What is a Bessemer converter?
The Bessemer converter was a machine and surrounding process that involved the removal of impurities from pig iron (a type of iron with a high carbon content) and its conversion into steel – a material that had historically been costly and time consuming to manufacture.
What is the Bessemer process?
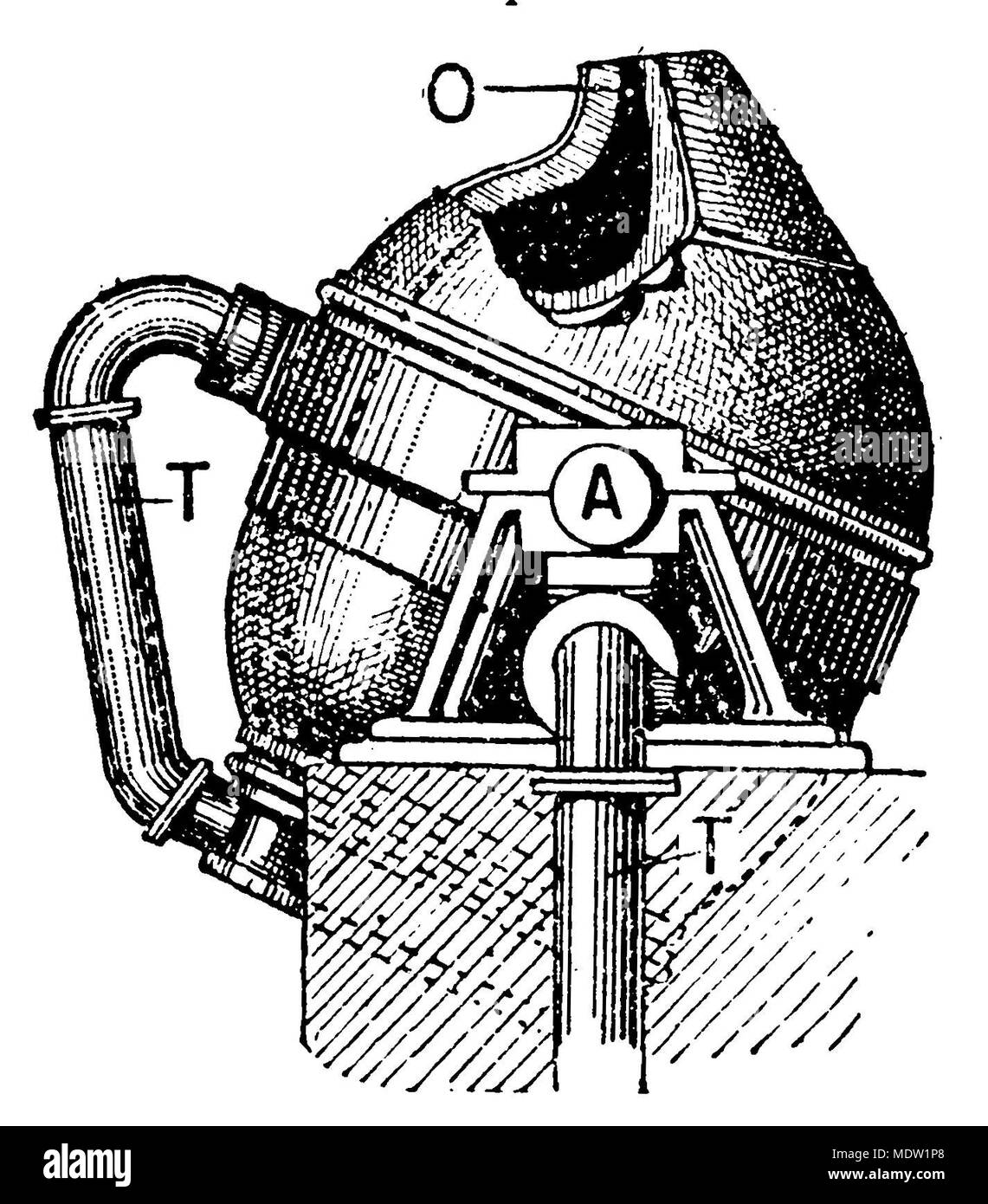
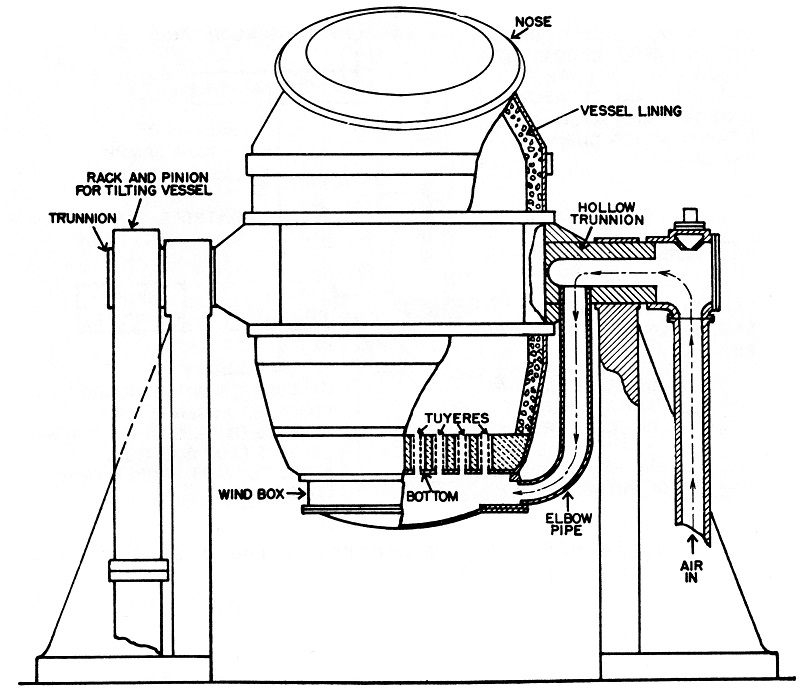
The Bessemer process - the conversion of iron into steel - was invented and patented by Henry Bessemer in 1856. The egg-shaped converter was tilted down to pour molten pig iron in through the top, then swung back to a vertical position and a blast of air was blown through the base of the converter in a dramatic fiery ‘blow'.
Why was Bessemer steel used in the United States?
He built a mill in 1876 using the Bessemer process for steel rails and quadrupled his production. Bessemer steel was used in the United States primarily for railroad rails. During the construction of the Brooklyn Bridge, a major dispute arose over whether crucible steel should be used instead of the cheaper Bessemer steel.
How much did Benjamin Bessemer patent his process for?
Bessemer licensed the patent for his process to four ironmasters, for a total of £27,000, but the licensees failed to produce the quality of steel he had promised—it was "rotten hot and rotten cold", according to his friend, William Clay —and he later bought them back for £32,500.
Where were Bessemer converters in operation?
