
Why was this period called the Cold War?
Why was this time period called the Cold War? The term “cold” is used because there was no large-scale fighting directly between the two superpowers, but they each supported major regional conflicts known as proxy wars. The first phase of the Cold War began immediately after the end of the Second World War in 1945.
What was the Cold War and why did it occur?
COLD WAR 1. What is the Cold War? Why did it happen? Who were the enemies?-A conflict that was between the US and the Soviet Union.The nations never directly confronted each other on the battlefield but deadly threats went on for years.-The Cold War began because the USA (capitalists) were afraid the Soviet Union (USSR) government (communist) was going to dominate all countries and they did ...
What was the Cold War, and when did it start?
When did the Cold War Start exact date? The Cold War was the geopolitical, ideological, and economic struggle between two world superpowers, the USA and the USSR, that started in 1947 at the end of the Second World War and lasted until the dissolution of the Soviet Union on December 26, 1991.
What were people scared of during the Cold War?
What were the fears of the Cold War? Central to the Cold War on the American homefront was the fear that communist spies were trying to destroy the country from within.This fear rose to a fever pitch between 1947 and 1957 during what is known as the Red Scare or the Great Fear.
When did the Cold War stand and end?
1991During 1989 and 1990, the Berlin Wall came down, borders opened, and free elections ousted Communist regimes everywhere in eastern Europe. In late 1991 the Soviet Union itself dissolved into its component republics. With stunning speed, the Iron Curtain was lifted and the Cold War came to an end.
What started the Cold War era?
As World War II transformed both the United States and the USSR, turning the nations into formidable world powers, competition between the two increased. Following the defeat of the Axis powers, an ideological and political rivalry between the United States and the USSR gave way to the start of the Cold War.
When did the Cold War begin and why then?
The Cold War began after the surrender of Nazi Germany in 1945, when the uneasy alliance between the United States and Great Britain on the one hand and the Soviet Union on the other started to fall apart.
Why is it called a Cold War?
The term cold war is used because there was no large-scale fighting directly between the two superpowers, but they each supported major regional conflicts known as proxy wars.
What were 5 main causes of the Cold War?
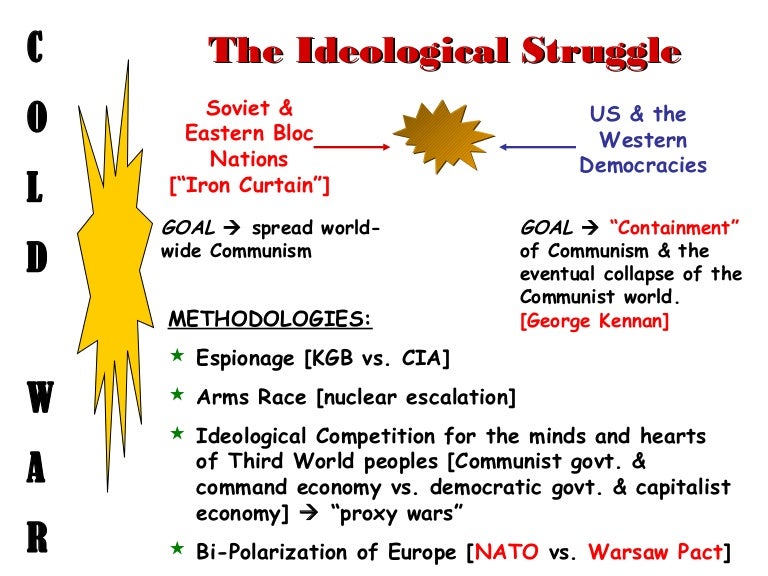
Causes of the Cold WarDifferences in ideologies. The United States and the Soviet Union represented two opposing systems of government. ... Post-war Economic Reconstruction. ... Differences between Truman and Stalin. ... Support of Proxy-wars. ... US Atomic Bomb. ... USSR's expansion west into Eastern Europe. ... The Berlin Crisis.
