See more

What was Rutherford's experiment simple?
Physicist Ernest Rutherford established the nuclear theory of the atom with his gold-foil experiment. When he shot a beam of alpha particles at a sheet of gold foil, a few of the particles were deflected. He concluded that a tiny, dense nucleus was causing the deflections.
What was Rutherford experiment known as?
1 Answer. The Geiger–Marsden experiments (also called the Rutherford gold foil experiment) were a series of landmark experiments by which scientists discovered that every atom contains a nucleus where its positive charge and most of its mass is concentrated.
What is the Rutherford experiment and how did it work?
What is the Rutherford gold-foil experiment? A piece of gold foil was hit with alpha particles, which have a positive charge. Most alpha particles went right through. This showed that the gold atoms were mostly empty space.
What are the main points of Rutherford theory?
Rutherford's model proposed that the negatively charged electrons surround the nucleus of an atom. He also claimed that the electrons surrounding the nucleus revolve around it with very high speed in circular paths. He named these circular paths as orbits.
What is Ernest Rutherford atomic model called?
The Rutherford atomic model was also known as the "Rutherford nuclear atom" and the "Rutherford Planetary Model". In 1911, Rutherford described the atom as having a tiny, dense, and positively charged core called the nucleus.
Why is it called the Bohr Rutherford model?
Niels Bohr proposed the Bohr Model of the Atom in 1915. Because the Bohr Model is a modification of the earlier Rutherford Model, some people call Bohr's Model the Rutherford-Bohr Model. The modern model of the atom is based on quantum mechanics.
Why Rutherford model is called nuclear model?
Rutherford's model is called the nuclear model because it is associated with the discovery of the nucleus.
Why was Rutherford's model called the planetary model?
In Rutherford's model of the atom, the electrons move around the massive nucleus like planets orbiting the sun. Hence, this model is also called the planetary model.
What did Ernest Rutherford discover about the atom?
Ernest Rutherford found that the atom is mostly empty space, with nearly all of its mass concentrated in a tiny central nucleus. The nucleus is pos...
What is Ernest Rutherford most famous for?
Ernest Rutherford is known for his pioneering studies of radioactivity and the atom. He discovered that there are two types of radiation, alpha and...
What is Ernest Rutherford’s most famous experiment?
Ernest Rutherford’s most famous experiment is the gold foil experiment. A beam of alpha particles was aimed at a piece of gold foil. Most alpha par...
What did Ernest Rutherford discover?
He discovered that there are two types of radiation, alpha and beta particles, coming from uranium. He found that the atom consists mostly of empty space, with its mass concentrated in a central positively charged nucleus.
Where did Rutherford study?
He chose to continue his study at the Cavendish Laboratory of the University of Cambridge, which J.J. Thomson, Europe’s leading expert on electromagnetic radiation, had taken over in 1884.
What did Rutherford and Thomson study?
Thomson then studied the charge-to-mass ratio of the most common ion, which later was called the electron, while Rutherford pursued other radiations that produced ions. Rutherford first looked at ultraviolet radiation and then at radiation emitted by uranium.
What school did Ernest Rutherford attend?
Ernest Rutherford attended the free state schools through 1886, when he won a scholarship to attend Nelson Collegiate School, a private secondary school. He excelled in nearly every subject, but especially in mathematics and science.
What was Rutherford's apparatus for detecting?
Rutherford’s apparatus for detecting electromagnetic waves, or radio waves , was simpler and had commercial potential. He spent the next year in the Cavendish Laboratory increasing the range and sensitivity of his device, which could receive signals from half a mile away.
Where did Rutherford go to college?
Another scholarship took Rutherford in 1890 to Canterbury College in Christchurch, one of the four campuses of the University of New Zealand. It was a small school, with a faculty of eight and fewer than 300 students. Rutherford was fortunate to have excellent professors, who ignited in him a fascination for scientific investigation tempered with the need for solid proof.
Where were X-rays discovered?
X-rays were discovered in Germany by physicist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen only a few months after Rutherford arrived at the Cavendish. For their ability to take silhouette photographs of the bones in a living hand, X-rays were fascinating to scientists and laypeople alike.
