What type of heart valve separates the atrium and the ventricle?
Tricuspid Valve The tricuspid heart valve separates the right atrium from the right ventricle and allows deoxygenated blood to flow between them. Once blood has cycled through the body, it is returned to the right atrium, which is located on the right side of the heart.
Are valves located between the atria and the ventricles?
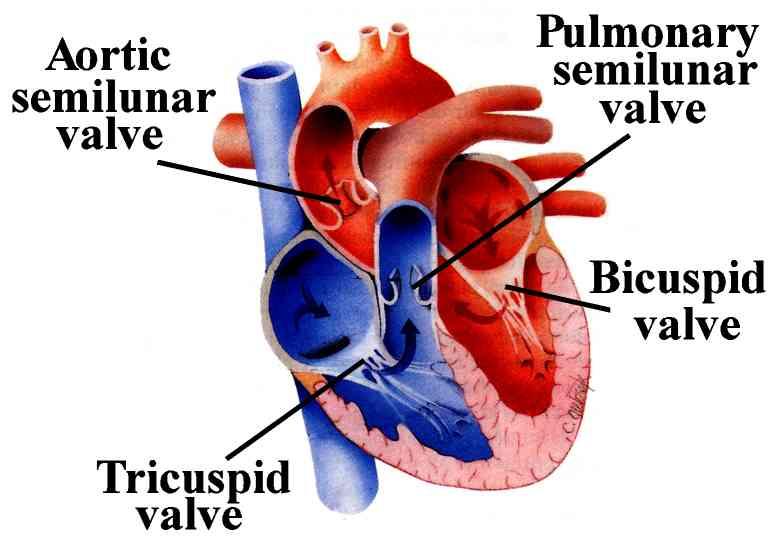
The mitral valve and tricuspid valve are located between the atria (upper heart chambers) and the ventricles (lower heart chambers). The aortic valve and pulmonic valve are located between the ventricles and the major blood vessels leaving the heart. The valves are made of strong, thin flaps of tissue called leaflets or cusps.
What valve prevents blood from returning to the right ventricle?
right ventricle. the chamber that pumps blood to the lungs. pulmonary valve. the valve that prevents blood from returning to the right ventricle. left atrium.
Why does the right atrium have a tricuspid valve?
“Noticeable signs and symptoms of tricuspid valve regurgitation may include:
- Fatigue.
- Declining exercise capacity.
- Swelling in your abdomen, legs or veins in your neck.
- Abnormal heart rhythms.
- Pulsing in your neck.
- Shortness of breath with activity”, from a Google snippet.
What valve is in the right ventricle?
Tricuspid ValveTricuspid Valve Separates the top right chamber (right atrium) from the bottom right chamber (right ventricle). Opens to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle. Prevents the back flow of blood from the right ventricle to the right atrium.
What valve is between the LA and LV?
The mitral valveThe mitral valve connects the left atrium (LA) and the left ventricle (LV). The mitral valve opens during diastole to allow the blood flow from the LA to the LV. During ventricular systole, the mitral valve closes and prevents backflow to the LA.
What is another name for the bicuspid valve?
Mitral valveSolution : Mitral valve.
What is the bicuspid valve?
A bicuspid aortic valve is an aortic valve with only two cusps (or flaps) instead of three. The aortic valve controls the flow of blood from the left ventricle (chamber) to the aorta, the main artery delivering blood to your body.
Where is bicuspid valve located?
Normally, the mitral valve is the only bicuspid valve and this is situated between the heart's left atrium and left ventricle. Heart valves play a crucial role in ensuring the unidirectional flow of blood from the atrium to the ventricles, or from the ventricle to the aorta or pulmonary trunk.
Is aortic valve tricuspid or bicuspid?
The normal aortic valve has three leaflets, also known as cusps. Some people can be born with one, two or even four cusps of their aortic valve. The most common of these abnormalities is an aortic valve with two cusps — thus, a bicuspid aortic valve.
Is mitral valve bicuspid or tricuspid?
The mitral valve is also called the bicuspid valve because it contains two leaflets or cusps. The mitral valve gets its name from the resemblance to a bishop's mitre (a type of hat). It is on the left side of the heart and allows the blood to flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle.
Is the mitral valve a bicuspid valve?
role in cardiovascular system opening is guarded by the mitral, or bicuspid, valve, so named because it consists of two flaps. The mitral valve is attached in the same manner as the tricuspid, but it is stronger and thicker because the left ventricle is by nature a more powerful pump working under high pressure.
How do you feel someone's heart beat?
You can normally feel someone’s heart beat if you put your hand on their chest. Blood enters the right atrium of the heart through the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava. The right atrium contracts and pushes the blood cells through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle.
What is the name of the valve that passes blood from the right atrium to the right ventricle?