What was the Cold War Short answer?
The Cold War was the tense fighting between the United States and its allies and the Soviet Union (also called the USSR) and its allies between the end of World War II and the fall of the Soviet Union. It is called the "Cold" War because the Americans and the Soviet Union never actually fought each other directly.
What happened during Cold War?
The Cold War rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union lasted for decades and resulted in anti-communist suspicions and international incidents that led the two superpowers to the brink of nuclear disaster.
Why was the Cold War important?
The Cold War shaped American foreign policy and political ideology, impacted the domestic economy and the presidency, and affected the personal lives of Americans creating a climate of expected conformity and normalcy. By the end of the 1950's, dissent slowly increased reaching a climax by the late 1960's.
What were two primary causes of the Cold War?
Historians have identified several causes that led to the outbreak of the Cold War, including: tensions between the two nations at the end of World War II, the ideological conflict between both the United States and the Soviet Union, the emergence of nuclear weapons, and the fear of communism in the United States.
Who was to blame for the Cold War?
The United States and the Soviet Union both contributed to the rise of the Cold War. They were ideological nation-states with incompatible and mutually exclusive ideologies. The founding purpose of the Soviet Union was global domination, and it actively sought the destruction of the United States and its allies.
What is the Cold War short summary?
The term “Cold War” became a shorthand to describe the ideological struggle between capitalism in the West and communism in the East. American journalist Walter Lippmann popularized the term in a series of articles in 1947 as nations chose sides in the standoff.
When did the Cold War begin?
March 12, 1947 – December 26, 1991Cold War / Period
What was the Cold War?
The Cold War was an ongoing political rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies that developed after World...
How did the Cold War end?
The Cold War came to a close gradually. The unity in the communist bloc was unraveling throughout the 1960s and ’70s as a split occurred between Ch...
Why was the Cuban missile crisis such an important event in the Cold War?
In the late 1950s, both the United States and the Soviet Union were developing intercontinental ballistic missiles. In 1962 the Soviet Union began...
How did the Huac affect Hollywood?
In Hollywood, HUAC forced hundreds of people who worked in the movie industry to renounce left-wing political beliefs and testify against one another. More than 500 people lost their jobs.
What was the effect of postwar Soviet expansionism on Eastern Europe?
Postwar Soviet expansionism in Eastern Europe fueled many Americans’ fears of a Russian plan to control the world. Meanwhile, the USSR came to resent what they perceived as American officials’ bellicose rhetoric, arms buildup and interventionist approach to international relations.
What was the name of the atomic bomb that the Soviets used to build their own atomic bomb?
In response, President Truman announced that the United States would build an even more destructive atomic weapon: the hydrogen bomb, or “superbomb.”. Stalin followed suit.
What was the National Security Council report called in 1950?
In 1950, a National Security Council Report known as NSC–68 had echoed Truman’s recommendation that the country use military force to contain communist expansionism anywhere it seemed to be occurring. To that end, the report called for a four-fold increase in defense spending.
What was the only choice of the United States to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation?
As a result, America’s only choice was the “long-term, patient but firm and vigilant containment of Russian expansive tendencies.” “It must be the policy of the United States,” he declared before Congress in 1947, “to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation…by outside pressures.”.
How did the Cold War affect American life?
The ever-present threat of nuclear annihilation had a great impact on American domestic life as well. People built bomb shelters in their backyards. They practiced attack drills in schools and other public places. The 1950s and 1960s saw an epidemic of popular films that horrified moviegoers with depictions of nuclear devastation and mutant creatures. In these and other ways, the Cold War was a constant presence in Americans’ everyday lives.
When did West Germany join NATO?
In 1955, The United States and other members of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) made West Germany a member of NATO and permitted it to remilitarize. The Soviets responded with the Warsaw Pact, a mutual defense organization between the Soviet Union, Albania, Poland, Romania, Hungary, East Germany, Czechoslovakia and Bulgaria that set up a unified military command under Marshal Ivan S. Konev of the Soviet Union.