How did Rutherford's experiment work?
The equipment needed for Rutherford's experiment was as follows: Here are the steps that were completed: Step 1: Position the piece of gold foil between the alpha source and the screen. Step 2: Point the alpha particles being created by the alpha source at the piece of gold foil.
What did Ernest Rutherford's gold foil experiment help scientists understand?
Ernest Rutherford's gold foil experiment helped scientists understand the charge of an atom. Follow along with Rutherford's experiment in this lab and understand the surprising results and conclusions of his experiment. Updated: 11/01/2021
What Did His Results Show?
Rutherford's results were, at the time, surprising. Most of the alpha particles went straight through the gold foil as if it wasn't even there, and hit the screen at an angle of zero degrees. The further they moved around the screen, the less particles were found. But even then, there were some particles that deflected at HUGE angles.
Why is the plum pudding model called the gold foil experiment?
This was called the plum pudding model, because the negative charges were like plums stuck in the positively charged plum pudding. But Rutherford's gold foil experiment (otherwise known as ...
Which model showed that atoms contain a large area of positive charge, with negative charges stuck on the outside?
This model said that atoms contain a large area of positive charge, with negative charges stuck on the outside. Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that atoms are mostly empty space, with the positive charge concentrated in a nucleus.
Who is Ernest Rutherford?
Lesson Summary. Ernest Rutherford was a British physicist who is particularly famous for studying the structure of the atom. He discredited the previous model of the atom, known as the plum pudding model. This model said that atoms contain a large area of positive charge, with negative charges stuck on the outside.
Do you have to be a Study.com member to unlock this lesson?
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member.
What was Rutherford's discovery?
Rutherford's "gold foil experiment" led to the discovery that most of an atom's mass is located in a dense region now called the nucleus. Prior to the groundbreaking gold foil experiment, Rutherford was granted the Nobel Prize for other key contributions in the field of chemistry. History.
What was Rutherford's gold foil experiment?
Features. The gold foil experiment consisted of a series of tests in which a positively charged helium particle was shot at a very thin layer of gold foil.
What was the first theory of atomic structure?
The popular theory of atomic structure at the time of Rutherford's experiment was the "plum pudding model." This model was developed in 1904 by J.J. Thompson, the scientist who discovered the electron. This theory held that the negatively charged electrons in an atom were floating in a sea of positive charge--the electrons being akin to plums in a bowl of pudding. Although Dr. Nagaoka had published his competing theory that electrons orbit a positive nucleus, akin to the way the planet Saturn is orbited by its rings, in 1904, the plum pudding model was the prevailing theory on the structure of the atom until it was disproved by Ernest Rutherford in 1911.
Who discovered the nucleus?
Rutherford's discovery of the nucleus and proposed atomic structure was later refined by physicist Niels Bohr in 1913. Bohr's model of the atom, also referred to as the Rutherford Bohr model, is the basic atomic model used today. Rutherford's description of the atom set the foundation for all future atomic models and the development ...
Who was the scientist who led the Gold Foil experiment?
The gold foil experiment was conducted under the supervision of Rutherford at the University of Manchester in 1909 by scientist Hans Geiger (whose work eventually led to the development of the Geiger counter) and undergraduate student Ernest Marsden. Rutherford, chair of the Manchester physics department at the time of the experiment, is given primary credit for the experiment, as the theories that resulted are primarily his work. Rutherford's gold foil experiment is also sometimes referred to as the Geiger-Marsden experiment.
Who is the father of atomic models?
Five Types of Atomic Models. Updated April 25, 2017. By Jessica Pestka. Ernest Rutherford, originally from New Zealand, is credited as being the father of nuclear physics for his discoveries in atomic structure, even though Hantaro Nagaoka, a physicist from the Imperial University of Tokyo, first proposed the theory of the nucleus as it is known ...
What is the CERN plan to search for?
CERN Plans to Search for Mysterious Fifth Force Particle
What did Rutherford find?
