Who was the first person to propose the atomic theory?
Thomas Thomson published the first brief account of Dalton’s atomic theory in the third edition of his book, A System of Chemistry. In 1808 Dalton published a fuller account in the first part of A New System of Chemical Philosophy. However, it was not until 1811 that Dalton provided his rationale for his theory of multiple proportions.
What chemist was the first to propose the atomic theory?
atomic theory. , first stated by John Dalton, an English scientist, in 1808. It consists of three parts: All matter is composed of atoms. Atoms of the same element are the same; atoms of different elements are different. Atoms combine in whole-number ratios to form compounds. These concepts form the basis of chemistry.
Who introduced atomic theory?
The main points of Dalton’s atomic theory are:
- Everything is composed of atoms, which are the indivisible building blocks of matter and cannot be destroyed.
- All atoms of an element are identical.
- The atoms of different elements vary in size and mass.
- Compounds are produced through different whole-number combinations of atoms.
What is the most recent atomic theory?
The current model of atomic theory is called the Quantum Mechanical Model, otherwise known as the Electron Cloud Model. This current atomic model evolved from the earlier Rutherford-Bohr model, which compared electrons orbiting an atomic nucleus to planets orbiting the sun. The newest understanding of atomic makeup in the Electron Cloud Model ...

Who Discovered 1st atomic theory?
John DaltonJohn Dalton (1766-1844) is the scientist credited for proposing the atomic theory.
When was the first atomic theory developed?
It was the English chemist, John Dalton, who put the pieces of the puzzle together and developed an atomic theory in 1803. Dalton 's atomic theory contains five basic assumptions: All matter consists of tiny particles called atoms.
What are the 5 atomic theories?
List of Atomic TheoriesAncient Greek Beliefs. ... Dalton's Atomic Theory. ... J.J. ... Rutherford's Hypothesis. ... Bohr's Theory. ... Einstein, Heisenberg and Quantum Mechanics.
What was Aristotle's atomic theory?
2.1 Atomism in Aristotle and Boyle. In Aristotle's time, atomists held that matter was fundamentally constructed out of atoms. These atoms were indivisible and uniform, of various sizes and shapes, and capable only of change in respect of position and motion, but not intrinsic qualities.
What was Dalton's atomic theory?
The first part of his theory states that all matter is made of atoms, which are indivisible. The second part of the theory says all atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties. The third part says compounds are combinations of two or more different types of atoms.
How many atomic theory are there?
1 What are the 4 atomic models? Ans. 1 Dalton's Model of the Atom, J.J Thomson's Model of Atom, Rutherford's Atomic Model, and Neil Bohr's Atomic Theory.
Is Dalton's atomic theory correct?
It does not account for subatomic particles: Dalton's atomic theory stated that atoms were indivisible. However, the discovery of subatomic particles (such as protons, electrons, and neutrons) disproved this postulate.
What are the 3 atomic theories?
Although two centuries old, Dalton's atomic theory remains valid in modern chemical thought. 1) All matter is made of atoms. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible. 3) Compounds are formed by a combination of two or more different kinds of atoms.
When did John Dalton discover the atomic theory?
1808In 1808 John Dalton published his first general account of chemical atomic theory, a cornerstone of modern chemistry. The theory originated in his earlier studies of the properties of atmospheric gases.
When did John Dalton make his discovery?
Modern Atomic Theory (John Dalton) Experiments with gases that first became possible at the turn of the nineteenth century led John Dalton in 1803 to propose a modern theory of the atom based on the following assumptions.
What is the history of atomic theory?
Atomic theory originated as a philosophical concept in ancient India and Greece. The word "atom" comes from the ancient Greek word atomos, which means indivisible. According to atomism, matter consists of discrete particles. However, the theory was one of many explanations for matter and wasn't based on empirical data.
When did Niels Bohr contribute to the atomic theory?
1913In 1913, Niels Bohr proposed a theory for the hydrogen atom, based on quantum theory that some physical quantities only take discrete values. Electrons move around a nucleus, but only in prescribed orbits, and If electrons jump to a lower-energy orbit, the difference is sent out as radiation.
Who came up with the atomic theory?
The ancient atomic theory was proposed in the 5th century bc by the Greek philosophers Leucippus and Democritus and was revived in the 1st century bc by the Roman philosopher and poet Lucretius.
What is the theory of atoms?
Atomic theory, ancient philosophical speculation that all things can be accounted for by innumerable combinations of hard, small, indivisible particles (called atoms) of various sizes but of the same basic material; or the modern scientific theory of matter according to which the chemical elements that combine to form ...
