What did the poor Romans do?
Most Romans, were poor and performed unskilled labor for work. In contrast to the opulent homes on Palatine Hill, the working poor of Rome crowded into the ancient equivalent of apartment buildings. Their neighborhoods were noisy, and dirty.
How did the Romans treat the poor?
Occupation of the Poor in Ancient Rome The poor people generally had to work as unskilled workers, getting themselves hired on a daily basis to perform a variety of menial jobs. They were known as a mercenarius—the modern equivalent word being 'mercenary'—meaning a person who works for money.
What was life like for a Roman peasant?
The average peasant wasn't necessarily treated like a slave, but they definitely weren't treated like the wealthy either. They worked long hours in the sun, ate the food that they could afford (the salary wasn't very much). They weren't allowed to carry weapons either. But they often did, if they were smuggled.
How was life different for poor Romans and wealthy Romans?
If you were richer, you would live in larger single homes called domus. These usually had many rooms off an atrium which was a room in the centre of the house with an open roof. Poor Romans who lived in the countryside would live in shacks or cottages while rich Romans would live in large, sprawling villas.
What did poor Romans eat?
As you might expect, the poor people in Rome did not eat the same food as the wealthy. The main food of the poor was a porridge call "puls." Puls was made by mixing ground wheat and water. Sometimes they might get some vegetables or fruit to eat with their puls. The poor ate very little meat.
What were poor Romans called?
PlebeiansThe term plebeian referred to all free Roman citizens who were not members of the patrician, senatorial or equestrian classes. Plebeians were average working citizens of Rome – farmers, bakers, builders or craftsmen – who worked hard to support their families and pay their taxes.
Was the average Roman poor?
The average citizen worked hard and lived reasonably comfortably in modest housing. Despite the riches of the Roman Empire, the largest class lived in what can only be described as poverty. Roman children wore pendants called bullas, from the Latin word for "bubble," around their necks.
What did peasants do in ancient Rome?
The Roman peasant was a 'peasant of obligation', charged with the duty of supporting a militarist and oligarchic state with supplies and manpower, but without security of tenure over his land.
What would a poor Roman citizen do to move up in status?
Soldier - The Roman Army was large and needed soldiers. The army was a way for the poorer class to earn a regular wage and to gain some valuable land at the end of their service. It was a good way for the poor to move up in status. Merchant - Merchants of all sorts sold and bought items from around the Empire.
Where did poor people live in Rome?
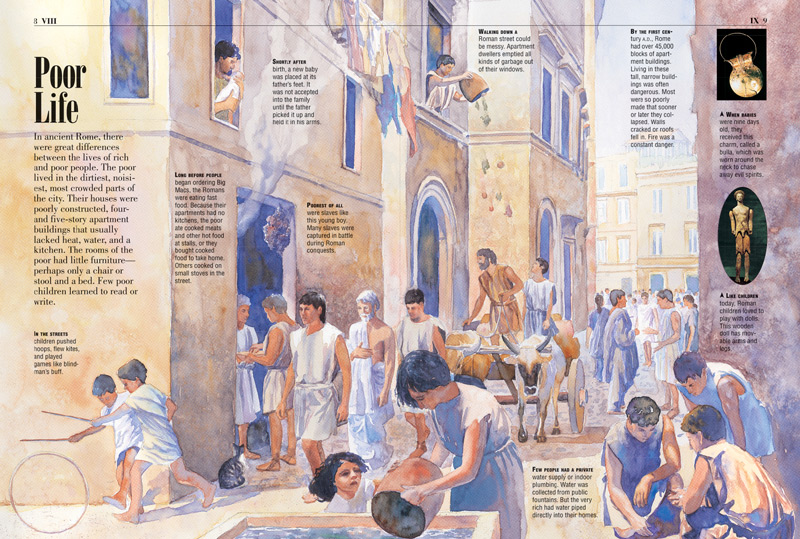
insulaeIn Rome, poor people lived in blocks of flats called insulae. Most were at least five stories high. However they were often badly built, and their walls sometimes cracked and roofs caved in. Most people lived in just one or two rooms.
Were there homeless people in ancient Rome?
Others slept in tombs, which could become homes for the living as well as the dead: They could double up as bathrooms and triple up as brothels. Massive homelessness is also nothing new. Ancient Rome at its height may have had one million inhabitants, 300,000 of whom were desperately poor.
What was daily life like in Rome?
The higher floors, where rent was paid by the day or week, were cramped, often with only one room to a family. A family lived in constant fear of eviction. They had no access to natural light, were hot in the summer and cold in the winter with little or no running water - this even meant a latrina or toilet.
Where did poor people live in Rome?
insulaeIn Rome, poor people lived in blocks of flats called insulae. Most were at least five stories high. However they were often badly built, and their walls sometimes cracked and roofs caved in. Most people lived in just one or two rooms.
Was the average Roman poor?
The average citizen worked hard and lived reasonably comfortably in modest housing. Despite the riches of the Roman Empire, the largest class lived in what can only be described as poverty. Roman children wore pendants called bullas, from the Latin word for "bubble," around their necks.
Did Rome have a welfare system?
The alimenta was a Roman welfare program that existed from around 98 AD to 272 AD. According to most modern historians, including Nerva biographers Nathan Elkins and John Grainger, it was initiated by emperor Nerva and expanded by Trajan. It helped orphans and poor children throughout Italy.
Was the Roman Empire poor?
Poor in wealth but strong in numbers, they were the Roman mob, who relaxed in front of the popular entertainment of the time – chariot races between opposing teams, or gladiators fighting for their life, fame and fortune. Although their lives may have been different, they did have some things in common.