
Why is the feudal system important? Feudalism helped protect communities from the violence and warfare that broke out after the fall of Rome and the collapse of strong central government in Western Europe. Feudalism secured Western Europe’s society and kept out powerful invaders. Feudalism helped restore trade.
Was the feudal system good or bad?
Feudalism was neither good nor bad, it just was. It bridged the time between the ancient world and the early modern era. The modern western world was a direct outgrowth of the Medieval Period and feudal states were precursors of modern nation states with monarchs derving from strong feudal leaders.
Who benefited from the feudal system?
Who benefited most from the feudal system? Feudalism benefited lords, vassals, and peasants. Lords gained a dependable fighting force in their vassals. Vassals received land for their military service. Peasants were protected by their lords.
What contributed to the end of the feudal system?
- The depletion of the fertility of the land , due to its constant use and despite the use of the crop rotation system.
- The repopulation of cities , from the increase in population that occurred since the eleventh century.
- The spread of the bubonic plague that, between 1348 and 1353, killed a third of the European population. ...
Why was fief so important to the feudal system?
Why is the fief important?
- Each fief was organized like the kingdom.
- The help afforded by Ertoghrul to the Seljukian monarch on a critical occasion led to the addition of Sugut to his fief, with which he was now formally invested.
- His daughter Marie sold the fief of Coucy to Louis, duke of Orleans, in 1400.
Why is feudal system important?
Feudalism in Western Europe was a politico-economic system that created a social fabric with military obligations. It produced a set of manners and norms – chivalry – and spawned an elegant form of literature that helped Europeans capture and develop pride in their histories.
Who is most important in the feudal system?
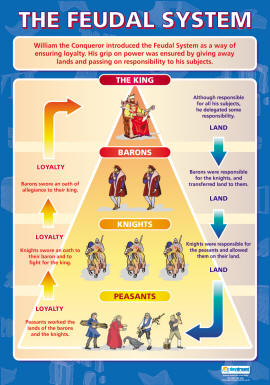
The King. At the very top of the feudal system was the king. He presided over the land he ruled, directing and controlling what happened in his kingdom.
What were the most important features of feudalism?
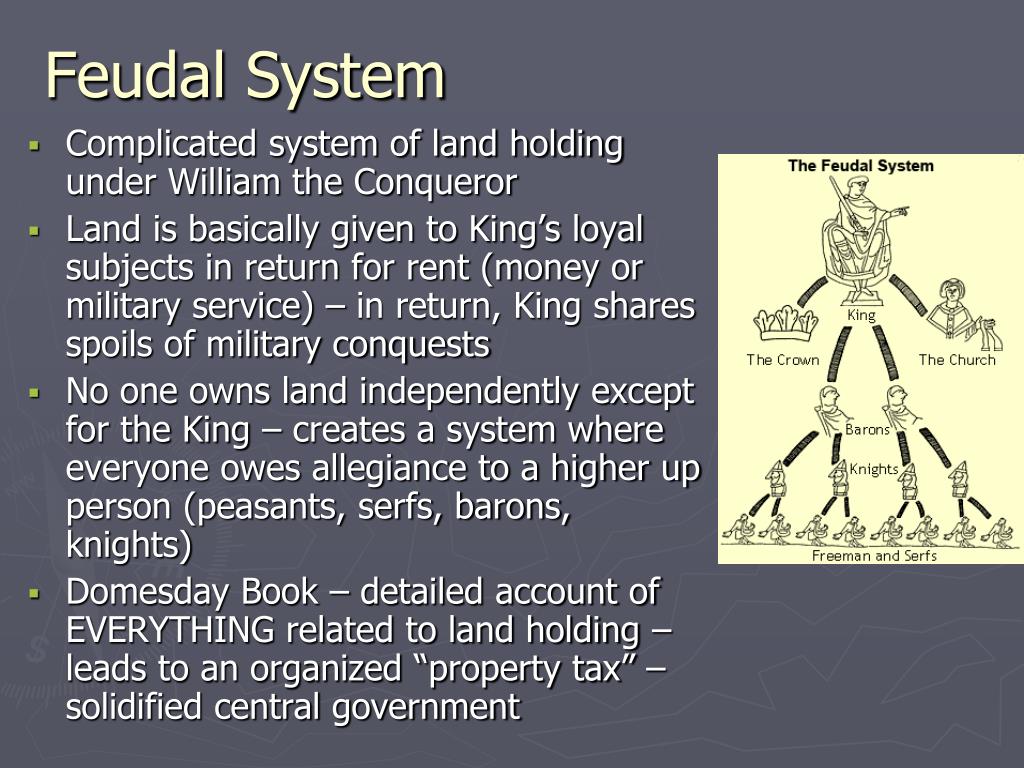
Three primary elements characterized feudalism: Lords, vassals, and fiefs; the structure of feudalism can be seen in how these three elements fit together. A lord was a noble who owned land, a vassal was a person who was granted possession of the land by the lord, and the land was known as a fief.
