What's new in vmfs-6?
With earlier versions of VMFS, something like esxcli storage vmfs unmap or vmkfstools is used to reclaim these blocks. With VMFS-6, the functionality is now automated and fully integrated in the vSphere 6.5 UI as shown in Fig. 1.
What is VMware vSphere VMFS?
VMFS is a high-performance reliable proprietary file system that is designed to run virtual machines (VMs) in a scalable environment - from small to large and extra-large datacenters. VMware vSphere VMFS functions as a volume manager and allows you to store VM files in logical containers called VMFS datastores.
What is the difference between VMware vMotion and VMFS 6?
VMware VMFS 6 supports sharing a VM virtual disk file (VMDK) with up to 32 ESXi hosts in vSphere. VMware vMotion is a feature used for the live migration of VMs between ESXi hosts (CPU, RAM, and network components of VMs are migrated) without interrupting their operation.

What is VMFS used for?
VMware® Virtual Machine File System (VMFS) is a high- performance cluster file system that provides storage virtualization optimized for virtual machines. Each virtual machine is encapsulated in a small set of files and VMFS is the default storage system for these files on physical SCSI disks and partitions.
What is VMFS version?
Virtual Machine File System (VMFS) You can create VMFS datastores on Fibre Channel, iSCSI, FCoE, and local storage devices. ESXi 7.0 supports VMFS Versions 5 and 6 for reading and writing.
What is the difference between VMFS 5 and 6?
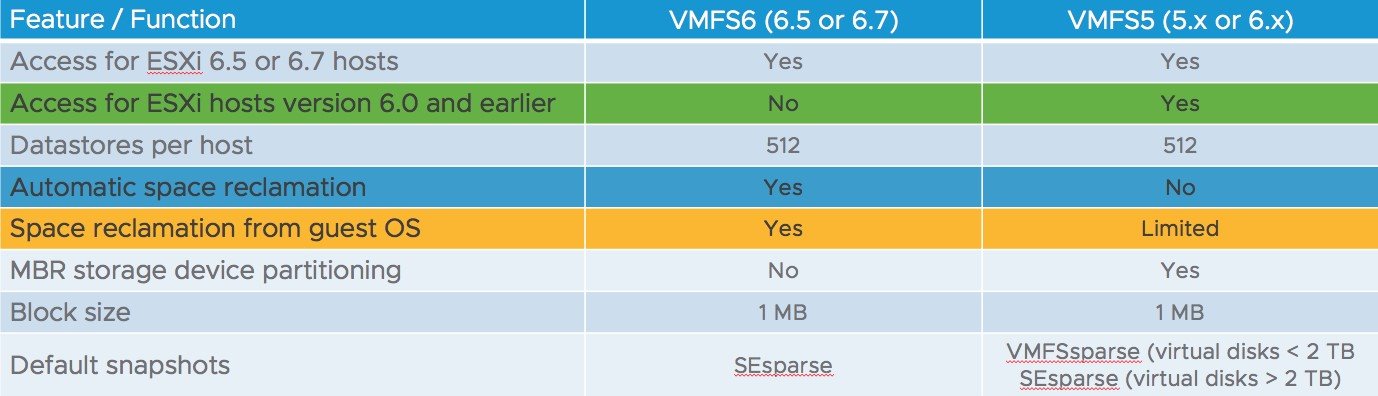
You cannot upgrade the VMFS5 datastore to VMFS6. Below are the some of the new features of VMFS 6: Automatic Space Reclamation (which allows storage arrays to reclaim deleted or unmapped disk blocks from a VMFS datastore so it can be used elsewhere) Support for 4K Native Drives in 512e mode.
What is VMFS datastore?
VMware VMFS (Virtual Machine File System) is VMware, Inc.'s clustered file system used by the company's flagship server virtualization suite, vSphere. It was developed to store virtual machine disk images, including snapshots.
What is vmfs5 VMFS 6 block size?
The VMFS-5 file system uses a fixed data block size of 1 MB. Supporting VMFS-5, VMware ESXi 5.0/5.1 supports a maximum VMDK file size of 2 TB, and VMware ESXi 5.5/6.0/6.5/6.7/7.0 supports a maximum VMDK file size of 62 TB. The VMFS-6 file system also uses a fixed data block size of 1 MB.
