
What is the celiac trunk?
Along with the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries, it is one of three frontal branches of the abdominal aorta, the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. Although the celiac trunk is only one of three arteries that branches off the abdominal aorta, it is essential to many major organs.
What is the anatomical position of the coeliac trunk?
Anatomical Position. The coeliac trunk is the second branch of the abdominal aorta (the first branches are the paired inferior phrenic arteries). It arises from the anterior aspect of the aorta, at the aortic hiatus of the diaphragm (T12 level).
How common is variation in the anatomy of the celiac artery?
Variant anatomy. Variations are present in approximately 30%. In general, any of the three celiac branches may arise independently from the aorta or SMA, or the celiac artery may give rise to other branches. A coeliacomesenteric trunk occurs when both the SMA and the celiac trunk originate as a single trunk from the aorta.
What are the different types of celiac branches of the heart?
In general, any of the three celiac branches may arise independently from the aorta or SMA, or the celiac artery may give rise to other branches. A coeliacomesenteric trunk occurs when both the SMA and the celiac trunk originate as a single trunk from the aorta. left gastric artery: 2-3%. splenic artery: <1%.
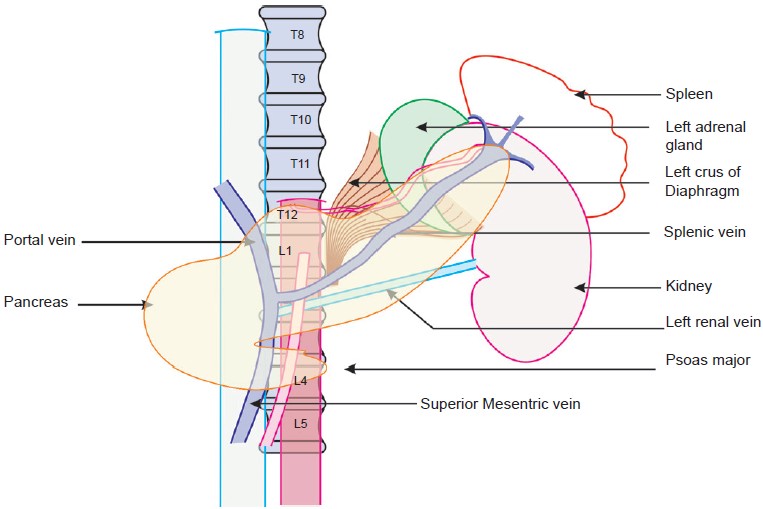
What vertebral level is SMA?
Structure. It arises anterior to lower border of vertebra L1 in an adult. It is usually 1 cm lower than the celiac trunk. It initially travels in an anterior/inferior direction, passing behind/under the neck of the pancreas and the splenic vein.
What vertebral level is superior mesenteric artery?
The origins of all the branches varied between exactly two vertebral levels (Fig. 2). The celiac artery originated at T11/T12–L1/L2, followed by the superior mesenteric artery at T12–L2, the paired renal arteries at T12/L1–L2/L3, the inferior mesenteric artery at L2–L4, and the common iliac arteries at L3–L5.
At which vertebral level do the 1 coeliac trunk 2 superior mesenteric artery and 3 inferior mesenteric artery leave the abdominal aorta?
twelfth thoracic vertebraeThe coeliac trunk (or celiac trunk) is a major artery that supplies the foregut of the gastrointestinal tract. It arises from the abdominal aorta at the level of the twelfth thoracic vertebrae. It gives off three major branches called left gastric, common hepatic and splenic arteries.
At which vertebral level does the Coeliac axis branch from the aorta?
It is about 1.25 cm in length. Branching from the aorta at thoracic vertebra 12 (T12) in humans, it is one of three anterior/ midline branches of the abdominal aorta (the others are the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries). The celiac artery and its branches. (Celiac artery visible at center.)
What vertebral level is inferior mesenteric artery?
third lumbar vertebraThe inferior mesenteric artery arises from the abdominal aorta at the level of the third lumbar vertebra. It supplies the hindgut and has four major branches called left colic, sigmoid and superior rectal arteries.
What level is the inferior mesenteric artery?
The inferior mesenteric artery (IMA) is another major blood supply to the lower GI tract (Fig. 25.4). It is located at the level of L2-L4 (most often at the L3-L4 disk space level, 2–3 cm above the aortic bifurcation). The IMA supplies the distal transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum.
Where is the celiac trunk located?
The celiac trunk, also known as the celiac artery, is a short vessel that arises from the aorta and passes below the median arcuate ligament, just as the aorta enters the abdomen at the level of the T12 vertebra.
Where is the celiac axis located?
The celiac artery, also known as the celiac axis or celiac trunk, is a major splanchnic artery in the abdominal cavity supplying the foregut. It arises from the abdominal aorta and commonly gives rise to three branches: left gastric artery, splenic artery, and common hepatic artery.
What are the 3 branches of the celiac trunk?
Classification of the celiac trunk becomes easy if one considers the trunk to be composed of three main stems: the splenic, the hepatic and the left gastric artery, other vessels being less important collaterals.
How do you draw a celiac trunk?
