
What is the De stijl style?
His furniture pieces and houses look like the de Stijl paintings come to life! The movement was founded in the Netherlands and means “The Style” in Dutch. Let’s take a look at the ideas that inspired the movement and the works of the three of its most famous artists: Piet Mondrian, Theo van Doesburg, and Gerrit Rietveld.
Why is De Stijl considered a utopian movement?
It was utopian in nature in the sense that the members of De Stijl believed art to have a transformative power. For them, art was a means towards social and spiritual redemption. De Stijl art was seen as a universal visual language which fit with what its artists wanted for the modern era: a new, spiritualised world order.
Who were the members of the De Stijl movement?
The other primary members and founders were the Dutch painters Piet Mondrian and Bart van der Leck, as well as the Hungarian painter, Vilmos Huszár. The architects J.J.P. Oud, Gerrit Rietveld, and Robert van Hoff were also part of the De Stijl movement.
How did De Stijl influence neopositivism?
The De Stijl movement was also influenced by Neopositivism. The works of De Stijl would influence the Bauhaus style and the international style of architecture as well as clothing and interior design.
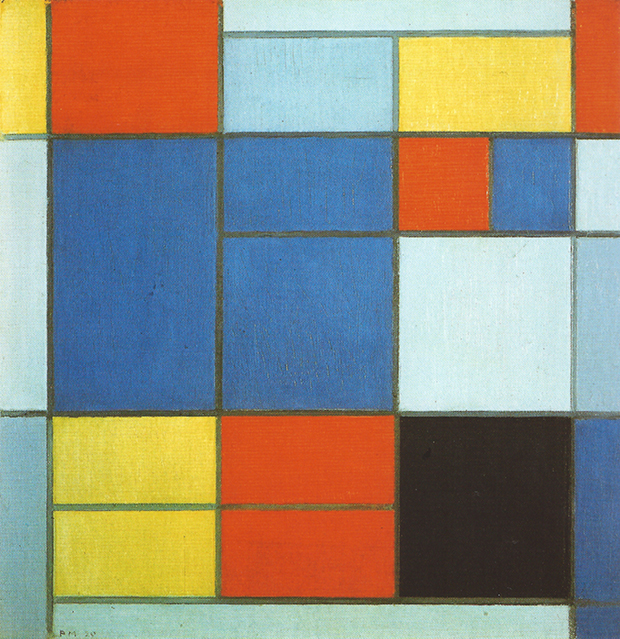
What was the De Stijl design movement?
From 1917 to 1931, De Stijl, also known as neoplasticism, was a famous modern art form that valued abstraction and simplicity. Clean lines, right angles, and primary colors characterized this aesthetic and art movement expressed via architecture and paintings.
What are 2 characteristics of the De Stijl movement?
De Stijl is a Dutch art movement which started in 1917. These De Stijl artists were known for their Neoplasticist style: an abstract use of geometric shapes, specifically rectangles, and primary colors, along with black and white.
How did De Stijl affect society?
The members of De Stijl, people like Piet Mondriaan, Gerrit Rietveld and Bart van der Leck, intended to modernize society with their “new art.” Their approach was to achieve maximum simplicity and abstraction in painting, product design, and architecture.
What influenced the De Stijl movement?
De Stijl was influenced by Cubist painting as well as by the mysticism and the ideas about "ideal" geometric forms (such as the "perfect straight line") in the neoplatonic philosophy of mathematician M. H. J. Schoenmaekers.
What is the goal of De Stijl quizlet?
-formulated in large response to the unprecedented devastation of World War I, with the movement's members seeking a means of expressing a sense of order and harmony in the new society that was to emerge in the wake of the war.
What is the purpose of De Stijl?
The artists of De Stijl worked in a wide range of media across the fine and applied arts. They aimed for an ideal fusion of form and function, therefore not only focusing on painting and sculpture but extending their artistic vision to all other art forms including literature, music, typography and industrial design.