What is VMFS in ESXi?
VMFS (Virtual Machine File System) is a clustered file system from VMware that provides storage virtualization. VMFS offers many virtalization-based features, such as: concurrent access to shared storage. Multiple ESXi hosts can read and write to the same storage device at the same time.
How do I upgrade VMFS-5 to VMFS 6?
To upgrade:Perform version check for vCenter Server and all ESX hosts. ... Perform all pre checks for free space availability on datastore DS-2. ... Ensure that the datastore DS-2 is VMFS 6 type and is empty.Add datastore DS-2 to this datastore cluster.Put datastore DS-1 into maintenance mode.More items...•
What is the maximum size of VMFS 6 Datastore?
64 TBVMware VMFS supports up to a maximum size of 64 TB. The FlashArray supports far larger than that, but for ESXi, volumes should not be made larger than 64 TB due to the filesystem limit of VMFS. Using a smaller number of large volumes is generally a better idea today.
What is the block size of the VMFS 6.0 file system?
1 MBThe size of small file blocks (SFB) in VMFS 6 is 1 MB. VMFS 6 can also use large file blocks (LFB), which are 512 MB in size, to improve performance when creating large files. LFBs are primarily used to create thick provisioned disks and swap files.
What is VMFS and NFS?
VMFS (Virtual Machine File System) and NFS (Network File System) - VMware vSphere: Advanced Storage Configuration and Administration Video Tutorial | LinkedIn Learning, formerly Lynda.com.
What is VMDK and VMFS?
VMware virtual machines comprise a set of files in typically one of two given formats: virtual machine file system (VMFS) or raw device mapping (RDM). Both formats enable you to access the virtual machine's disk (VMDK), but they differ in approach to storage, and VMware recommends VMFS for the vast majority of VMs.
What is VMFS volumes?
VMFS is both a volume manager and a file system that is laid down on the aggregate of storage resources made available to either a single ESX host or a cluster of ESX hosts.
What is difference between VMFS and NFS?
Like we stated above, VMFS is a block level file system, while NFS is a file level file system. When creating a VMFS Datastore, the VMFS file system is created by the vSphere, while the NFS file system is on Storage side and is only mounted has a shared folder on the vSphere.
What is the difference between VMFS and VMDK?
Getting VMware terminology straight With RDM, VMDK files are only pointers to a VM's disk data, while on VMFS the files also hold the data. VMFS holds disk data from multiple VMs; RDM does not. VMFS was designed specifically to support virtualization.
Where do I find VMFS version?
To check tha LUN version, on the configuration tab, select the Storage option and click on the desired LUN. So, why did it happen ? VMFS version depends on the version of your ESX host by the time when you last formatted the LUN.
What is VMFS volumes?
VMFS is both a volume manager and a file system that is laid down on the aggregate of storage resources made available to either a single ESX host or a cluster of ESX hosts.
How does VMFS 6 work?
VMFS 6 enables Automatic Space Reclamation based on VAAI Unmap which has been around for a while and allows you to unmap previously used blocks, reclaim dead or stranded space on thinly-provisioned VMFS volumes .#N#Storage Capacity is reclaimed and released to the array so that when needed other volumes can use these blocks. In vSphere 6.0, you were doing this manually via the command line interface which has now been integrated in the UI and can simply be turned on or off.#N#vSphere 6.5 allows you to automate the process by tracking the deleted VMFS blocks and reclaiming this space from the storage array in the background every 12 hours. The effect on storage I/O is minimal.#N#UNMAP works not only at the array level, but also at a guest OS level with newer versions of Windows and Linux. The benefit of UNMAP is obvious. You can reclaim disk space from within your provisioned VMs on a regular basis with the scrubber. The space reclamation priority can further be adjusted per datastore. This means that you can directly specify the priority of execution when the deleted or unmapped blocks are reclaimed on the LUN.
What does "use all available partitions" mean?
Use all available partitions - Dedicates the entire disk to a single VMFS datastore. If you select this option, all file systems and data currently stored on this device are destroyed.
What is the block size of VMFS?
Block Size - The block size on a VMFS datastore defines the maximum file size andthe amount of space the file occupies. VMFS6 supports the block size of 1 MB.
How many bytes are in a standard disk?