What was the impact of the feudal system?
Feudalism had two enormous effects on medieval society. Feudalism discouraged unified government and it also discouraged trade and economic growth.
What is the main reason feudalism developed?
Because kings were often too weak to repel the invaders, many city dwellers moved into the countryside in hopes of greater safety. As a result of the invasions, and a weak central government, a new social and political system known as feudalism developed.
Why was feudalism created?
This resulted in a collapse of law and order, a decline in trade, and collapse of local economies. To counter these threats, Frankish kings needed warriors. They created a system of military and political relationships called feudalism. Feudalism was the medieval model of government.
What are 5 facts about feudalism?
15 Feudalism FactsThe Feudal Period Began in the 9th century.Feudalism Arrived in England in 1066.Feudal Economies are Based on Land Ownership.Your Position in Society was Fixed for Life.The King was Top Dog.You Were Expected to Fight For the King When Requested.More items...•
Why was feudalism important in the Middle Ages?
Feudalism allowed societies in the Middle Ages to retain a relatively stable political structure even as the centralized power of empires and kingdoms began to dissolve.
What are 2 features of the feudal system?
The King owned all the land and granted land for loyalty to his tenants-in-chief. The tenants-in-chief granted land to the under-tenants (knights) in return for military service.
Who benefited the most in a feudal society?
Answer and Explanation: The two groups at the top of the feudal system, lords and churchmen, probably benefited the most from the system. They tended to be the wealthiest, were immune from some forms of taxation, were able to collect dues and tithes from the general public, and were the most likely to be literate.
How did the feudal system work?
In broad terms a lord was a noble who held land, a vassal was a person who was granted possession of the land by the lord, and the land was known as a fief. In exchange for the use of the fief and protection by the lord, the vassal would provide some sort of service to the lord.
What is feudal system Short answer?
Feudalism was a system in which people were given land and protection by people of higher rank, and worked and fought for them in return.
Who benefited the most in a feudal society?
Answer and Explanation: The two groups at the top of the feudal system, lords and churchmen, probably benefited the most from the system. They tended to be the wealthiest, were immune from some forms of taxation, were able to collect dues and tithes from the general public, and were the most likely to be literate.
Who made the feudal system?
Feudalism is the name given to the system of government William I introduced to England after he defeated Harold at the Battle of Hastings. Feudalism became a way of life in Medieval England and remained so for many centuries.
Who were the people involved in the feudal system?
A broader definition of feudalism, as described by Marc Bloch (1939), includes not only the obligations of the warrior nobility but the obligations of all three estates of the realm: the nobility, the clergy, and the peasantry, all of whom were bound by a system of manorialism; this is sometimes referred to as a " ...
Who had the most power in feudal Europe?
At the very top of feudal society were the monarchs, or kings and queens. As you have learned, medieval monarchs were also feudal lords. They were expected to keep order and to provide protection for their vassals.
When was feudalism first used?
The adjective feudal was in use by at least 1405, and the noun feudalism, now often employed in a political and propagandistic context, was coined by 1771, paralleling the French féodalité ( feudality ).
Who invented feudalism?
In 1771, in his History of Manchester, John Whitaker first introduced the word "feudalism" and the notion of the feudal pyramid. The term "feudal" or "feodal" is derived from the medieval Latin word feodum.
What are some examples of feudalism?
For feudalism in other societies, as well as that of the Europeans, see Examples of feudalism. Investiture of a knight (miniature from the statutes of the Order of the Knot, founded in 1352 by Louis I of Naples ). Orava Castle in Slovakia. A Medieval castle is a traditional symbol of a feudal society. Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was ...
What is feudalism in the military?
According to a classic definition by François-Louis Ganshof (1944), feudalism describes a set of reciprocal legal and military obligations which existed among the warrior nobility and revolved around the three key concepts of lords, vassals and fiefs, though Ganshof himself noted that his treatment was only related to the "narrow, technical, legal sense of the word".
What are the three concepts of feudalism?
The classic François-Louis Ganshof version of feudalism describes a set of reciprocal legal and military obligations which existed among the warrior nobility, revolving around the three key concepts of lords, vassals and fiefs . In broad terms a lord was a noble who held land, a vassal was a person who was granted possession of the land by the lord, and the land was known as a fief. In exchange for the use of the fief and protection by the lord, the vassal would provide some sort of service to the lord. There were many varieties of feudal land tenure, consisting of military and non-military service. The obligations and corresponding rights between lord and vassal concerning the fief form the basis of the feudal relationship.
