only require one substrate molecule for the forward reaction, and two for the reverse reaction.
What is the application of DNA ligase?
DNA ligases are critical DNA replication and repair enzymes; they have been widely used in molecular biology and biotechnology applications, such as cloning and next-generation DNA sequencing [1, 2]. DNA ligases catalyze the joining of adjacent 3′-hydroxyl and 5′-phosphorylated DNA termini in duplex DNA.
Is ligase used in DNA replication?
Abstract. DNA ligases are critical enzymes of DNA metabolism. The reaction they catalyse (the joining of nicked DNA) is required in DNA replication and in DNA repair pathways that require the re-synthesis of DNA.
Is ligase used in PCR?
In this thermostable DNA ligase-mediated whole-plasmid amplification method, the resultant DNA nick between the 5′ end of the PCR primer and the extended newly synthesized DNA 3′ end of each PCR cycle is ligated by Tma DNA ligase, resulting in circular plasmid DNA product that can be directly transformed.
Is ligase used in RNA synthesis?
T4 RNA ligase 1 is used for ligation of ssRNA and DNA, RNA ligase–mediated rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RLM-RACE), ligation of oligonucleotide adapters to cDNA or single-stranded primer extension products for PCR, oligonucleotide synthesis, and various 5′ nucleotide modifications of nucleic acids.
What is the difference between a synthetase and a lyase?
A synthase is also acknowledged as a lyase that catalyzes the cleavage of various chemical bonds through means excluding hydrolysis and oxidation without demand for any energy, whereas a synthetase is a ligase joining two chemicals or compounds with requirement for energy.
What enzyme is responsible for recombination of DNA?
DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme that promotes the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond between phosphate and deoxyribose. DNA ligase is active during the replication, repair and recombination process of DNA.
Which ligase is capable of catalyzing the ATP-dependent covalent joining of single-strand?
As another typical example of ligase, T4 RNA ligase 1 is capable of catalyzing the ATP-dependent covalent joining of single-stranded 5'-phosphoryl termini of RNA to single-stranded 3'-hydroxyl termini of RNA.
What is the process of ligase?
In biochemistry, ligase, also called synthetase, is an enzyme catalyzing the joining of two large molecules through the formation of a new chemical bond such as C-O, C-S, C-N, or the linking together of two compounds, usually accompanied with the hydrolysis of a small attached chemical group to one of the larger molecules. This procedure usually assimilates the needed energy from the cleavage of an energy-rich phosphate bond, involves the conservation of chemical energy and offers a linkage between energy-requiring synthetic processes and energy-yielding breakdown reactions. In most cases, the simultaneous conversion of ATP to adenosine ADP functions as a source of energy. The ligase catalyzed reaction has a general formulation as following:
What is the role of E3 ubiqutin ligases in cell cycle regulation?
It is of profound importance in cell biology. E3 ligases also occupy a position in cell cycle control and the degradation of cyclins.
What is the name of the enzyme that links DNA fragments together?
The common names of ligases often contain the word "ligase", like DNA ligase, a frequently used enzyme in molecular biolaboratory to link DNA fragments together. Synthetase is another commonly adopted name for ligases since they are applied in the synthesis of new molecules.
How many subclasses are there in ligases?
In the EC number classification system, ligases are classified as EC 6 and can be further classified into six subclasses.
What are the different types of enzymes?
Based on the type of catalyzed biochemical reaction, enzymes are classified into one of eight classes: oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, ligases or phosphorylases. Enzymesare biological catalysts, and nearly all of them are proteins.
What is the term for a reaction in which a molecule breaks down when it reacts with water?
Oxidation: a reaction in which loss of the electrons occurs. Reduction: a reaction in which gain of electrons occurs. Catalyze: accelerate or speed up. Hydrolysis : a reaction in which a molecule breakdown when it reacts with water. Isomer: molecules with the same formula but a different arrangement of atoms.
What are the six major classes of enzymes?