Who created the equation for the quantum dynamics of atomic electrons?
Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger devised a partial differential equation for the quantum dynamics of atomic electrons, including the electrostatic repulsion of all the negatively charged electrons from each other and their attraction to the positively charged nucleus.
Who believed that matter is made of atoms?
The idea that matter is composed of atoms goes back to the Greek philosophers, notably Democritus, and has never since been entirely lost sight of, though there have been periods when alternative views were more generally preferred. Newton’s contemporaries, Robert…
Who was the English chemist and physicist who extended Proust’s work and converted the?
English chemist and physicist John Dalton extended Proust’s work and converted the atomic philosophy of the Greeks into a scientific theory between 1803 and 1808. His book A New System of Chemical Philosophy(Part I, 1808; Part II…
Where did the atom theory come from?
Atomic theory originated as a philosophical concept in ancient India and Greece. The word "atom" comes from the ancient Greek word atomos, which means indivisible. According to atomism, matter consists of discrete particles. However, the theory was one of many explanations for matter and wasn't based on empirical data.
Who came up with the theory of atoms?
Dalton 's Atomic Theory. Vladimir Godnik / Getty Images. It took until the end of the 18th century for science to provide concrete evidence of the existence of atoms. In 1789, Antoine Lavoisier formulated the law of conservation of mass, which states that the mass of the products of a reaction is the same as the mass of the reactants.
What is the atomic theory of quantum mechanics?
Quantum mechanics led to an atomic theory in which atoms consist of smaller particles. The electron can potentially be found anywhere in the atom but is found with the greatest probability in an atomic orbital or energy level. Rather than the circular orbits of Rutherford's model, modern atomic theory describes orbitals that may be spherical, dumbbell-shaped, etc. For atoms with a high number of electrons, relativistic effects come into play, since the particles are moving at a fraction of the speed of light.
How are atoms different from other elements?
Atoms of a given element are identical in many respects and different from atoms of other elements. Atoms combine in fixed proportions with other atoms to form molecules and compounds. The theory has evolved over time, from the philosophy of atomism to modern quantum mechanics. Here's a brief history of atomic theory:
What is the atom theory?
Updated November 19, 2019. Atomic theory is a scientific description of the nature of atoms and matter that combines elements of physics, chemistry, and mathematics. According to modern theory, matter is made of tiny particles called atoms, which are in turn made up of subatomic particles.
What is the atomic theory of orbitals?
Rather than the circular orbits of Rutherford's model, modern atomic theory describes orbitals that may be spherical, dumbbell-shaped, etc. For atoms with a high number of electrons, relativistic effects come into play, since the particles are moving at a fraction of the speed of light.
What is the name of the science that describes the nature of atoms?
Helmenstine holds a Ph.D. in biomedical sciences and is a science writer, educator, and consultant. She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels. Atomic theory is a scientific description of the nature of atoms and matter ...
Who first stated that atoms are fundamental to chemistry?
The concept that atoms play a fundamental role in chemistry is formalized by the modern. atomic theory. , first stated by John Dalton , an English scientist, in 1808. It consists of three parts: All matter is composed of atoms. Atoms of the same element are the same; atoms of different elements are different.
What is the atomic symbol?
atomic symbol. is a one- or two-letter abbreviation of the name of the element. By convention, the first letter of an element’s symbol is always capitalized, while the second letter (if present) is lowercase. Thus, the symbol for hydrogen is H, the symbol for sodium is Na, and the symbol for nickel is Ni.
How many neutrons does uranium have?
Carbon-12 represents an isotope of carbon with 6 protons and 6 neutrons, while uranium-238 is an isotope of uranium that has 146 neutrons. Key Takeaways. Chemistry is based on the modern atomic theory, which states that all matter is composed of atoms. Atoms themselves are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
How many protons and neutrons are in carbon?
The most common carbon atoms have six protons and six neutrons in their nuclei. What are the atomic number and the mass number of these carbon atoms?
What is the structure of an atom?
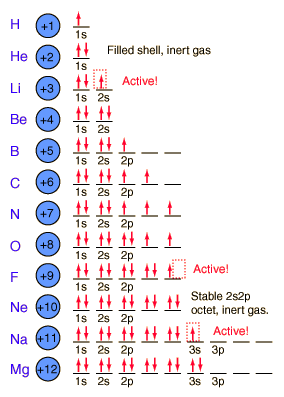
Figure 3.4 “The Structure of the Atom.”. Atoms have protons and neutrons in the centre, making the nucleus, while the electrons orbit the nucleus. The modern atomic theory states that atoms of one element are the same, while atoms of different elements are different.