What is a medieval castle?
A Medieval castle is a traditional symbol of a feudal society. Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, and cultural customs that flourished in Medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structuring society around relationships ...
When did the French abolish feudal order?
Historian Georges Lefebvre explains how at an early stage of the French Revolution, on just one night of August 4, 1789, France abolished the long-lasting remnants of the feudal order. It announced, "The National Assembly abolishes the feudal system entirely." Lefebvre explains:
What are some interesting facts about feudalism?
The Feudal Period Began in the 9th Century. Feudalism Arrived in England in 1066. Feudal Economies are Based on Land Ownership. Your Position in Society was Fixed for Life. The King was Top Dog. You Were Expected to Fight For the King When Requested.
What is the history of feudalism?
Feudalism was an was a fascinating social and economic system to live under, read on for 15 interesting facts... Feudalism was a land based economic system that combined certain social and legal customs in Europe during the Middle Ages . Feudal society was split into strict hierarchies with each group having obligations and expectations from ...
What was the Catholic Church like during the feudal period?
The catholic church and the papacy were very powerful in the feudal period, often rivaling or usurping royalty. The First World War, and especially the latest one, largely swept away what was left in Europe of feudalism and of feudal landlords, especially in Poland, Hungary, and the South East generally.
What is feudal economics?
Feudal Economies are Based on Land Ownership. There is an element of free market economics in that surplus goods produced could be exchanged for other goods or sold for currency. Feudalism brought with it a judicial system, which provided lots of rights for barons and lords, but far less rights for serfs and peasants.
What was the economic system of Europe during the Middle Ages?
Feudalism was a land based economic system that combined certain social and legal customs in Europe during the Middle Ages.
How did feudalism end?
In England, for instance, Feudalism was eventually ended by the devastation and upheaval caused by the Black Death, the evolution from a land-based economy to a money based one, and the establishment of a centralized government.
How long did men have to fight in the Feudal Levy?
Men were generally expected to fight for 40 days (although under certain circumstances this could be extended to 90 days). The limited time period was meant to make sure that the land would not be neglected for too long.
What were the main features of feudalism?
The most prominent feature of Feudalism was that the people directly depended on the feudal order due to the lack of state union because the union was divided into different classes, such as nobles , serfs , vassals , priests , bourgeois, peasants, and big landlords or seniors who had absolute rights over the people living in their lands. Before capitalism, the socio-economic system was covered by feudal structures in Western Europe. Peasants depended on lesser lords who were also connected with greater lords. The system was ended with the king at the top. Stronger people guarded weaker people, but the price was high.…
What was feudalism based on?
Feudalism was not only based on land, but also obligations and loyalties. Nobles came right after the king they lived much like the king, but they had less power, they dressed the same and were treated with many off the same services as the king was treated with. Knights were usually sons of nobles and protected the king and the noble, they mainly followed the nobles orders which sometimes were to fight for the king since the noble swore to give the king protection using the knights. Serfs mainly farmed and would trade if they were free in a lord’s manor. The Feudal system is not still used today, yet some levels of the feudal system are similar to classes of civilians and ranks of government…
What did the Lord's Manor do?
The lord’s manor was basically a self-sufficient community. The serfs and peasants did nearly everything to raise and produce things that they and their lord needed for basic life which was fuel, milk, cheese, lumber, leather products, cloth, and crops. The crops typically grown where rye, wheat, oats, and barley. Some vegetables that they grew where beans, peas, onions, beans, and beets. But even then they had to still trade for things like iron, salt, and not normal objects like millstones.…
What was the most unjust system in medieval Europe?
Throughout history, the world has faced numerous different social systems and feudalism was by far the most unjust system during medieval Europe. At the top of the feudal system were the kings. The king would own all of the land, giving it out to the nobles to manage portions of it.…
What was the most important part of the Middle Ages?
MIP-1) Feudalism was one of the most important parts of the middle ages.
What was the economic system of the Middle Ages?
Supporting it was an economic system called manorialism, which centered around self-sufficient estates called manors. Farmers worked the fields on the manor and were crucial to keeping it running, both through the work they did and the taxes they paid. Feudalism was an important part of the Middle Ages and would not have existed without the manor or the work of farmers.…
What is the social structure of the peasant life in China?
The social structure of the peasant life in China was the peasant worked and gave the earning to the landlord. The workers them self needed more labor therefore producing more kids meant having more help for the farm. In the novel Frog Mo’s narrative tadpole gives us a look of poverty in the beginning by saying “people would eat coal” that’s how worse it got for the peasant people of China. The landlords were not looked upon as saviors because they were also the officials therefore if you couldn’t pay the landlord the fees not only would there be punishment for that, but also a government punishment as well.…
Why was feudalism important?