What is the most important examples of De Stijl architecture?
As one of the most prominent examples of the De Stijl movement, the 1925 Rietveld Schroder House represents a radical moment in modern architecture.
How did De Stijl end?
In the end, De Stijl dissolved on its own and died with Theo van Doesburg in 1931.
What are 3 characteristics of expressionism?
The German Expressionists soon developed a style notable for its harshness, boldness, and visual intensity.
Which characteristic did the De Stijl group reject?
In 1917 Piet Mondrian cofounded the De Stijl movement, which rejected visually perceived reality as subject matter and restricted form to the most basic elements. Such works as Composition with Red, Blue, and Yellow (c. 1930) reflect this criteria.
What is the most important examples of De Stijl architecture?
As one of the most prominent examples of the De Stijl movement, the 1925 Rietveld Schroder House represents a radical moment in modern architecture.
What is the purpose of De Stijl?
The artists of De Stijl worked in a wide range of media across the fine and applied arts. They aimed for an ideal fusion of form and function, therefore not only focusing on painting and sculpture but extending their artistic vision to all other art forms including literature, music, typography and industrial design.
What is the De Stijl movement?
According to Theo van Doesburg in the introduction of the magazine De Stijl 1917 no.1, the "De Stijl"-movement was a reaction to the "Modern Baroque" of the Amsterdam School movement ( Dutch expressionist architecture) with the magazine Wendingen (1918–1931).
How did the journal begin?
He first met Piet Mondrian at an exhibition in Stedelijk Museum Amsterdam. Mondrian, who had moved to Paris in 1912 (and there, changed his name from "Mondriaan"), had been visiting the Netherlands when war broke out. He could not return to Paris, and was staying in the artists' community of Laren, where he met Bart van der Leck and regularly saw M. H. J. Schoenmaekers. In 1915, Schoenmaekers published Het nieuwe wereldbeeld ("The New Image of the World"), followed in 1916 by Beginselen der beeldende wiskunde ("Principles of Plastic Mathematics"). These two publications would greatly influence Mondrian and other members of De Stijl.
What is De Stijl?
Originally a publication, De Stijl, which means Style in Dutch, was a magazine in which the artists promoted their ideas on art and abstraction. De Stijl soon became a full-fledged movement which advocated a visual language consisting of precise geometric forms (primarily straight lines, squares and rectangles) and primary colours.
What is the meaning of De Stijl?
De Stijl, meaning ‘Style’ was a modern art movement developed in the Netherlands in the early twentieth century. Encompassing painting, architecture and design, de Stijl was founded by Piet Mondrian and Theo van Doesberg in 1917 based upon strict ideals of vertical and horizontal geometry.
When did the de Stijl movement start?
In 1917 the de Stijl movement formed in the Netherlands around him, with lasting consequences for the architecture, design, and typography of the century.…
What did De Stijl influence?
As a movement, De Stijl influenced painting, decorative arts (including furniture design), typography, and architecture, but it was principally architecture that realized both De Stijl’s stylistic aims and its goal of close collaboration among the arts.
What did De Stijl do for architecture?
As a movement, De Stijl influenced painting, decorative arts (including furniture design), typography, and architecture, but it was principally architecture that realized both De Stijl’s stylistic aims and its goal of close collaboration among the arts. The Worker’s Housing Estate in Hoek van Holland(1924–27), designed by Oud, expresses the same clarity, austerity, and order found in a Mondrian painting. Gerrit Rietveld, another architect associated with De Stijl, also applied its stylistic principles in his work; the Schröder Housein Utrecht (1924), for example, resembles a Mondrian painting in the severe purity of its facade and in its interior plan. Beyond the Netherlands, the De Stijl aestheticfound expression at the Bauhaus in Germany during the 1920s and in the International Style.
Who were the members of the De Stijl group?