Bessemer converters in operation at a steel mill, 1886, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, U.S. Library of Congress, Washington, D.C.
How high is a Bessemer converter?
The Bessemer converter is a cylindrical steel pot approximately 6 metres (20 feet) high, originally lined with a siliceous refractory. Air is blown in through openings (tuyeres) near the bottom, creating oxides of silicon and manganese, which become part of the slag, and of carbon, which…
What is Thomas steel?
…in Europe) of manufacturing in Bessemer converters a kind of low-phosphorus steel known as Thomas steel. In the Thomas-Gilchrist process the lining used in the converter is basic rather than acidic, and it captures the acidic phosphorus oxides formed upon blowing air through molten iron made from the high-phosphorus iron…
Who invented the phosphorus lining?
invention by Bessemer. …by the fireclay lining of Bessemer’s converter. It was not until about 1877 that the British metallurgist Sidney Gilchrist Thomas developed a lining that removed phosphorus and made possible the use of phosphoric ores of the Continent.
What is a Bessemer converter?
The Bessemer Converter is one of only three converters left in the world. It was used by the British Steel Corporation in Workington until 1974/5 and produced the last Bessemer Steel made in Britain in 1974. It was brought to the Museum in 1978 as an example of the revolutionary steelmaking process which first took off in Sheffield.
When was the Bessemer process invented?