From a very Eurocentric point of view, Feudalism was an all-important development because it rendered obsolete slave-based models. It increased local efficiency and provided a better life for inhabitants of places where it took ground . A fief was the world, and the world (the fief) was a very stable place, yet scary as always.
How did feudalism contribute to modern economics?
Feudalism was the one the biggest steps toward a modern economical system, as it provided the framework for Socialism and Capitalism, arguably. The wealthy lords would hire vassals, who, in exchange for a place to live, would work the land. Further, these vassals could give some of their land for their own vassals and so forth. This hierarchy, headed by the Church (the king was subordinate), had the foundations for a working economy, though its efficiency can be debated. Once it collapsed, followed by the eventual decline of Mercantilism, Capitalism would emerge roughly with the implementation of the Cottage Industries.
Why did feudalism flourish?
After the fall of the Western Rome in 476, feudalism as a system flourished. This was because it provided a semblances of order in a chaotic time of. Continue Reading. Feudalism was considered to be a practical system of the medieval ages. While it was not perfect, it was good for its time.
What was the law of Charlemagne?
Laws of Charlemagne put feudalism in writing and made it sacral by the catholic church.
What is the top down structure of feudalism?
Indeed, it was the introduction of money that led feudalism to transition to a modern capitalist economy.
Is a local lord good or bad?
The local lord could be good or bad, and all-out psychopaths weren’t unknown. Still, there was a clear idea of who was in charge, and could be expected to maintain social order. The relationship between local and national authority was essentially contractual in nature. The king simply couldn’t exercise military, let alone administrative, control over his nominal domain, so a bunch of barons, satraps, lords and knights were the only solution.
Is feudalism a system?
Feudalism is a system which has been and still is present within other system of goverment. It’s universal but has been defined and institutionalized in early Medieval Europe.
What was the most important factor concerning the feudal system?
What was the most important factor concerning the feudal system?#N#a) It provided basic needs.#N#b) It made people rich.#N#c) It separated the poor from the rich.#N#d) It made the poor and rich equal.
When did welfare reform begin?
c) The first major effort toward welfare reform climaxed in 1988 with the passage of the Family Support Act.
Overview
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, and cultural customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structuring society around relationships that were derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour. Although it is derived from the Latin word feod…
Definition
There is no commonly accepted modern definition of feudalism, at least among scholars. The adjective feudal was in use by at least 1405, and the noun feudalism, now often employed in a political and propagandist context, was coined by 1771, paralleling the French féodalité.
According to a classic definition by François Louis Ganshof (1944), feudalism describes a set of reciprocal legal and military obligations which existed among the warrior nobility and revolved ar…
Etymology
The root of the term "feudal" originates in the Proto-Indo-European word *péḱu, meaning "cattle", and possesses cognates in many other Indo-European languages: Sanskrit pacu, "cattle"; Latin pecus (cf. pecunia) "cattle", "money"; Old High German fehu, fihu, "cattle", "property", "money"; Old Frisian fia; Old Saxon fehu; Old English feoh, fioh, feo, fee. The term "féodal" was first used in 17th-ce…
History
Feudalism, in its various forms, usually emerged as a result of the decentralization of an empire: especially in the Carolingian Empire in 9th century AD, which lacked the bureaucratic infrastructure necessary to support cavalry without allocating land to these mounted troops. Mounted soldiers began to secure a system of hereditary rule over their allocated land and their power ov…
Feudal society
The phrase "feudal society" as defined by Marc Bloch offers a wider definition than Ganshof's and includes within the feudal structure not only the warrior aristocracy bound by vassalage, but also the peasantry bound by manorialism, and the estates of the Church. Thus the feudal order embraces society from top to bottom, though the "powerful and well-differentiated social group of the urb…
Historiography
The idea of feudalism was unknown and the system it describes was not conceived of as a formal political system by the people living in the medieval period. This section describes the history of the idea of feudalism, how the concept originated among scholars and thinkers, how it changed over time, and modern debates about its use.
The concept of a feudal state or period, in the sense of either a regime or a period dominated by …
See also
• Barons in Scotland
• Bastard feudalism
• Cestui que
• English feudal barony
• Feudal baron
Further reading
• Bloch, Marc, Feudal Society. Tr. L.A. Manyon. Two volumes. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1961 ISBN 0-226-05979-0
• Ganshof, François Louis (1952). Feudalism. London; New York: Longmans, Green. ISBN 978-0-8020-7158-3.
• Guerreau, Alain, L'avenir d'un passé incertain. Paris: Le Seuil, 2001. (Complete history of the meaning of the term.)