Industry standard disk drives have been using a native (physical) 512 bytes sector size. However, due to the increasing demand for larger capacities, the storage industry recently introduced new advanced formats that use 4KB (4096 bytes) physical sectors.
How to select host in vSphere?
Login to vSphere or Web Client. Go to Host Inventory and Select Host.
What is the difference between 512n and 512e?
The main difference between 512n & 512e is the sector sizes on the drive. Traditional 512n storage devices have been using a native 512-bytes sector size, whereas 512e is the advanced format in which the physical sector size is 4,096 bytes. Logical sector size are same 512 bytes in both 512n and 512e.
Why use SE sparse disk?
SE Sparse disks give better space efficiency to virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) deployed on this virtual disk format because they have the ability to reclaim stranded space from within the guest OS automatically. SE Sparse is used primarily View and for LUNs larger than 2TB. When on VMFS 6 the default will be SE Sparse.
What is VMFS 6?
VMFS 6 (Virtual Machine File system 6) is released with vSphere 6.5. VMFS 6 released with vSphere 6.5 contains a lot of new features as compared to earlier version of VMFS (VMFS 5). I will help you to understand the difference between VMFS 5 & VMFS 6 in this article.
What is sector in storage?
A sector is a subdivision of a track on a storage disk or device. Each sector stores a fixed amount of data. Traditional 512n storage devices have been using a native 512-bytes sector size. In addition, due to the increasing demand for larger capacities, the storage industry has introduced advanced formats, such as 512-byte emulation, or 512e. 512e is the advanced format in which the physical sector size is 4,096 bytes, but the logical sector size emulates 512-bytes sector size. Storage devices that use the 512e format can support legacy applications and guest operating systems.
Can VMFS 6 be used with ESXi 6.5?
VMFS-6 is only available in vSphere 6.5 and later. You still can create VMFS 5 & VMFS 6 with ESXi 6.5. After you upgrade your ESXi hosts to version 6.5, you can continue using any existing VMFS5 datastores.
Is VMFS 6 available in vSphere 6.5?
if you consider additional reason to upgrade your vSphere to vSphere 6.5, I would say VMFS 6. VMFS-6 is only available in vSphere 6.5 and later.
What is a spanned VMFS?
A spanned VMFS datastore must use only homogeneous storage devices, either 512n, 512e, or 4Kn. The spanned datastore cannot extend over devices of different formats. Block Size. The block size on a VMFS datastore defines the maximum file size and the amount of space a file occupies.
Can VMFS5 and VMFS6 coexist?
VMFS5 and VMFS6 can coexist in the same datastore cluster. However, all datastores in the cluster must use homogeneous storage devices. Do not mix devices of different formats within the same datastore cluster. Device Partition Formats.
What is VMFS in VMware?
VMware’s Virtual Machine File System (VMFS) is the filesystem of choice for local and block-level storage (ex. SAN) based datastores. If you haven’t upgraded to vSphere 6.5, chances are that you’re still running VMFS-5 or earlier. Upgrading VMFS datastores to the latest version, might be a task to include in your project plan when upgrading to the latest vSphere release. Today’s post takes you through the process of moving a VMFS-5 datastore to VMFS-6.
Why upgrade to VMFS 6?
As we have seen, there are several reasons why you would want to upgrade to VMFS-6, the most salient feature being Automatic Space Reclamation, which is UI driven, and support for 4KN drives. Keep in mind that there is no in-place upgrade path, so reformatting the datastore is your only option. You can do this using the vSphere Web Client or command-line tools.
Do you need to unmount a datastore?
You may need to unmount a datastore first more so if it resides on a SAN provisioned LUN or volume which is accessed by multiple ESXi hosts.
Is a datastore visible in ESXi?
Note: At this point, the device or LUN on which the datastore originally resided is still visible to ESXi or vCenter. You can verify from the list of devices under Storage Devices for a selected ESXi host. It’s now just a matter of running the New Datastore wizard and re-create the datastore afresh this time formatted with VMFS-6.
Is VMFS 6 available in vSphere 6.5?
VMFS-6 is only available in vSphere 6.5 . There are several reasons why you would want to upgrade to this latest version. One of its most anticipated features is Automatic Space Reclamation (ASR) which allows storage arrays to reclaim deleted or unmapped disk blocks from a VMFS datastore so they can be used elsewhere.