De Stijl, (Dutch: “The Style”) group of Dutch artists in Amsterdamin 1917, including the paintersPiet Mondrian, Theo van Doesburg, and Vilmos Huszár, the architect Jacobus Johannes Pieter Oud, and the poet A. Kok; other early associates of De Stijl were Bart van der Leck, Georges Vantongerloo, Jan Wils, and Robert van’t Hoff. Its members, working in an abstract style, were seeking laws of equilibriumand harmony applicable both to art and to life.
Where did the De Stijl aesthetic come from?
Beyond the Netherlands, the De Stijl aesthetic found expression at the Bauhaus in Germany during the 1920s and in the International Style. This article was most recently revised and updated by Laura Etheredge, Associate Editor.
Who is the architect who influenced De Stijl?
Gerrit Rietveld, another architect associated with De Stijl, also applied its stylistic principles in his work; the Schröder House in Utrecht (1924), for example, resembles a Mondrian painting in the severe purity of its facade and in its interior plan.
Who was the most important artist of De Stijl?
De Stijl’s most outstanding painter was Mondrian, whose art was rooted in the mystical ideas of Theosophy.
What is the de Stijl movement?
The de Stijl art movement, also known as Neoplasticism, lasted from 1917 to 1931. Two of the most famous painters who created artworks within this movement are Piet Mondrian and Theo van Doesburg. The de Stijl also functioned as an architectural style which can be seen in works designed by the architect Gerrit Rietveld. His furniture pieces and houses look like the de Stijl paintings come to life! The movement was founded in the Netherlands and means “The Style” in Dutch. Let’s take a look at the ideas that inspired the movement and the works of the three of its most famous artists: Piet Mondrian, Theo van Doesburg, and Gerrit Rietveld.
What was the art movement of De Stijl?
The artist was also spiritual and interested in theosophy. The art of the de Stijl art movement was supposed to represent spiritual and total harmony. The style was also supposed to be universal and present itself in many different fields like architecture, furniture, and product design. Mondrian used simple forms and primary colors but created many fascinating and perplexing pieces.
How many phases of the De Stijl movement?
The de Stijl art movement can be divided into three phases. The first phase is the formative one, centered in Holland from 1916 to 1921. After the first phase, some of the original members of the movement moved on to other things and resigned from the group. The second phase, a more international one, lasted until 1925. This period was marked by the influence of the Proun style developed by the Russian avant-garde artist El Lissitzky. While the third phase lasted until the movement’s end in 1931.
What is the last true de Stijl architectural piece?
The house may become a treasure box, a reliquary, and one can always look at it with new eyes.” The Cafe L’Aubette is the last true de Stijl architectural piece.
What is Mondrian's composition?
Mondrian’s Composition with Red, Blue, and Yellow is a typical work of the de Stijl art movement and it’s widely recognized in the history of modern art. Mondrian’s paintings served as an inspiration to the famous French fashion designer Yves Saint Laurent. In 1965, Saint Laurent designed six dresses in the famous de Stijl colors and shapes. These dresses became one of the most iconic fashion pieces of the sixties.
What were the main influences of the De Stijl movement?
Three colors dominate the movement: red, yellow, and blue. The art movement was also influenced by Cubism and its abandonment of realistic representation of things. Things in paintings no longer had to look like they do in real life.
What were Mondrian's influences?
Some of Mondrian’s influences were the Barbizon School and the Hague School. These influences are visible in the artist’s early works like At Work (On the Land). Artists like Jan Sluyters and Jan Toorop, who painted spots in pure colors in pointillistic manners inspired Mondrian as well. He was also influenced by Impressionist art and Neo-Impressionist works. Mondrian also had his Symbolism phase. In these works, you can see traces of what was yet to come with the de Stijl art movement.
What was the Dutch De Stijl movement?
