
On the basis of gold foil experiment, Rutherford
Ernest Rutherford
Ernest Rutherford, 1st Baron Rutherford of Nelson, OM, FRS, HFRSE, LLD, was a New Zealand physicist who came to be known as the father of nuclear physics. Encyclopædia Britannica considers him to be the greatest experimentalist since Michael Faraday.
Atom
An atom is the smallest constituent unit of ordinary matter that has the properties of a chemical element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are extremely small; typical sizes are around 100 picometers (1×10⁻¹⁰ m, a ten-milliont…
Why was Rutherford use gold foil in his experiment?
Why did Rutherford use gold foil? This experiment was used to depict the structure of atoms. The reason for using gold foil was that very thin foil for the experiment was required, since gold is malleable from all other metals so it can be easily shaped into very thin sheets. So, Rutherford used gold foils.
What did the gold foil experiment prove?
What is the Gold Foil Experiment?
- Description. The method used by scientists included the following experimental steps and procedure. ...
- Observation. Though most of the alpha particles behaved as expected, there was a noticeable fraction of particles that got scattered by angles greater than 90 degrees.
- Conclusion. ...
What scientist devised the gold foil experiment?
The gold foil experiment was conducted under the supervision of Rutherford at the University of Manchester in 1909 by scientist Hans Geiger (whose work eventually led to the development of the Geiger counter) and undergraduate student Ernest Marsden.
What did Ernest Rutherford learn from his gold foil experiment?
Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that atoms are mostly empty space, with the positive charge concentrated in a nucleus. He realized this because most of the alpha particles passed straight through the piece of gold foil, with just a few deflected at huge angles.
What was concluded from the gold foil experiment?
Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the atom is mostly empty space with a tiny, dense, positively-charged nucleus. Based on these results, Rutherford proposed the nuclear model of the atom.
What did Rutherford conclude about the structure of the atom?
Ernest Rutherford concluded that the atom is almost entirely empty space, and has a tiny, hard nucleus that carries the positive charge and almost all the mass of the atom. The negatively charged electrons orbit around this nucleus.
What can be concluded about the structure of the atom?
Through his experiments, Rutherford concluded that the atom had a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged atoms. He discovered the nucleus in 1911. Eight years later, in 1919, Rutherford conclusively proved the existence of positively-charged particles, called protons, in the nucleus of the atom.
What were the conclusions of Rutherford experiment?
Observation And Conclusion Of Rutherford's Scattering Experiment. Most of the fast moving α-particles passed straight through the gold foil. Most of the space inside the atom is empty. Some of the α-particles were deflected by the foil by small angles.
What did Rutherford conclude about gold atoms?
What is the Rutherford gold-foil experiment? A piece of gold foil was hit with alpha particles, which have a positive charge. Most alpha particles went right through. This showed that the gold atoms were mostly empty space.
What were his three conclusions about the structure of an atom?
Conclusions made by Rutherford based on the alpha particle scattering experiment are : There is a positively charged centre in an atom called the nucleus. Nearly all the mass of an atom resides in the nucleus. The electrons revolve around the nucleus in circular paths.
What two surprising conclusions did Rutherford make when he analyzed the results of his gold foil experiments?
But even then, there were some particles that deflected at HUGE angles. Rutherford's conclusions from the experiment were that atoms must be mostly empty space, and that the positive charge is concentrated in a nucleus.
What is atom conclusion?
The atom is the smallest particle of an element that take part in a chemical reaction. The atom is made up of three subatomic particles: Protons. Electrons.
What did Thomson conclude about the structure of the atom?
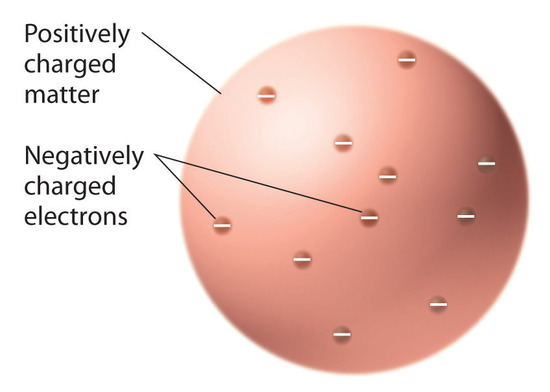
Structure of the Atom and Mass Spectrography. In 1904 Thomson suggested a model of the atom as a sphere of positive matter in which electrons are positioned by electrostatic forces.
