What was the capital of the Nubian Empire?
Nubia was known as Kush for 2000 years Whether it reflects an indigenous term is not known. The Kushites developed powerful kingdoms. The first was centered at Kerma (2000–1650 BC). The later kingdom had capitals at Napata (800–270 BC) and Meroe (270 BC–370 AD).
When was the 25th dynasty of Egypt?
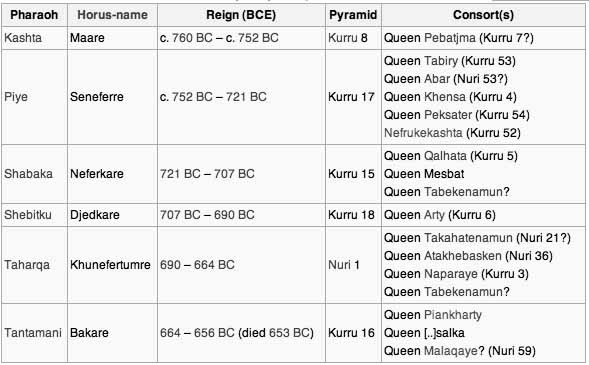
Kushite kings ruled Egypt He was the first of the Nubian line of kings who ruled as Egypt's 25th dynasty (747–656 BC). Piye, the following king, carried the conquest of Egypt to the Nile delta, responding dramatically to a threat from a combination of powerful dynasts to the north.
What is the 25th dynasty called?
The 25th Dynasty refers to the kings of Kush (which included Nubia) who ruled all or part of Egypt from around 746 to 653 BC. This period parallels the Egyptian Third Intermediate Period (1070-653 BC).
What were the two capitals of Kush?
The capital of Cush was thereafter transferred to Meroe, some 150 miles (240 km) southeast on the opposite bank of the Nile. Napata remained the religious capital of Cush, however, and royal burials continued to take place at Nuri until 315 bce.
How long was the 25th dynasty of Egypt?
approximately 91 yearsThe pharaohs of the 25th Dynasty ruled for approximately 91 years in Egypt, from 747 BC to 656 BC.
Who was the most influential pharaoh of the 25th Dynasty?
Pharaoh Taharqa one of the most famous rulers of the 25th Egyptian Dynasty of Napatan Kush reigned from 690 to 664 BCE. He was also ruler and King of Ethiopia.
Was there a black pharaoh?
In the 8th century BCE, he noted, Kushite rulers were crowned as Kings of Egypt, ruling a combined Nubian and Egyptian kingdom as pharaohs of Egypt's 25th Dynasty. Those Kushite kings are commonly referred to as the “Black Pharaohs” in both scholarly and popular publications.
How long did Nubia rule Egypt?
In fact, Nubian kings ruled over Egypt as pharaohs for nearly 100 years. When the Egyptian pharaohs occupied Nubia between 1970 and 1520 B.C., Egyptian culture increasingly influenced Nubia.
Who was the first black king of Egypt?
King PiankhiKing Piankhi is considered the first African Pharaoh to rule Egypt from 730 BC to 656 BC.
Who came first Kush or Egypt?
The Kingdom of Kush lasted for over 1400 years. It was first established around 1070 BCE when it gained its independence from Egypt.
Is Kush black?
Kush, the Egyptian name for ancient Nubia, was the site of a highly advanced, ancient black African civilization that rivaled ancient Egypt in wealth, power and cultural development. The first capital of Kush lay at Kerma just south of the Third Cataract of the Nile.
What does Kush mean in Africa?
The Kingdom of Kush or Kush (/kʊʃ, kʌʃ/) was an ancient African kingdom situated on the confluences of the Blue Nile, White Nile and River Atbara in what is now the Republic of Sudan.
When was the 26th dynasty of Egypt?
Saite Period, or Dynasty 26 (664–525 B.C.) Elevated to power by the invading Assyrians, Dynasty 26 faced a world in which Egypt was no longer concerned with its role in international power politics but with its sheer survival as a nation.