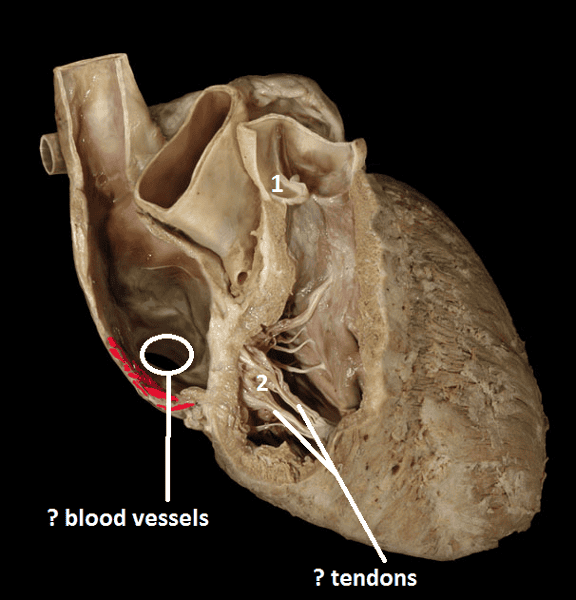
Blood passes from the right atrium into the right ventricle through a valve that is called the tricuspid valve (tri- = three; -cuspid = point) because it consists of three cusps or leaflets (Figure 2). The tricuspid valve is also called the right atrioventricular valve. The valves of the heart are composed of dense connective tissue covered by ...
What happens when the impulse reaches the ventricles?
When the impulse reaches the ventricles, the ventricles both contract, pushing the blood out of your heart to your lungs, your brain, and the rest of your body. In a normal heart rhythm, each impulse from the sinus node makes the atria and the ventricles contract regularly. Figure 3. Right atrium function.
What is the right atrium?
The right atrium is the receiving chamber for oxygen-poor blood (deoxygenated) returning from the systemic circuit. The right atrium receives oxygen-poor blood from three veins: the superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, and coronary sinus (Figures 1 and 2).
Which ventricle pumps blood to the lungs?
The right ventricle then contracts and pushes the blood through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery, which takes it to the lungs. In the lungs, the blood cells exchange carbon dioxide for oxygen. The oxygenated blood returns to the heart via the pulmonary veins and enters the left atrium. The left atrium contracts and pumps ...
What is the tricuspid valve?
The tricuspid valve is also called the right atrioventricular valve. The valves of the heart are composed of dense connective tissue covered by endocardium. Externally the right atrium is a small flap shaped like a dog’s ear (auricle = little ear) called the right auricle, projects anteriorly from the superior corner of the atrium (Figure 1).
What is the heart's natural pacemaker?
Your heart’s pumping action is controlled by tiny electrical impulses produced by a part of the right atrium called the sinus node . The sinus node is sometimes called your heart’s ‘natural pacemaker’.
Atrium vs Ventricle
The main difference between the atrium and ventricle is that they are the different sections of most advanced animals. Due to their location, they also differ in their blood supply into and out of the chamber. They also differ in size and types of values present in them.
What is Atrium?
Atrium is the singular word for auricles which refer to the upper half of the heart. These chambers of the human heart are separated by the interauricular or interatrial septum to form two auricles. The right auricle or atrium receives deoxygenated blood from two veins blood vessels, the inferior vena cava and superior vena cava.
What is Ventricle?
The ventricle is the singular for the ventricles that refers to the lower half of the heart. The lower divisions of the heart are separated by the interventricular septum. The left ventricle receives fresh blood from the auricles, and it pumps it to the rest of the body from the right ventricle through the aorta.
Conclusion
The proper functioning of each of the chambers of the heart is necessary for uniform blood circulation. Blockage in any of the draining or supplying channels may lead to a lack of blood supply to the heart itself, which may cause a heart attack.
Structure
The human heart is in the middle of the thorax, with its apex pointing to the left.
Development
Development of the human heart during the first eight weeks (top) and the formation of the heart chambers (bottom). In this figure, the blue and red colors represent blood inflow and outflow (not venous and arterial blood). Initially, all venous blood flows from the tail/atria to the ventricles/head, a very different pattern from that of an adult.
Physiology
The heart functions as a pump in the circulatory system to provide a continuous flow of blood throughout the body. This circulation consists of the systemic circulation to and from the body and the pulmonary circulation to and from the lungs.
Clinical significance
The stethoscope is used for auscultation of the heart, and is one of the most iconic symbols for medicine. A number of diseases can be detected primarily by listening for heart murmurs.
History
Humans have known about the heart since ancient times, although its precise function and anatomy were not clearly understood. From the primarily religious views of earlier societies towards the heart, ancient Greeks are considered to have been the primary seat of scientific understanding of the heart in the ancient world.
Transplantation of pig heart to human
The first successful transplant of a heart from a genetically modified pig to a human, was performed January 7, 2022 in Baltimore by heart surgeon Bartley P. Griffith, recipient was David Bennett (57).
Other animals
The size of the heart varies among the different animal groups, with hearts in vertebrates ranging from those of the smallest mice (12 mg) to the blue whale (600 kg). In vertebrates, the heart lies in the middle of the ventral part of the body, surrounded by a pericardium. which in some fish may be connected to the peritoneum.