The Malthusian Theory of Population
Malthusian catastrophe
A Malthusian catastrophe (also known as Malthusian check) is a prediction of a forced return to subsistence-level conditions once population growth has outpaced agricultural production.
Thomas Robert Malthus
Thomas Robert Malthus FRS was an English cleric and scholar, influential in the fields of political economy and demography. In his 1798 book An Essay on the Principle of Population, Malthus observed that an increase in a nation's food production improved the well-being of the popula…
Full Answer
Was Malthus completely wrong?
So yes, in retrospect Thomas Malthus was spectacularly wrong. But what about the future of our children and grand-children? Could Malthus still be proven right in the end? The fact that Malthus’ fears have proven unwarranted so far does not prove that they will remain so for ever. We need to consider the reasons for his mistake and ask if these will continue to apply.
What does the Malthus theorem states?
The Malthus Theorem is a prediction that was created by an English economist named Thomas Malthus. He is known for his world acclaimed book, “An Essay on the Principle of Population”. He believed that population is geometrically doubling as it grows, while the food supply is increasing arithmetically. This eerie thought implies that if the ...
What does the Malthusian model predict?
Malthusian growth model
- P0 = P (0) is the initial population size,
- r = the population growth rate, which Ronald Fisher called the Malthusian parameter of population growth in The Genetical Theory of Natural Selection, and Alfred J. ...
- t = time.
What's the Malthusian premise?
The Malthusian theory is based on the fact that "a population can never increase beyond the food supplies necessary to support it". Malthus believed that human population increased geometrically while food supplies can only grow arithmetically, which means that food supply should be high enough before any geometric population growth takes place.

What is Malthusian theory explain?
Thomas Malthus was an 18th-century British philosopher and economist noted for the Malthusian growth model, an exponential formula used to project population growth. The theory states that food production will not be able to keep up with growth in the human population, resulting in disease, famine, war, and calamity.
What is the importance of Malthusian theory of population?
The Importance of The Malthusian Theory This is to maintain the family lineage and legacy. So the population is bound to grow rapidly if birth control measures are not taken. Malthus's assumptions regarding positive checks are true to a certain extent.
What is Malthusian theory and why is it criticized?
Malthus' objection was that the pressure of increasing population on the food supply would destroy perfection and there would be misery in the world. Malthus was severely criticised for his pessimistic views which led him to travel on the continent of Europe to gather data in support of his thesis.
What did Malthusians believe?
Malthus believed that the population would always increase more rapidly than food supply, which meant that large numbers of people would always suffer from starvation and poverty. His calculations demonstrated that while food supply grew at a linear rate, populations tended to grow at an exponential one.
What are the main principles of Malthusian theory of population?
Malthusianism is the idea that population growth is potentially exponential while the growth of the food supply or other resources is linear, which eventually reduces living standards to the point of triggering a population die off.
What solutions did Malthus suggest to correct overpopulation?
What solutions did Malthus suggest to correct overpopulation? He proposed the gradual abolition of poor laws. Essentially what this resulted in was the promotion of legislation which degenerated the conditions of the poor in England, lowering their population but effectively decreasing poverty.
Is Malthusian theory still valid today?
In modern times, Malthus's population theory has been criticized. Although the theory of Malthus proved somewhat true in contemporary terms, this doctrine is not acceptable at present.
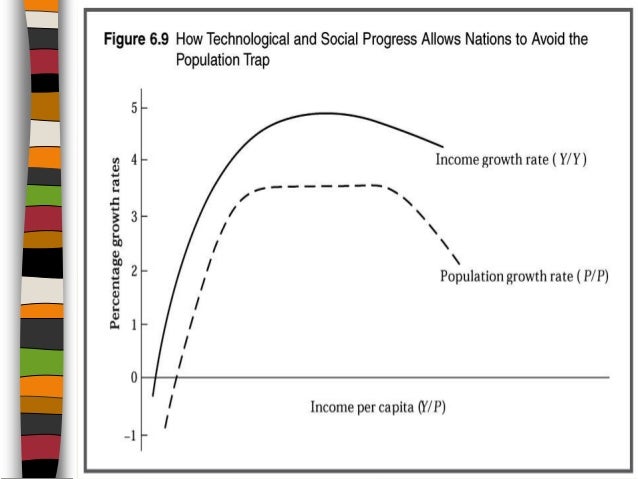
How did we escape the Malthusian trap?