Why is the 25th dynasty significant in the history of both Egypt and Kush?
The 25th dynasty is significant for Egypt and Kush because it was where Kushite culture thrived the most. What advantages did the location of Meroe offer to the Kushites? Some advantages include iron ores, gold, and much more. How were Kushites and Egyptians culture similar?
Who ruled the 24th dynasty?
BakenranefBocchorisApis stela dated to Year 6 of Bakenranef's reign, found in Saqqara.PharaohReign725-720 BC (24th Dynasty (Western Delta))3 more rows
Who took the title of pharaoh and established the 25th Egyptian dynasty?
Shabaka, also called Sabacon, (flourished 8th century bce), Kushite king who conquered Egypt and founded its 25th (Kushite) dynasty (see ancient Egypt: The 24th and 25th dynasties). He ruled Egypt from about 719/718 to 703 bce.
What dynasty was the 25th?
25th Dynasty (Nubians) Nubian or Kushite Pharaohs: other, common name of the pharaohs of the Twenty-fifth dynasty, which originally ruled the Nubian kingdom of Napata. They ruled over Egypt from the late eighth century to 666 BCE. Nubia, Kush, and Napata, are the names of a group of towns near the fourth cataract of the Nile, of which Gebel Barkal, ...
Who is the best known Nubian ruler?
Taharqo venerating the falcon-god Hemen. Taharqo is the best known of all Nubian rulers. He was crowned king in c.690 in Memphis and devoted himself to all kinds of peaceful works, like the restoration of ancient temples in both Egypt and Nubia and building new sanctuaries, like the one at Kawa.
What are the names of the towns near the fourth cataract of the Nile?
Statues of the two last kings of the Kushite Dynasty and five successors from Napata. Nubia, Kush, and Napata, are the names of a group of towns near the fourth cataract of the Nile, of which Gebel Barkal, El-Kurru, Sanam, and Nuri are the most important. The area produced gold and was conquered by the Egyptian pharaohs of the Eighteenth Dynasty ...
Where was the first Nubian king buried?
Taharqo was the first Nubian king to be buried in a pyramid near Nuri. This cemetery would be used for more than three centuries, although the capital was transferred to Meroe.
Who were the governors of Lower Egypt?
In Lower Egypt, Esarhaddon appointed the native princes as governors. One of these was Necho I, a descendant of Tefnakht, who resided in Sais in the western Delta. Meanwhile, Taharqo fought back, reoccupied in Memphis in 669, and forced the princes into submission. Alara.
What was the most important product of the 20th dynasty?
During the Twentieth Dynasty (1188-1069), it became independent, although it still traded with Egypt; the most important product in this age was ivory, which also reached Assyria. The elite that monopolized this trade was probably also able to seize power and become king.
Who succeeded Piye in 716?
Piye was succeeded by Shabaqo, who may have been his brother, in 716 (the date is contested). Unlike his predecessor, he was often in Egypt, probably residing in Thebes, where he revived the office of high priest, which he awarded to his son Horemakhet.
Which dynasty ruled Egypt for almost a century?
Taharqa however could not turn back the invading Assyrian military forces in Egypt, and he ultimately retreated to Napata. The 25th Dynasty ruled for almost a century and provided Egypt with a revival of its intellectual and artistic roots.
What dynasty was the Kushite king in?
25th Dynasty, Ancient Egypt (ca. 746 BC to 653 BC) The 25th Dynasty refers to the kings of Kush (which included Nubia) who ruled all or part of Egypt from around 746 to 653 BC. This period parallels the Egyptian Third Intermediate Period (1070-653 BC). The Kushite kings of this period considered themselves the bodily sons of the god Amun;
How did Shabaqo promote the culture of ancient Egypt?
Continuing the tradition of his brother, Shabaqo promoted the culture of ancient Egypt by commissioning the reproduction of religious texts of earlier periods. Later monarchs include Shebitqo ( ca. 702-690 BC) and Taharqa (690-664 BC); the reign of Taharqa was the most glorious of the dynasty with military victories expanding Nubian rule ...