T he Dutch De Stijl movement developed as a response to the existential heaviness and stress caused by World War I. De Stijl artists pioneered an abstract form of art that was all about geometric designs and solid colors for the sake of finding a deeper and simpler spiritual and “universal” meaning in art and life. These artists expressed themselves through painting, sculpture, architecture, design, and many other modalities. Below, we take a closer look at this avant-garde art (and cultural) movement.
When did the De Stijl movement end?
The De Stijl movement came to an end around the time when van Doesburg died in the early 1930s. Although this may have put a stop to the movement, it was kept alive by what van Doesburg contributed and started within the movement, along with many of the other artists, who all developed in their own way artistically. The De Stijl movement influenced Modern Art, the International Style in architecture, the Bauhaus movement, and many other modern artists like Mark Rothko, Frank Stella, Dan Flavin, and Donald Judd.
What is the purpose of the De Stijl journal?
The journal set the theoretical foundations for the abstracted visual expressions while also giving De Stijl artists a platform to explore and express their theories so that others could be involved and build upon them.
What are the shapes of De Stijl's paintings?
Shapes include horizontal and vertical lines, or straight lines and rectangles. The surface of the composition, or the canvas, also needed to be a rectangular shape. Sometimes Mondrian tilted the canvas at an angle (45 degrees), and these De Stijl paintings are known as his Lozenge series.
What color is the house in De Stijl?
The house appears as a three-dimensional version of a De Stijl painting; we notice the primary colors yellow, blue, and red in the beams near the windows and the larger areas of white, gray, and black that make up the outer walls of the house .
What is the style of Mondrian?
We start seeing the characteristic De Stijl style in Mondrian’s oils, Composition with Color Planes (1917) and Composition with large red plane, bluish gray, yellow, black, and blue (1922). In both paintings, the artist depicts square planes of color in seeming balance and harmonious structure on the canvas.
What is De Stijl's style?
De Stijl became the overall art movement of the time with various other stylistic subsets related to painting and aesthetics within it , such as Neo-Plasticism and Elementarism. In fact, it was a whole new “style”.
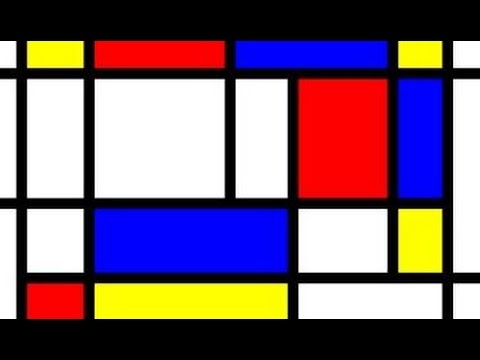
Overview
De Stijl , Dutch for "The Style", also known as Neoplasticism, was a Dutch art movement founded in 1917 in Leiden. De Stijl consisted of artists and architects. In a more narrow sense, the term De Stijl is used to refer to a body of work from 1917 to 1931 founded in the Netherlands. Proponents of De Stijl advocated pure abstraction and universality by a reduction to the essentials of form and colour; …
Principles and influences
Mondrian sets forth the delimitations of Neoplasticism in his essay "Neo-Plasticism in Pictorial Art". He writes, "this new plastic idea will ignore the particulars of appearance, that is to say, natural form and colour. On the contrary, it should find its expression in the abstraction of form and colour, that is to say, in the straight line and the clearly defined primary colour". With these …
History
From the flurry of new art movements that followed the Impressionist revolutionary new perception of painting, Cubism arose in the early 20th century as an important and influential new direction. In the Netherlands, too, there was interest in this "new art".
However, because the Netherlands remained neutral in World War I, Dutch artis…
See also
• Art Concret
• Abstraction-Création
• Concrete art
• Form follows function
• Fourth dimension in art
References and sources
References
Sources
• "De Stijl Architecture". Design Arts. Art and Culture. Archived from the original on 27 March 2006. Retrieved 31 July 2006.