The Industrial Revolution, the first escape from the Malthusian trap, occurred when the efficiency of production at last accelerated, growing fast enough to outpace population growth and allow average incomes to rise.
What did Thomas Malthus think of the poor laws?
Malthus vehemently opposed the poor laws, claiming that these “diminish both the power and the will to save among the common people, and thus to weaken one of the strongest incentives to sobriety and industry…” Malthus went even further, framing aid to the poor as a huge waste of resources “that would otherwise belong ...
Why is it important that the population does not exceed the carrying capacity?
If a population exceeds carrying capacity, the ecosystem may become unsuitable for the species to survive. If the population exceeds the carrying capacity for a long period of time, resources may be completely depleted. Populations may die off if all of the resources are exhausted.
How does Malthusian theory of population relate to food production?
Malthusian Theory: Malthus stated that population increased in a geometric progression (ie., 2, 4, 16, 132…) while food production increased in arithmetic progression (ie., 2, 4, 6, 8…). Thus population grew faster than food production and tended to outstrip it in a short time.
1. Is the Malthusian theory of population applicable today?
Despite the criticism that the theory has faced since it was introduced, the theory does apply to overpopulated countries. One such example is Indi...
2. What is the Malthusian Trap?
The Malthusian Trap, which is also known as the “Malthusian Population Trap” is the idea that increased levels of food production created by modern...
3. State one reason for which The Malthusian Theory of the population is criticized.
The Malthusian Theory of Population was criticized for a variety of reasons. One of the most crucial things for which it was criticized was because...
4. Where can I read more articles like this on other topics of Biology?
The Vedantu website is the ultimate stop for every student to find the free resources that they are looking for. They can easily get a lot of resou...
How does the Malthusian theory explain the growth of the population?
The Malthusian theory explained that the population grows in a geometrical fashion. The population would double in 25 years at this rate. However, the food supply grows in an arithmetic progression. Food supply increases at a slower rate than the population. That is, the food supply will be limited in a few years.
What is the Malthusian theory of population?
The Malthusian Theory of Population is the theory of exponential population and arithmetic food supply growth. The theory was proposed by Thomas Robert Malthus. He believed that a balance between population growth and food supply can be established through preventive and positive checks.
Which theory of population is based on the relationship between population growth and resources?
A.1. Malthus examined the relationship between population growth and resources in one of his works. He then proposed the Malthusian theory of population where he said that the population grows exponentially and the food supply grows arithmetically and that a balance between the two can be established through positive and preventive checks. Q.2.
Why do people die in the food crisis?
As a result, people will not get enough food even for survival. People will die due to lack of food supply. Adversities such as epidemics, wars, starvation, famines and other natural calamities will crop up which are named as positive checks by Malthus.
Which theory explained that the human population grows more rapidly than the food supply until famines, war or disease reduce?
A.2. The Malthusian theory explained that the human population grows more rapidly than the food supply until famines, war or disease reduces the population. He believed that the human population has risen over the past three centuries.
Did Malthus provide the rate of growth?
The estimations for the geometric growth of population and arithmetic growth of population were not provided by Malthus. It was stated that the rate of growth is not consistent with Malthus’ theory.
What is the Malthusian theory?
Based on the principles of the Malthusian theory it can be summarised into the following points: The growth of the human population is much faster than the rate of growth for the means of subsistence such as food, clothing, and other agro-products. As the production rate of agro products is slower it is surpassed by ...
Why Was The Malthusian Theory of Population Criticised?
Since its inception, the Malthusian theory attracted criticism because of its principles. Below is a summary of some of the grounds on which the theory has been criticised.
How many elements are there in Malthusian theory?
There are four major or critical elements of Malthusian theory. These are explained below.
Why did Malthus believe that food production would not be able to keep pace with population growth?
One of the major supporting factors behind Malthus’s theory was that food production would not be able to keep pace with population growth due to the operation of diminishing returns in agriculture.
Which theory applies to countries' growth of population rate is more, food production is less and natural calamities are?
Thus the Malthusian theory applies to countries' growth of population rate is more, food production is less and natural calamities are not kept in check. 2.
Which theory of population is the oldest?
Amongst the well-known theories of population, the Malthusian theory is one of the oldest. Thomas Robert Malthus, an economist explained this theory in his 1798 essay on the ‘Principle of population’. He then modified some parts in the essays next edition in 1803.
Does the theory of overpopulation apply to overpopulated countries?