What period was the Kushite kings in?
This period parallels the Egyptian Third Intermediate Period (1070-653 BC). The Kushite kings of this period considered themselves the bodily sons of the god Amun; they sought to reunite the ancient original domain of Amun, with Egypt and Nubia as the northern and southern halves.
Who was the Kush king in 743 BC?
The Kush king Piankye (or Piankhi), also known as Piye or Piya ruling from 743 to 712 BC, conquered and ruled Upper Egypt and Nubia from Napata and Thebes. One monument associated with his rule depicts ...
Who was the king of Egypt in 1200 BC?
Piye proclaimed himself king of Egypt and “of all lands” on stelae erected in the Temple of Amun of Gebel Barkal. Piye’ s reign emphasized a revival of the culture of the New Kingdom, a period around 1200 BC.
What was the third intermediate period in Egypt?
The Third Intermediate Period of Egyptian history represented a fragmentation of central authority in Egypt. Regional chieftains and elites vied for power. Ultimately, Lower Egypt had a kingship in place, but priests of Amun ruled the larger Upper Egypt from Thebes.
Piye Period
The twenty-fifth dynasty originated in Kush, which is presently in Northern Sudan. The city-state of Napata was the spiritual capital, and it was from there that Piye (spelt Piankhi or Piankhy in older works) invaded and took control of Egypt.
Shabaka and Shebitku Chronology Dispute
Although the Manethonic and classical traditions maintain that it was Shabaka’s invasion which brought Egypt under Kushite rule, the most recent archaeological evidence shows that Shabaka ruled Egypt after Shebitku and not before, as previously thought.
Shebitku Period
According to the newer chronology, Shebitku conquered the entire Nile Valley, including Upper and Lower Egypt, around 712 BC. Shebitku had Bocchoris of the preceding Sais dynasty burned to death for resisting him. After conquering Lower Egypt, Shebitku transferred the capital to Memphis.
Shabaka Period
There is no direct evidence that Shabaqo butchered Bakenranef, and although earlier scholarship generally accepted the tradition, it has recently been treated more sceptically.
Taharqa Period
In 690 BC, Taharqa was crowned in Memphis and ruled Upper and Lower Egypt as Pharaoh from Tanis in the Delta. Taharqa’s reign was a prosperous time in the empire with a vast Nile river flood and abundant crops and wine. Taharqa’s inscriptions indicate that he gave large amounts of gold to the temple of Amun at Kawa.
Tantamani Period
Taharqa’s successor, Tantamani, sailed north from Napata, through Elephantine, and to Thebes with a large army to Thebes, where he was “ritually installed as the king of Egypt”. Tantamani began his reconquest from Thebes and regained control of Egypt as far north as Memphis.
Revenge of Psamtik II
Psamtik II, the third ruler of the following dynasty, the Twenty-Sixth Dynasty, deliberately destroyed monuments belonging to the 25th Dynasty of Kushite kings in Egypt, erasing their names and their emblems of royalty from statues and reliefs in Egypt.
Where is Nubia located?
Located to the south of Egypt in modern Sudan, Nubia was intermittently ruled by Egypt over the millennia, but it was also a land full of fascinating history and culture. The Nubian kingdom of Kush was alternately centered at Napata or Meroe; both sites exhibit Nubian and Egyptian influences on their religious and funerary monuments.
Who was the puppet ruler of Egypt?
The Assyrians appointed puppet ruler named Psamtik I to reign over Egypt, and Tanwetamani ruled concurrently with him. The final Kushite pharaoh was at least nominally acknowledged as pharaoh until 656 B.C. when it became clear Psamtik (who later expelled his Assyrian patrons from Egypt) was in charge.
When did the Assyrians invade Egypt?
In 674 B.C. , the Assyrians attempted to invade Egypt, but Taharqa was able to repel them (this time); the Assyrians were successful in taking Egypt in 671 B.C. But, during this series of back-and-forth conquests and tossing out of the invaders, Taharqa died.