• The six major classes of enzymes are oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases. • Oxidoreductases enzymes catalyze oxidation and reduction reactions. • Transferases enzymes move ...
How are enzymes classified?
Consequently, enzymes are classified by reaction type. The names for classes of enzymes are generally descriptive of the type of reaction they catalyzeand ...
What is an isomer?
Isomer: molecules with the same formula but a different arrangement of atoms.
What is the Michaelis constant for enzyme binding?
K m is the Michaelis constant for the enzyme binding substrate. The Michaelis constant is analogous to, but not identical to, the binding constant for the substrate to the enzyme. V max is the maximal velocity available from the amount of enzyme in the reaction mixture. If you add more enzyme to a given amount of substrate, the velocity of the reaction (measured in moles of substrate converted per time) increases, because the increased amount of enzyme uses more substrate. This is accounted for by the realization that V max depends on the total amount of enzyme in the reaction mixture:
How does phosphate inhibit enzymes?
Phosphate ion, a product of the reaction, also inhibits it by binding to the same phosphate site used for binding substrate. When phosphate is bound, the enzyme cannot bind substrate, so it is inhibited by the phosphate. How to overcome the inhibitor? Add more substrate: R – O – PO 3 2 ‐. Because the substrate and the inhibitor bind to the same site on the enzyme, the more substrate that binds, the less inhibitor binds. When is the most substrate bound to the enzyme? Under V max conditions. Phosphate ion reduces the velocity of the alkaline phosphate reaction without reducing V max. If velocity decreases, but V max doesn't, the only other thing that can change is K m. Remember that K m is the concentration where v = V max /2. Because more substrate is required to achieve V max, K m must necessarily increase. This type of inhibition, where K m increases but V max is unchanged, is called competitive because the inhibitor and substrate compete for the same site on the enzyme (the active site).
How do competitive inhibitors affect the velocity of an enzyme reaction?
Competitive inhibitors decrease the velocity of an enzymatic reaction by increasing the amount of substrate required to saturate the enzyme; therefore, they increase the apparent K m but do not affect V max. A Lineweaver‐Burk plot of a competitively inhibited enzyme reaction has an increased slope, but its intercept is unchanged.
What are inhibitors of enzymes?
In the terms of the Michaelis‐Menten equation, inhibitors can raise K m, lower V max, or both. Inhibitors form the basis of many drugs used in medicine. For example, therapy for high blood pressure often includes an inhibitor of the angiotensin converting enzyme, or ACE.
How does covalent inhibition work?
Covalent inhibition involves the chemical modification of the enzyme so that it is no longer active. For example, the compound diisopropylfluorophosphate reacts with many enzymes by adding a phosphate group to an essential serine hydroxyl group in the enzymes' active sites. When phosphorylated, the enzyme is totally inactive. Many useful pharmaceutical compounds work by covalent modification. Aspirin is a covalent modifier of enzymes involved in the inflammatory response. Penicillin covalently modifies enzymes required for bacterial cell‐wall synthesis, rendering them inactive. Because the cell wall is not able to protect the bacterial cell, the organism bursts easily and is killed.
What happens when an enzyme is added to a solution?
If an enzyme is added to a solution containing substrate, the substrate is converted to product, rapidly at first, and then more slowly, as the concentration of substrate decreases and the concentration of product increases. Plots of substrate (S) or product (P) against time, called progress curves, have the forms shown in Figure . Note that the two progress curves are simply inverses of each other. At the end of the reaction, equilibrium is reached, no net conversion of substrate to product occurs, and either curve approaches the horizontal.
Why does the curve in Figure flatten out?
Why does the curve in Figure flatten out? Because if the substrate concentration gets high enough, the enzyme spends all its time carrying out catalysis and no time waiting to bind substrate. In other words, the amount of substrate is high enough so that the enzyme is saturated, and the reaction rate has reached maximal velocity, or V max. Note that the condition of maximal velocity in Figure is not the same as the state of thermodynamic equilibuium in Figures 1 and 2.