Despite the criticism that the theory has faced since it was introduced, the theory does apply to overpopulated countries. One such example is India because of the following reasons
Who was the author of Malthusianism?
One proponent of Malthusianism was the novelist Harriet Martineau whose circle of acquaintances included Charles Darwin, and the ideas of Malthus were a significant influence on the inception of Darwin's theory of evolution.
What is the purpose of neo-Malthusianism?
Neo-Malthusianism is the advocacy of human population planning to ensure resources and environmental integrities for current and future human populations as well as for other species . In Britain the term 'Malthusian' can also refer more specifically to arguments made in favour of preventive birth control, hence organizations such as the Malthusian League. Neo-Malthusians differ from Malthus's theories mainly in their support for the use of contraception. Malthus, a devout Christian, believed that "self-control" (i.e., abstinence) was preferable to artificial birth control. He also worried that the effect of contraceptive use would be too powerful in curbing growth, conflicting with the common 18th century perspective (to which Malthus himself adhered) that a steadily growing population remained a necessary factor in the continuing "progress of society", generally. Modern neo-Malthusians are generally more concerned than Malthus with environmental degradation and catastrophic famine than with poverty.
What is the name of the theory that population growth is exponential?
Thomas Robert Malthus, after whom Malthusianism is named. Malthusianism is the idea that population growth is potentially exponential while the growth of the food supply or other resources is linear, which eventually reduces living standards to the point of triggering a population die off. This event, called a Malthusian catastrophe (also known as ...
What is the Malthusian catastrophe?
This event, called a Malthusian catastrophe (also known as a Malthusian trap, population trap, Malthusian check, Malthusian crisis, Malthusian spectre, or Malthusian crunch) occurs when population growth outpaces agricultural production, causing famine or war, resulting in poverty and depopulation.
How did Malthus suggest that technological advances could increase a society's supply of resources, such as food,?
Malthus suggested that while technological advances could increase a society's supply of resources, such as food, and thereby improve the standard of living, the resource abundance would enable population growth, which would eventually bring the per capita supply of resources back to its original level.
Why was Malthus's Principle of Population written?
Principle of Population was specifically written as a rebuttal to thinkers like William Godwin and the Marquis de Condorcet, and Malthus's own father who believed in the perfectibility of humanity. Malthus believed humanity's ability to reproduce too rapidly doomed efforts at perfection and caused various other problems.
When did the Neo-Malthusian revival start?
There was a general "neo-Malthusian" revival in the mid-to-late 1940s, continuing through to the 2010s after the publication of two influential books in 1948 ( Fairfield Osborn 's Our Plundered Planet and William Vogt 's Road to Survival ). During that time the population of the world rose dramatically. Many in environmental movements began to sound the alarm regarding the potential dangers of population growth. In 1968, ecologist Garrett Hardin published an influential essay in Science that drew heavily from Malthusian theory. His essay, "The Tragedy of the Commons", argued that "a finite world can support only a finite population" and that "freedom to breed will bring ruin to all." The Club of Rome published a book entitled The Limits to Growth in 1972. The report and the organisation soon became central to the neo-Malthusian revival. Paul R. Ehrlich has been one of the most prominent neo-Malthusians since the publication of The Population Bomb in 1968. Leading ecological economist Herman Daly has acknowledged the influence of Malthus on his concept of a steady-state economy. : xvi Other prominent Malthusians include the Paddock brothers, authors of Famine 1975! America's Decision: Who Will Survive?
When did the Malthusian theory appear?
The Malthusian Theory appeared during a time when the majority of the population left the countryside for cities, the main case in England at the end of the 18th century.
What is the Malthusian population theory?
Malthusian population theory, or Malthusianism, says that at high population growth the food supply would not be able to maintain its pace, generating poverty on a large scale.
Why did Malthus argue for birth control?
At the time, Malthus argued that there should be birth control for the most humble people, in order to avoid possible “demographic chaos”. What the economist did not foresee was the arrival of more technology that would allow a much higher production of food, avoiding the catastrophe of his theory.
Why did the Neomalthusians believe that underdeveloped countries were growing?
With the return of Malthus’ theory, by the Neomalthusians, there was a perception of population growth in underdeveloped countries due to the greater access to health care for these people.
When was the accelerated population theory developed?
This theory, developed at the end of the 1920s, disagrees with previous theories about the accelerated increase of the population.
What is the Malthusian theory?