Who allowed Piye to make Egypt his own?
He encouraged his soldiers to pray to Amun on his behalf, according to the stele; Amun listened and allowed Piye to make Egypt his own by the late eighth century B.C. Unusually, once Piye conquered all of Egypt, he went home to Kush, where he died in 716 B.C.
Who was the priest of Amun?
After a brief, if unremarkable, reign by a relative named Shebitqo, Piye's son Taharqa (ruled c. 690 to 664 B.C.) took the throne.
What were the two capitals of the Kush Dynasty?
Two possible capitals were related to Kush dynasty, one is Napata and the other is Meroe. The shift from Napata to Meroe happened around 591 BC due to greater woodlands around Meroe providing fuel for ironwork. Another reason was the shift of trade from the Nile to Red Sea coast near Meroe where Greek traders travelled extensively.
What was the Egyptian empire before the 25th Dynasty?
Before the rule of 25th dynasty, Egyptian empire was fragmented with countless invasions. The Black pharaohs brought the revitalization through religious harmony and loyalty pledges by local rulers.
When did the Kushite rule end?
Kushite rule ended 656 BC with overwhelming Assyrian advance and repeated efforts were made by victors and racist historians to bury the magnificent civilization. The threats of flooding still loom over the remains of 25th dynasty and archaeologists need to discover their glory as soon as possible.
Where are the rulers of Nubia buried?
The region of Lower Nubia saw one of the earliest phases of state formation in the world: rulers of the A-Group culture—who were buried in a cemetery at Qustul, excavated by the Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago in the 1960s—adopted symbols of kingship similar to those of contemporary kings of Egypt of the Naqādah II–III period. With the rise of the 1st dynasty in Egypt ( c. 2950 bce ), the A-Group culture and Nubia’s independence were extinguished. No archaeological remains of the native Lower Nubians of the next 500 years have been discovered.
What is the southern part of Nubia called?
The southern portion, which extended north to the southern end of the second cataract of the Nile was known as Upper Nubia; this was called Kush (Cush) under the 18th-dynasty pharaohs of ancient Egypt and was called Ethiopia by the ancient Greeks. Lower Nubia was the northern part ...
What was the name of the Egyptian outpost in the 6th dynasty?
West of the Nile, quarries for gneiss were opened as mineral exploitation intensified. During the 6th dynasty, the Egyptian governors of Aswān started long-range trading expeditions, sometimes combined with military raids. The most-famous governor among them, Harkhuf, penetrated southward far beyond the second cataract of the Nile to a land he named Yam, whence he obtained a Pygmy whom he brought to Pepi II. Toward the end of Harkhuf’s career, the Nubian chiefs united, imperiling the Aswān expeditions. A new population (called C-Group by archaeologists) inhabited Wawat, while a group known in the present day as the Karmah culture occupied Kush. During the First Intermediate Period many Nubians served as mercenaries in Egypt.
When did the Kushites conquer Egypt?
The Kushite ruler Piankhi ( Piye) completed the Egyptianization and about 730 bce raided Lower Egypt.
Where did the Kushite kingdom survive?
The Kushite capital was then transferred to Meroe, where the Kushite kingdom survived for another 900 years. The Persians are also believed to have tried to invade Nubia (522). Cut off from Egypt, the Egyptian culture of Nubia grew increasingly Africanized until the accession in 45 bce of Queen Amanishakhete.
Where did the Egyptians record the Nile inundation levels during the Middle Kingdom?
Semna was also where the Egyptians recorded the Nile inundation levels during the Middle Kingdom. Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content. Subscribe Now. The kingdom of Kush eventually broke through the frontier as Egyptian control waned in the later 13th dynasty.
When did Sesostris I invade Nubia?