Is there an upgrade path for VMFS 6?
The term upgrade is somewhat misleading since in reality no upgrade path is available . Instead, you must format the volume or LUN on which the current datastore resides using VMFS-6. The easiest way to this is as follows:
Can you use ESXi command line?
Similarly, you can use ESXi’s command line tools such as esxcli to retrieve the same. Using putty or otherwise, SSH to an ESXi host and run the following:
Why Use RDMs?
This section specifies the use cases where RDM storage access is preferred over VMFS.
What is VMFS in virtual disk?
VMFS simplifies administration with an intelligent interface that makes it easy to manage allocation and access of virtual disk resources, providing the ability to recognize and mount snapshot copies at the datastore or LUN level. VMFS has a volume signature that can be resignatured to manage additional but convergent copies of a given datastore on block-based storage.
How many virtual machines can you have per LUN?
The key is to remember the upper limit of 512 LUNs per vSphere host and consider that this number can diminish the consolidation ratio if you take the concept of “one LUN per virtual machine” too far.
What is VMFS volume management?
Through the use of a volume management layer, VMFS enables an interface to storage resources so that several types of storage (Fibre Channel, iSCSI and FCoE) can be presented as datastores on which virtual machines can reside. Enabling dynamic growth of those datastores through aggregation of storage resources provides the ability to increase a shared storage resource pool without incurring downtime. Through the VMFS Volume Grow feature, a datastore on block-based storage now can be expanded on an underlying LUN that has been expanded within the storage array. VMFS also enables dynamic growth of the virtual machine disk.
How to configure a LUN for a given VMFS volume?
The best way to configure a LUN for a given VMFS volume is to size for throughput first and capacity second. That is, you should aggregate the total I/O throughput for all applications or virtual machines that might run on a given shared pool of storage; then make sure you have provisioned enough back-end devices and appropriate storage service to meet the requirements.
What is on disk lock in VMFS?
On-disk locking in VMFS ensures that a virtual machine is not powered on by multiple installations of a vSphere host at the same time. With vSphere HA enabled, if a server fails, the on-disk lock for each virtual machine is released, enabling the virtual machine to be restarted on other vSphere hosts. Moreover, VMFS provides virtual machine–level snapshot capability, enabling fast point-in-time recovery. VM Backup products from many VMware partners leverage this feature to provide consistent backup of virtual environments.
What is VMFS in VMware?
VMFS provides on-disk locking that enables concurrent sharing of virtual machine disk files across many vSphere hosts. In fact, VMFS enables virtual disk files to be shared by as many as 32 vSphere hosts (depending on the use-case).
What is VMFS
Virtual Machine File System (VMFS) is a cluster file system that is optimized to store virtual machine files, including virtual disks in VMware vSphere, for the most effective storage virtualization.
VMFS Versions
VMware VMFS has evolved significantly since the release of the first version. Here is a short overview of VMFS versions to track the main changes and features.
VMFS Features
VMware VMFS is optimized to store big files because VMDK virtual disks typically consume a large amount of storage space. A VMFS datastore is a logical container using the VMFS file system to store files on a block-based storage device or LUN. A datastore runs on top of a volume. A VMFS volume can be created by using one or multiple extents.
How to Mount VMFS in Linux
If a hardware failure occurs, you may need to mount a VMware VMFS file system on a Linux machine to copy VM data for disaster recovery if you don’t have the ability to mount disks with VMFS datastores to another ESXi server.
Conclusion
This blog post covered the VMFS file system and explained the features of this cluster file system. VMware VMFS is a reliable, scalable, and optimized file system to store VM files.
What is ESXi datastore?
To store virtual disks, ESXi uses datastores. The datastores are logical containers that hide specifics of physical storage from virtual machines and provide a uniform model for storing the virtual machine files. The datastores that you deploy on block storage devices use the native vSphere Virtual Machine File System (VMFS) format.
What is VMFS in ESXi?
Several versions of the VMFS file system have been released since its introduction. Currently, ESXi supports VMFS5 and VMFS6.
What is delta in VMFS?
A delta or child disk is created. The delta represents the difference between the current state of the VM disk and the state that existed when you took the previous snapshot. On the VMFS datastore, the delta disk is ...