What is Malthusian theory? The Malthusian theory of population growth is a sociological theory originally proposed by Thomas Robert Malthus to explain what he saw as the dangers of overpopulation. Malthus first published his influential essay on population growth in 1798. Since that time, Malthusianism has been both praised and criticized for its approach to population theory.
What is the importance of Malthusian theory?
Works like The Population Bomb brought Neo-Malthusian thought into the mainstream and have had real-world consequences. Despite widespread criticism and the failure of the proposed point of crisis to materialize, Malthusianism continues to be a pervasive force in the popular imagination, with many people blaming population growth for environmental issues without reference to things like wealthy countries' disproportionate energy consumption or the dangers of violent checks on the population.
What is the Malthusian theory of population growth?
Resource production can even be accelerated through industrialization, as Malthus was seeing during his own lifetime. This was more or less consistent with other philosophers' descriptions of the world around them. However, Malthus went on to explain that population growth was exponential and that populations would , at some point grow too fast for their society to sustain them.
What did Thomas Malthus believe?
On the contrary, he believed that many things could be done to prevent it by curbing population growth. He proposed two kinds of checks on the population. The first were called positive checks. These were any natural or incidental phenomena that lowered populations. For example, Malthus considered warfare, disease, and famine to be positive checks on the population. He also described preventative checks, which he described as behavioral modifications that could be made to discourage people from reproducing. Most importantly, Malthus encouraged moral restraint, or the delaying of marriage and reproduction until one was financially able to support a family. He also encouraged celibacy.
What did Malthus believe about the point of crisis?
He believed that this was what England and other nations were heading towards if they did not slow their population growth. He also believed that following the point of crisis, society would collapse and people would be forced to revert to a simpler, less industrialized way of life with a smaller population to reduce the strain on resources. This idea was contrary to popular conceptions of the future as a realm of progress and prosperity.
What was Malthus concerned about?
Looking at the rapidly changing world around him, Malthus became concerned about population growth. He noted that population growth was, or was quickly becoming, exponential, while the growth of resources and people's ability to produce them was essentially arithmetic. How industrialization was going to impact the world was a question that many intellectuals at the time were asking, but Malthus's answer to that question has been one of the most enduring.
What is the problem with Malthus's theory?
The other major problem with Malthus's theory in the real world is that when it comes to resource consumption, heavily industrialized and wealthy nations have far higher per capita resource consumption than poorer or less industrialized countries, regardless of population and population growth. Population growth does not seem to be the major factor in resource consumption; wealth does. Additionally, Malthus's calculations of resource increase as arithmetic rather than exponential seem to be lacking in detail and, while they may have been applicable to England in 1798, they do not seem to be applicable on a worldwide scale, especially in a globalized world that functions on international trade.
How did the Malthusian theory of population affect the British economy?
The Malthusian theory of population made a strong and immediate impact on British social policy.
What did Malthus propose?
In his summary Principles of Political Economy Considered with a View to Their Practical Application (1820), Malthus went so far as to propose public works and private luxury investment as possible solutions for economic distress through their ability to increase demand and prosperity. He criticized those who valued thrift as a virtue knowing no limit; to the contrary, he argued that “the principles of saving, pushed to excess, would destroy the motive to production.” To maximize wealth, a nation had to balance “the power to produce and the will to consume.” In fact, Malthus, as an economist concerned with what he called the problem of “gluts” (or, as they would be called today, the problems of economic recession or depression ), can be said to have anticipated the economic discoveries made by the English economist John Maynard Keynes in the 1930s.
What was Malthus's biggest criticism?
Then again, a fundamental criticism of Malthus was his failure to appreciate the ongoing British agricultural revolution, which eventually caused food production to meet or exceed population growth and made prosperity possible for a larger number of people .
What is the argument in the first edition of Malthus's Population?
The argument in the first edition of his work on population is essentially abstract and analytic. After further reading and travels in Europe, Malthus produced a subsequent edition (1803), expanding the long pamphlet of 1798 into a longer book and adding much factual material and illustration to his thesis.
When did Malthus publish his book?
In subsequent editions (published from 1803 to 1826), he expanded his argument, adding more factual material and illustrations. Malthus also published a variety of pamphlets and tracts on economics and the book-length summary Principles of Political Economy (1820).
Where did Thomas Malthus go to college?
Thomas Malthus was educated largely at home until his admission in 1784 to Jesus College, Cambridge, where he studied many subjects and took prizes in Latin and Greek, graduating in 1788. He earned a master of arts degree in 1791, was elected a fellow of Jesus College in 1793, and took holy orders in 1797.