Which is true about the structure of the atom quizlet?
Which of the following is true about the structure of an atom? Electrons, neutrons, and protons are made up of even smaller constituents, such as quarks and gluons.
What is the importance of knowing the structure of an atom?
As a result of the work done by previous scientists on atomic models, scientists now have a good idea of what an atom looks like. This knowledge is important because it helps us to understand why materials have different properties and why some materials bond with others.
How important is understanding the structure of the atom?
By learning about atomic structure, we can find out how atoms combine and form many compunds. By learning about atomic structure, we can find out how atoms collide. By learning about atomic structure, we can find out why atoms do not have mass.
What was Rutherford experiment and what did he discover?
The Rutherford gold foil experiment was used to understand the structure of the atom. Rutherford and his students fired positively charged alpha pa...
What happened in Rutherford's gold foil experiment and why was it significant in the development of atomic models?
The Rutherford gold foil experiment demonstrated that alpha particles fired through gold foil in order to interact with its atoms were scattered in...
How did the gold foil experiment work?
The Rutherford gold foil experiment worked by firing positively charged alpha particles through gold foil and observing where they ended up. To mak...
How did Rutherford's gold foil experiment work?
The Rutherford gold foil experiment worked by firing positively charged alpha particles through gold foil and observing where they ended up. To make their observations, Rutherford and his students used phosphorescent screens which emitted light when impacted by alpha particles. The alpha particles would also leave scintillation marks on the screen which could observed under a microscope.
Why did the Rutherford experiment show that the alpha particles in gold foil were scattered?
The Rutherford gold foil experiment demonstrated that alpha particles fired through gold foil in order to interact with its atoms were scattered instead of almost entirely following a straight path through the foil. This meant that the atoms that make up the foil must have a large central positive charge in order to explain how the positively charged alpha particles could be deflected. This large, central, positively charged matter was named the nucleus.
How did the Rutherford gold foil experiment falsify Thomson's hypothesis?
The Rutherford gold foil experiment falsified Thomson's hypothesis by demonstrating that atoms scattered the alpha particles. Rutherford and his students made their observations by observing where alpha particles impacted a phosphorescent screen after being fired through the gold foil. The phosphorescent screen would emit light and leave marks upon impact by alpha particles, which could be observed under a microscope. The experiment concluded that the atom is mostly empty space but with a positive charge concentrated at the center of the atom: the nucleus.
What was the purpose of the gold foil experiment?
The purpose of the experiment was to understand atoms' structure by testing the atom's paradigm model at that time: the J.J. Thomson or plum pudding model. At the time, the atom was modeled as negatively charged electrons floating within some positively charged matter. The gold foil experiment set out to fire positively charged particles known as alpha particles through a thin piece of gold foil and observe how the foil influences the alpha particles. The preceding hypothesis and model of the atom entailed that the alpha particles ought to follow a path straight through the atoms of the foil, and if deflected, it would only be by a fraction of a degree.
Why did Rutherford and his students choose to fire alpha particles through the gold foil?
Rutherford and his students chose to fire alpha particles through the gold foil because gold is a heavy element that is exceptionally malleable and can be formed into thin foil. According to Thomson, even a large atom like gold should be mostly empty space, and the alpha particles would travel straight through. The piece of gold foil was surrounded by a tube with a phosphorescent screen which would emit light when impacted by alpha particles and leave scintillations upon impact; This allowed Rutherford and his students to observe the results and count the areas of impact using a microscope.
Which model of the atom was challenged by the Gold Foil experiment?
Eventually, the Thomson model of the atom was also challenged. The gold foil experiment results in the Rutherford model, where the atom is composed of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons.
Which model of the atom contains a central positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons?
The Ernest Rutherford model of the atom contains a central positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons. The atom is still mostly empty space.