2:286:17Anatomy and Physiology: Celiac trunk - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd wraps. Along its superior border also known as the lesser curvature. Next we'll draw the splenicMoreAnd wraps. Along its superior border also known as the lesser curvature. Next we'll draw the splenic artery. Which is often described as tortuous. Because it spirals along its length.
What are the three main branches of the celiac trunk quizlet?
splenic artery.left gastric artery.common hepatic artery.
Where is the celiac axis to pancreas?
The celiac axis (or trunk) is the artery, a branch of the aorta, in the upper abdomen that supplies blood to the stomach, pancreas, liver and spleen. In other words, I had stage IV pancreatic cancer, metastasized to the liver and wrapped around the artery.
At which level does the SMA typically originate?
The SMA arises from the anterior surface of the aorta at the level of the first lumbar vertebral body and passes posterior to the neck of the pancreas and SV and follows a course medial and anterior to the uncinate process of the pancreas and the third part of the duodenum.
At what vertebral level does the abdominal aorta bifurcate?
fourth lumbar vertebraThe abdominal aorta is a retroperitoneal structure that begins at the hiatus of the diaphragm and extends to its bifurcation into the right and left common iliac arteries at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra.
What is the superior mesenteric artery?
The superior mesenteric artery supplies the midgut from the ampullary region of the second part of the duodenum to the splenic flexure of the large intestine. The inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery arises from the SMA and, along with the superior pancreaticoduodenal artery, supplies the head of the pancreas.
Where does superior mesenteric artery branch from?
Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery- This is the first branch of the superior mesenteric artery, arising from its right side, and supplies the head of the pancreas as well as the inferior and ascending regions of the duodenum.
What is the celiac trunk?
Medically reviewed by the Healthline Medical Network — Written by the Healthline Editorial Team on January 20, 2018. The first major branch of the abdominal aorta, the celiac trunk is responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to the stomach, spleen, liver, esophagus, and also parts of the pancreas and duodenum.
What are the three main divisions of the celiac trunk?
There are three main divisions of the celiac trunk: the left gastric artery, the common hepatic artery, and the splenic artery. The left gastric artery runs along the smaller curve of the stomach and connects to the lower esophagus, while the common hepatic artery supplies blood to the liver, duodenum, pancreas, and part of the stomach.
Which artery is the largest in the abdominal cavity?
Along with the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries, it is one of three frontal branches of the abdominal aorta, the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. Although the celiac trunk is only one of three arteries that branches off the abdominal aorta, it is essential to many major organs.
Where is the coeliac trunk located?
It arises from the anterior aspect of the aorta, at the aortic hiatus of the diaphragm (T12 level).
What is the coeliac trunk?
The coeliac trunk is the second branch of the abdominal aorta (the first branches are the paired inferior phrenic arteries). It arises from the anterior aspect of the aorta, at the aortic hiatus of the diaphragm (T12 level). Major Branches. After emerging from the aorta, the coeliac trunk extends approximately 1cm before dividing ...
What are the three branches of the coeliac aorta?
After emerging from the aorta, the coeliac trunk extends approximately 1cm before dividing into three major branches – left gastric, splenic and common hepatic arteries. Of these branches, two go left and one goes to the right-hand side.
What is the surgical division of the median arcuate ligament?
The treatment of coeliac trunk compression syndrome is the surgical division of the median arcuate ligament.
Where does the splenic artery originate?
The splenic artery arises from the coeliac trunk just inferior to the left gastric artery. It then travels left towards the spleen, running posterior to the stomach and along the superior margin of the pancreas. During its course, it is contained within the splenorenal ligament. It terminates into five branches which supply the segments of the spleen.
Which artery supplies the spleen?
In addition to supplying the spleen, the splenic artery also gives rise to several important vessels:
Where is the median arcuate ligament located?
The median arcuate ligament (the fibrous anchor of the diaphragm that forms the aortic hiatus) occasionally lies anterior to the coeliac trunk , rather than its usual superior position.
What is the branching of the celiac artery into the left gastric artery?
Classic branching of the celiac artery into the left gastric artery, splenic artery , and the common hepatic artery is seen in approximately 70%. Variations are present in approximately 30%. In general, any of the three celiac branches may arise independently from the aorta or SMA, or the celiac artery may give rise to other branches. A celiacomesenteric trunk occurs when both the SMA and the celiac trunk originate as a single trunk from the aorta.
What percentage of the common trunk is bifurcated?
common trunk with bifurcation into the hepatosplenic trunk and left gastric artery: 50-76%. common trunk with trifurcation into the common hepatic artery, splenic artery and left gastric artery: 10-19%.
What is the name of the artery that supplies the foregut?
Celiac artery. The celiac artery, also known as the celiac axis or celiac trunk, is a major splanchnic artery in the abdominal cavity supplying the foregut. It arises from the abdominal aorta and commonly gives rise to three branches: left gastric artery, splenic artery, and common hepatic artery .
What arteries are located in the quadrifurcating trunk?
quadrifurcating or pentafurcating trunk with the gastroduodenal artery, right and left hepatic arteries and dorsal pancreatic artery potentially originating from the trunk: 10% 4.
Which artery is the first branch of the splenic artery?
The left gastric artery is usually the first branch, after which the celiac artery bifurcates into the splenic artery (coursing to the left) and the common hepatic artery (coursing to the right).