The Bessemer process - the conversion of iron into steel - was invented and patented by Henry Bessemer in 1856 . The egg-shaped converter was tilted down to pour molten pig iron in through the top, then swung back to a vertical position and a blast of air was blown through the base of the converter in a dramatic fiery ‘blow'.
Who made Bessemer steel?
In 1858 Henry Bessemer moved to Sheffield and licensed his method to two steelmakers, John Brown and George Cammell, who both began to produce Bessemer Steel on an unprecedented scale by 1860.
When was the Bessemer converter invented?
Bessemer Converter (steel) invented by Sir Henry Bessemer in year 1856.
What is the Bessemer process?
Bessemer process is a method for making steel by blasting compressed air through molten iron to burn out excess carbon and impurities. The process and the converter are both named after its inventor, Henry Bessemer, who took out a patent on the process in 1855. The process is carried on in a large ovoid steel container lined with clay or dolomite, ...
What is LD converter?
The LD converter is a refined version of the Bessemer converter where blowing of air is replaced with blowing oxygen. The Bessemer process revolutionized the world.
What was used in the Industrial Revolution?
Prior to its widespread use steel was far too expensive to use in most applications, and wrought iron was used throughout the industrial revolution. After its introduction steel and wrought iron were similarly priced, and all manufacture turned to steel.
When did Bessemer start making steel?
Starting in January 1855 he began working on a way to produce steel in the massive quantities required for artillery and by October he filed his first patent related to the Bessemer process. On 24 August 1856 Bessemer first described the process to a meeting of the British Association in Cheltenham which he titled "The Manufacture ...
Who invented the Bessemer steel mill?
The Dowlais Iron Company was the first licensee of the Bessemer process, constructing the world’s most powerful rolling mill in 1857, and producing its first Bessemer steel in 1865. In 1868, a process named as Siemens-Martin process was developed. It used 'Open-Hearth' Furnace to produce Steel.
Who developed the steel manufacturing technology?
The dominant steel manufacturing technology of today is an extension and refinement of the one developed by Bessemer.
class 5
The Fish Tale Across the Wall Tenths and HundredthsParts and Whole Can you see the Pattern?
class 9
Circles Coordinate Geometry What is Democracy? Why Democracy?Nazism and the Rise of Hitler Socialism in Europe and the Russian Revolution
How many tons of hot metal can a Bessemer converter treat?
A Bessemer converter could treat a "heat" (batch of hot metal) of 5 to 30 tons at a time. They were usually operated in pairs, one being blown while another was being filled or tapped.
What is the Bessemer process?
The Bessemer process was the first inexpensive industrial process for the mass production of steel from molten pig iron before the development of the open hearth furnace. The key principle is removal of impurities from the iron by oxidation with air being blown through the molten iron. The oxidation also raises the temperature of the iron mass and keeps it molten.
How much did Bessemer buy back?
Bessemer licensed the patent for his process to four ironmasters, for a total of £27,000, but the licensees failed to produce the quality of steel he had promised—it was "rotten hot and rotten cold", according to his friend, William Clay —and he later bought them back for £32,500.
Why did the Bessemer process decline?
Year after year, it has not only ceased to make progress, but it has absolutely declined." It has been suggested, both at that time and more recently, that the cause of this was the lack of trained personnel and investment in technology rather than anything intrinsic to the process itself. For example, one of the major causes of the decline of the giant ironmaking company Bolckow Vaughan of Middlesbrough was its failure to upgrade its technology. The basic process, the Thomas-Gilchrist process, remained in use longer, especially in Continental Europe, where iron ores were of high phosphorus content and the open-hearth process was not able to remove all phosphorus; almost all inexpensive construction steel in Germany was produced with this method in the 1950s and 1960s. It was eventually superseded by basic oxygen steelmaking .
What was steel used for?
At the time, steel was used to make only small items like cutlery and tools, but was too expensive for cannons. Starting in January 1855, he began working on a way to produce steel in the massive quantities required for artillery and by October he filed his first patent related to the Bessemer process.
Where was the air blowing process developed?
In the 15th century, the finery process, another process which shares the air-blowing principle with the Bessemer process, was developed in Europe.
Who first described the Bessemer process?
This process was first described by the prolific scholar and polymath government official Shen Kuo (1031–1095) in 1075, when he visited Cizhou.