When Sesostris I of the 12th dynasty invaded Nubia about 1915 bce, he named the land south of the second cataract Kush. Sesostris III, about 1826 bce, tried to occupy Sai Island but was compelled to fall back to Semna, where he built a chain of powerful fortresses.
Who ruled Egypt after the Nubians?
After the Nubians were driven out by the Assyrians, Egypt was ruled by a succession of foreign powers including the Persians, Macedonians and Romans. There were only brief periods when Egypt was fully independent.
What was the occupation of Nubia?
Egyptian occupation. Around 3,500 years ago, Egypt grew increasingly powerful and envious of Kerma's resources. They launched a series of military campaigns that destroyed Kerma and led to the occupation of Nubia. The pharaohs of Egypt sent governors to administer Nubia and used a series of towns as hubs to control it.
What did the Nubians do?
Nubian rulers, including the female rulers, were often buried with archery equipment, such as stone rings designed to make it easier to fire off arrows.
How many pyramids were found in Nubia?
Archaeologists have found fields of pyramids. In one recently uncovered cemetery, located at a site now called "Sedeinga," they found no less than 35 pyramids.
How did Egypt's power decline?
Independence and rule of Egypt. Egyptian power declined around 3,000 years ago with its central government falling apart. A number of factors, including attacks by a group that archaeologists sometimes call the "Sea People," played a role in this decline and government fragmentation.
What did ancient rulers call their women?
In ancient times, some of their rulers were woman who were sometimes referred to in ancient texts as "Candaces" or "Kandakes." Archaeologists have found carved images of them revealing that they sometimes liked to be depicted overweight.
When did the first hominids come to Sudan?
The first hominids likely ventured into what is now Sudan and southern Egypt more than 1 million years ago. By 7,000 years ago people in the region were moving from a hunting-and-gathering lifestyle to a lifestyle based around herding domesticated animals, wrote David Edwards, a lecturer in archaeology at the University of Leicester, in his book "The Nubian Past: An Archaeology of Sudan" (Routledge, 2004). Agriculture and permanent settlements began to appear in the time afterward.
What was the 25th Nubian dynasty?
The Establishment Of The 25th Nubian Dynasty In Egypt. The rise of Kush and the establishment of a new Capital at Napata, coupled with the decline of the New Kingdom provided the opportunity for the Nubians to take control of Egypt. In the 8th Century, the Kushite King Piye conquered Egypt and established the 25th Egyptian Dynasty in 727 BC.
Why did Memphis become the capital of the Nubian Pharaohs?
Memphis eventually became the capital of the Nubian Pharaohs as Egyptian Culture adopted influences from Nubia, with the Historical influence of Egyptian Culture on the Nubians continuing and strengthening. The result was a new blend of Egyptian and Nubian Culture that reflected the Historical relationship and contact between the peoples ...
What was the name of the capital of Kush during the Second Intermediate Period?
As Kush gained in confidence, its Kings progressively ruled independently of Egypt and established Napata as the new Capital of Kush.
How did the Nubians consolidate Egyptian power?
The Nubians also consolidated Egyptian power by exercising control over both Upper and Lower Egypt restoring the Ancient Egyptian Culture, Power and Prestige that had been lost with the fall of the 24th Dynasty.
Where did the Black Pharaohs live?
Thereafter the Kushite Kingdom whose Black Pharaohs had ruled Egypt survived in Nubia, and the Capital of the Black Pharaohs was subsequently moved to Moroe which would also become a great City in its own right until it was invaded by the Axumites who dealt a major blow to the Kingdom of Kush circa 330 CE.
What was the capital of the Black Pharaohs?
Memphis eventually became the capital of the Black Pharaohs of Egypt as Egyptian Culture adopted influences from Nubia, with the Historical influence of Egyptian Culture on the Nubians continuing and strengthening.
Where did the Kushite Kingdom survive?
Thereafter the Kushite Kingdom survived in Nubia, and the Capital was subsequently moved to Moroe which would also become a great City in its own right until it was invaded by the Axumites who dealt a major blow to the Kingdom of Kush circa 330 CE.