Here is what Rutherford deduced: because most of the fast-moving α particles passed through the gold atoms undeflected , they must have traveled through essentially empty space inside the atom. Alpha particles are positively charged, so deflections arose when they encountered another positive charge (like charges repel each other). Since like charges repel one another, the few positively charged α particles that changed paths abruptly must have hit, or closely approached, another body that also had a highly concentrated, positive charge. Since the deflections occurred a small fraction of the time, this charge only occupied a small amount of the space in the gold foil. Analyzing a series of such experiments in detail, Rutherford drew two conclusions:
What did Rutherford find out about gold foil?
Rutherford’s famous gold foil experiment was performed by aiming α particles at a sheet of gold foil and observing whether the α particles passed through, were deflected slightly or significantly. Because most of the α particles passed through undeflected, Rutherford deduced that the atom was mostly empty space.
Who discovered the positive charge of an atom?
The positively charged part of an atom, however, was not yet well understood. In 1904, an English physicist named J.J. Thomson proposed the “plum pudding” model of atoms, ...
Who proposed the atoms of Saturn?
A competing model had been proposed in 1903 by Hantaro Nagaoka, who postulated a Saturn-like atom, consisting of a positively charged sphere surrounded by a halo of electrons ( Figure 1 ). Figure 1. (a) Thomson suggested that atoms resembled plum pudding, an English dessert consisting of moist cake with embedded raisins (“plums”).
What were the results of Rutherford's experiment?
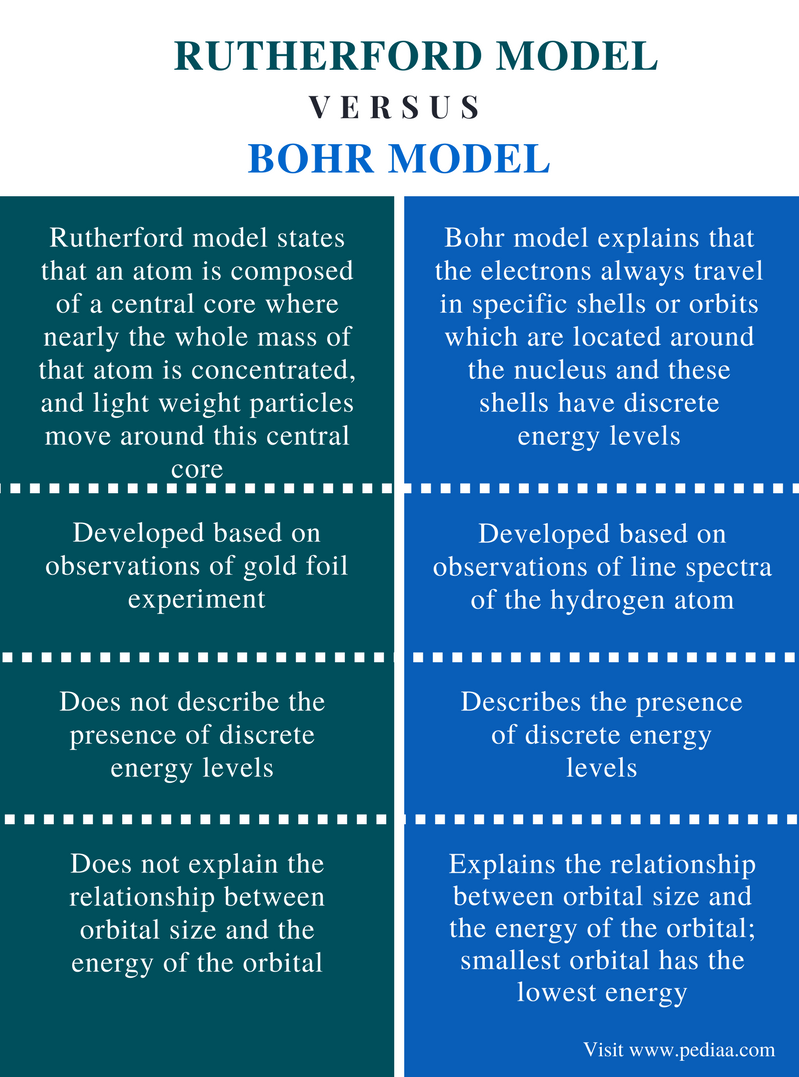
The Rutherford atomic model relied on classical physics. The Bohr atomic model, relying on quantum mechanics, built upon the Rutherford model to explain the orbits of electrons.