• van Doesburg, Theo (1924). "Towards a plastic architecture". Translation of original published in De Stijl, XII, 6/7. Architecture & CAAD. Archived from the original on 28 N…
References
Sources
• "De Stijl Architecture". Design Arts. Art and Culture. Archived from the original on 27 March 2006. Retrieved 31 July 2006.
• van Doesburg, Theo (1924). "Towards a plastic architecture". Translation of original published in De Stijl, XII, 6/7. Architecture & CAAD. Archived from the original on 28 No…
Further reading
• Blotkamp, Carel, ed. (1982). De beginjaren van De Stijl 1917–1922. Utrecht: Reflex.
• Blotkamp, Carel, ed. (1996). De vervolgjaren van De Stijl 1922–1932. Amsterdam: Veen.
• Jaffé, H. L. C. (1956). De Stijl, 1917–1931, The Dutch Contribution to Modern Art (1st ed.). Amsterdam: J.M. Meulenhoff.
External links
• Many sourced quotes and facts of De Stijl artists in: De Stijl 1917–1931 – The Dutch Contribution to Modern Art, by H.L.C. Jaffé; J.M. Meulenhoff, Amsterdam 1956
• De Stijl, The International Dada Archive, University of Iowa Libraries
• Jakob van Domselaer's Proeven van Stijlkunst, rare recording.
The Key Ideas of de Stijl
Neo-Plasticism
- Piet Mondrian came up with the term “de nieuwe beelding”, which became known internationally as Neo-plasticism. Mondrian published his essay Neo-Plasticism in Pictorial Artin De Stijl, in which he wrote: “As a pure representation of the human mind, art will express itself in an aesthetically purified, that is to say, abstract form. The new plastic idea cannot therefore, take the form of a n…
Disagreements Between Mondrian and Van Doesburg
- Mondrian famously withdrew from De Stijl in 1923, outraged at Van Doesburg’s adoption of diagonal elements in his work. Van Doesburg wanted to add more variety, movement and energy to the movement and had therefore developed Elementarism, with which he attempted to modify the in his view dogmatic nature of Mondrian’s Neo-plasticism by introducing the diagonal. Mond…
Iconic Artworks of de Stijl
- Piet Mondrian’sComposition II in Red, Blue, and Yellow, 1930 This is one of Mondrian’s artworks in his Composition series, and represents the height of Mondrian’s purity and sobriety in his art. Thick black lines cut between colour fields, creating squares and rectangles of only primary colours and non-colours. Theo van Doesburg’s Rhythm of a Russian Dance, 1918 Van Doesburg’…
The Legacy of de Stijl and Its Influence on Other Art Movements
- De Stijl significantly influenced other art movements. For one, several of the members of De Stijl, including Theo van Doesburg, taught at the Bauhaus. Therefore, it had a major influence on Bauhaus architecture and design. Furthermore, the geometric visual language and the idea of form following function made a significant impact on the architectural movement from the ‘20s …
Is de Stijl A Cubist?
- Despite the fact that the style’s origins can be traced back to Cubism, the movement’s origins can also be traced to the magazine De Stijl, which is the foundation of the style. Theo van Doesburg, the group’s organizer from 1917 to 1922, founded the journal De Stijl in Leiden in 1917 as a reaction to a diverse group of artists and architects.
What Kind of Art Is de Stijl?
- What is de Stijl? The Dutch were the first to adopt the De Stijl aesthetic, which translates as “style,” during the early twentieth century. De Stijl’s founding fathers, Piet Mondrian and Theo van Doesberg, developed the principle of vertical and horizontal geometry in 1917 as part of their involvement in art, architecture, and design. The De Stijl movement is one of the most well-know…
What Were The Major Concerns of de Stijl?
- De Stijl was a major concern for many artists in the early 20th century. The group was founded in the Netherlands in 1917 by Piet Mondrian and Theo van Doesburg. The members of De Stijl believed that art should be a universal language that could be understood by everyone. They believed that art should be simplified and that artists should use basic...