What is the mass number of neutrons in uranium?
Because the mass number is 235, then the number of neutrons in the nucleus is 235 − 92, or 143.
How many protons does iron have?
All atoms of hydrogen have one and only one proton in the nucleus; all atoms of iron have 26 pro tons in the nucleus. This number of protons is so important to the identity of an atom that it is called the. of the element. Thus, hydrogen has an atomic number of 1, while iron has an atomic number of 26.
Who was the first person to believe in the atom?
John Dalton. Born: September 6, 1766, Died: July 27, 1844. Democritus first suggested the existence of the atom but it took almost two millennia before the atom was placed on a solid foothold as a fundamental chemical object by John Dalton (1766-1844). Although two centuries old, Dalton's atomic theory remains valid in modern chemical thought.
Who created the atom model?
Erwin Schrodinger. A powerful model of the atom was developed by Erwin Schrödinger in 1926. Schrödinger combined the equations for the behavior of waves with the de Broglie equation to generate a mathematical model for the distribution of electrons in an atom.
What is the Bohr model?
The Bohr model shows the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons. A stylized representation of a lithium atom illustrates Niels Bohr's atomic model, that an atom is a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons.
What did Rutherford discover?
He discovered alpha and beta rays, set forth the laws of radioactive decay, and identified alpha particles as helium nuclei.
What did Democritus believe about atoms?
In addition, Democritus believed that the atoms differed in size and shape, were in constant motion in a void, collided with each other; and during these collisions, could rebound or stick together.
What did Aristotle believe?
died on 322 BC. Aristotle did not believe in the atomic theory and he taught so otherwise. He thought that all materials on Earth were not made of atoms, but of the four elements, Earth, Fire, Water, and Air. He believed all substances were made of small amounts of these four elements of matter. Most people followed Aristotle’s idea, causing ...
Who discovered the unit charge of an electron?
Robert Millikan (1868-1953) determined the unit charge of the electron in 1909 with his oil drop experiment at the University of Chicago. Thus allowing for the calculation of the mass of the electron and the positively charged atoms.
What is the origin of the atom?
The hypothesis of Greek scholars has become the basis of analysis by scientists. They have done a lot of discoveries and theories regarding the atom. Moreover, it derives from the Greek word “atomos,” which means indivisible. Since then, the scientific community has discovered ...
Who discovered that matter is made of atoms?
English chemist John Dalton subsequently made on the Greek notion of atoms in 1808. He postulated that matter is made of atoms, which are small indivisible particles. He also proposed that while all atoms of one element are identical, they are totally different from those that make up other elements.
What happens when atoms return to their original orbit?
At the time of returning to their original orbit, they leave this energy as electromagnetic radiation.
Which physicist proposed that the number of protons and electrons are equals in an atom?
He further hypothesized that the number of protons and electrons are equals in an atom. 5. Bohr’s Theory. In 1913, Danish physicist Niels Bohr proposed a planetary model, which states that electrons revolve about the nucleus just as the planets orbit the sun.
Who proposed the nuclear model?
In 1911, Ernest Rutherford (British physicist) proposed a nuclear model on atoms. An atom in which a nucleus exists. In the past, he discovered the part of activity such as the movement of protons and electrons within the central part of the atom. He further hypothesized that the number of protons and electrons are equals in an atom.
Who called the particles in the atoms quarks?
In the 1960s, physicists Murray Gell-Mann and George Zweig called these particles “quarks,” borrowing a word used in a James Joyce novel.
Who said all matter is made up of tiny units called atoms?
“All the matter is made up of tiny units called atoms” this was first proposed by Leucippus and Democritus, in the fifth century B.C., that all matter is made of tiny units called atoms.
Introduction to the Dalton Atomic Model
Dalton’s atomic theory was proposed in 1804 and was the first attempt to describe matter in terms of atoms. He believed that all compounds were made of indivisible particles that combined in set ratios. Although Dalton didn’t get it completely correct, his theory set the foundation for today’s atomic model.
Law of Multiple Proportions
The law of multiple proportions says that atoms or elements can combine to form various chemical compounds. The mass ratios will be whole-number ratios of each other.
Who is John Dalton?
John Dalton is an English chemist who lived from 1766 -1844. He was a teacher at a variety of schools throughout his life. He started his first teaching position assisting his brother when he was twelve years old.