What was the impact of Ernest Rutherford's theory?
The gold-foil experiment showed that the atom consists of a small, massive, positively charged nucleus with the negatively charged electrons being at a great distance from the centre. Niels Bohr built upon Rutherford’s model to make his own. In Bohr’s model the orbits of the electrons were explained by quantum mechanics.
What is the Rutherford gold-foil experiment?
A piece of gold foil was hit with alpha particles, which have a positive charge. Most alpha particles went right through. This showed that the gold atoms were mostly empty space. Some particles had their paths bent at large angles. A few even bounced backward. The only way this would happen was if the atom had a small, heavy region of positive charge inside it.
What did Ernest Rutherford's atomic model get right and wrong?
The Rutherford atomic model was correct in that the atom is mostly empty space. Most of the mass is in the nucleus, and the nucleus is positively charged. Far from the nucleus are the negatively charged electrons. But the Rutherford atomic model used classical physics and not quantum mechanics. This meant that an electron circling the nucleus would give off electromagnetic radiation. The electron would lose energy and fall into the nucleus. In the Bohr model, which used quantum theory, the electrons exist only in specific orbits and can move between these orbits.
Why did Rutherford know that the gold atom's mass must be concentrated in a tiny dense nucle?
Because only very few of the alpha particles in his beam were scattered by large angles after striking the gold foil while most passed completely through, Rutherford knew that the gold atom's mass must be concentrated in a tiny dense nucleus. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
Which model relied on classical physics?
The Rutherford atomic model relied on classical physics. The Bohr atomic model, relying on quantum mechanics, built upon the Rutherford model to explain the orbits of electrons. Read about the Thomson atomic model—the earliest model of atomic structure—and how Ernest Rutherford’s gold-foil experiment disproved it.
Who proposed the Rutherford model?
Rutherford model, also called Rutherford atomic model, nuclear atom, or planetary model of the atom, description of the structure of atoms proposed (1911) by the New Zealand-born physicist Ernest Rutherford. The model described the atom as a tiny, dense, positively charged core called a nucleus, in which nearly all the mass is concentrated, ...
How does Rutherford's experiment work?
In the experiment, Rutherford passes very high streams of alpha-particles from a radioactive source i.e. alpha-particle emitter , at a thin sheet of100 nm thickness of gold. In order to examine the deflection produced by the alpha particles, he placed a screen of fluorescent zinc sulphide around the thin gold foil. Rutherford made certain observations that oppose Thomson’s atomic model.
Who discovered that anodes emit positively charged particles with a different condition in the same tube?
Protons: In 1886, Ernest Goldstein discovered that anode emitted positively charged particles with a different condition in the same tube, known as Canal rays or as Protons.
Which scientist proposed that there is negatively charged electrons around the nucleus of an atom?
Rutherford proposed that there is negatively charged electrons around the nucleus of an atom. the electron surrounding the nucleus revolves around it in a circular path with very high speed. He named orbits to these circular paths.
How many alpha particles were deflected back?
Very few of the alpha-particles (1-2%) were deflected back, i.e. only a very less amount of α-particles had nearly 180° angle of deflection. this shows that the volume occupied by the positively charged particles is very small as compared to the total volume of an atom.
When were negatively charged particles discovered?
Electron: In 1897, J. J. Thomson discovered negatively charged particles towards the anode, these rays are emitted by the cathode in a cathode ray experiment. Then these negatively charged particles are proposed as Electrons.
Who proposed the atomic structure of elements?
Rutherford proposed the atomic structure of elements, on the basis of his experiment. According to Rutherford ’s atomic model:
Did Rutherford describe the arrangement of electrons in the orbit?
Rutherford also did not describe the arrangement of electrons in the orbit as one of the other drawbacks of his model.