What did Malthus' work help to justify?
Malthus’s work reined in economic optimism, helped to justify a theory of wages based on workers’ minimum cost of subsistence, and discouraged traditional forms of charity.
Which theory opposes the conclusions found by Malthus in his theory of population growth?
Any theory, by definition, that opposes the conclusions found by Malthus in his theory of population growth is an anti-Malthusian theory. The most popular anti-Malthusian theory tends to be the one developed by Ester Boserup.
What did Thomas Malthus say about human population?
Thomas Malthus first suggested in 1798, and then expanded upon his thoughts in 1803, that human populations will grow exponentially when food production grows at an arithmetic rate. According to Malthus, human populations could double if food output was able to keep up with the number of mouths to feed. If there is not enough food ...
What did Malthus believe would happen if men and women got married later?
Malthus believed that if men and women got married later, then families would be smaller and there could even be fewer families . Even though he believed an increase in births to non-family couples would occur, Malthus believed the offset would help to reduce population numbers. Any theory, by definition, that opposes the conclusions found by ...
What Is Boserup’s Theory of Population?
Instead of there being a limited food supply, which would eventually stop human populations from growing, her theory suggests that people have the power of ingenuity so that the supply of food will always be able to outweigh the demand for it.

Overview
Neo-Malthusian theory
Malthusian theory is a recurrent theme in many social science venues. John Maynard Keynes, in Economic Consequences of the Peace, opens his polemic with a Malthusian portrayal of the political economy of Europe as unstable due to Malthusian population pressure on food supplies. Many models of resource depletion and scarcity are Malthusian in character: the rate of energy consumption will outstrip the ability to find and produce new energy sources, and so lead to a cri…
History
In 1798, Thomas Malthus proposed his theory in An Essay on the Principle of Population.
He argued that although human populations tend to increase, the happiness of a nation requires a like increase in food production. "The happiness of a country does not depend, absolutely, upon its poverty, or its riches, upon its youth, or its age, upon its being thinly, or fully inhabited, but upon the rapidity with which it is increasing, upon the degree in which the yearly increase of food approac…
Preventive vs. positive population controls
To manage population growth with respect to food supply, Malthus proposed methods which he described as preventive or positive checks:
• A preventive check according to Malthus is ways that in which nature may alter population changes. Some primary examples are celibacy and chastity but also contraception, which Malthus condemned as morally indefensible along with i…
Evidence in support
Research indicates that technological superiority and higher land productivity had significant positive effects on population density but insignificant effects on the standard of living during the time period 1–1500 AD. In addition, scholars have reported on the lack of a significant trend of wages in various places over the world for very long stretches of time. In Babylonia during the period 1800 to 1600 BC, for example, the daily wage for a common laborer was enough to buy a…
Theory of breakout via technology
Some researchers contend that a British breakout occurred due to technological improvements and structural change away from agricultural production, while coal, capital, and trade played a minor role. Economic historian Gregory Clark, building on the insights of Galor and Moav, has argued, in his book A Farewell to Alms, that a British breakout may have been caused by differences in reprodu…
Criticism
Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels argued that Malthus failed to recognize a crucial difference between humans and other species. In capitalist societies, as Engels put it, scientific and technological "progress is as unlimited and at least as rapid as that of population". Marx argued, even more broadly, that the growth of both a human population in toto and the "relative surplus population" within it, occur…
See also
• Antinatalism
• Cliodynamics
• Conservative Party (UK)
• Demographic trap
• Food Race
Neomalthusian Theory
- With the return of Malthus’ theory, by the Neomalthusians, there was a perception of population growth in underdeveloped countries due to the greater access to health care for these people. The theorists of Neomalthusianismo justified that the offer of greater resources to the population would generate greater expenses to the governments, distribut...
Reformist Population Theory
- The Reformist Theory is approached mainly by defenders of Karl Marx and socialism, being against Neomalthusianism. It is also known as Antimalthusian Theory. For reformers, overpopulation is generated as a result of poverty due to capitalism, and not as a cause of better economic conditions as advocated by the neo-Malthusians. Because of this, the defenders of thi…
Demographic Transition Theory
- This theory, developed at the end of the 1920s, disagrees with previous theories about the accelerated increase of the population. The idea, in this case, relates the movement of people from the countryside to the city, where the population could have access to better conditions, increasing life expectancy. The statement is that, even with the increase in life expectancy (redu…