What was the New Deal economics?
However, New Deal economics felt the greatest impact of the Cold War. By the 1950's, New Deal reforms were often associated with the left. Its advocates were attacked for promoting programs close to the realm of socialism. The presidencies of Truman and Eisenhower kept away from the Rooseveltian ideals of social and economic reforms.
Why did Murrow and Friendly confront McCarthy?
Murrow and Friendly confronted McCarthy directly, accusing him of assaulting peoples integrity, destroying careers, and using "character assassinations to seize control of the political process.". (3) In the television and film industries, many actors and actresses were blacklisted for their assumed leftist views.
What were the themes of the 1950s?
Literature flourished with themes of individualism versus the system. With poets like Robert Lowell, critics like Dwight McDonald, movies like "Rebel Without a Cause" and "The Wild Ones", rock-and-roll music, and college student unions, "conformity" in the 1950's was all but secured. These critics of "conformity" championed individualism and the younger generation's anxiety over nuclear war. Another area of criticism was the economy. Even though poverty had declined, between one-fifth to one-fourth of the nation could not survive on the income earned. (4) It wasn't until the end of McCarthyism that dissent increased, reaching a crescendo during the Johnson/Nixon administrations of the late 60's and early 70's.
Why did Congress put drastic limits on lend-lease support?
Fearing a return to recession and misuse of funds , Congress placed drastic limits on lend-lease support pointing out that requests for loans after the war would meet deep uncertainty. Ultimately, the Soviets never received any monetary assistance. The final agenda separating the former allies was the atomic bomb.
What was the Cold War rhetoric?
The Cold War's rhetoric and anti-communist propaganda dictated foreign policy. In scaring "the hell out of the American people", Truman unleashed a fervor that would become part of American life and modify existing relationships to the outside world.
How many people could not survive on the income earned?
Even though poverty had declined, between one-fifth to one-fourth of the nation could not survive on the income earned. (4) It wasn't until the end of McCarthyism that dissent increased, reaching a crescendo during the Johnson/Nixon administrations of the late 60's and early 70's.
What were the major issues that separated the two future adversaries?
Some historians believed that five major issues separated the two future adversaries: the impending government of Eastern European countries, Poland, economic reconstruction, Germany's future, and the atomic bomb. Some issues focused on the notion of "sphere of influence".
What was the Helsinki Agreement?
• August 1: Helsinki Agreement/Accord/’Final Act’ signed between US, Canada and 33 European States including Russia: states the ‘inviolability’ of frontiers, gives principles for state peaceful interaction, co-operation in economics and science as well as humanitarian issues.
When was the Cold War fought?
The Cold War was 'fought' in the aftermath of World War Two, from the collapse of the wartime alliance between the Anglo-American led Allies and the USSR to the collapse of the USSR itself, with the most common dates for these identified as 1945 to 1991.
How did people experience the Cold War?
Ordinary people experienced the Cold War in real time, through one of the most intensive propaganda campaigns in human history. Cold War values and nuclear paranoia permeated all aspects of popular culture, including film, television and music.
What was the Berlin Wall?
The Berlin Wall, as it was known, became an enduring symbol of the Cold War. Cold War tensions also spread beyond the borders of Europe. In October 1949, the Chinese Revolution came to a conclusion with the victory of Mao Zedong and the Chinese Communist Party.
What was the Cold War?
The Cold War was a long period of international tension, unfolding in 1945 and lasting until 1991. It was marked by intense rivalry and occasional confrontation between the United States, the Soviet Union and their allies.
What was the capital of Germany divided into?
At the epicentre of this division was post-war Germany, now cleaved into two halves and its capital city Berlin occupied by four different powers. In 1948, Soviet and East German attempts to starve the Western powers out of Berlin were thwarted by the largest airlift in history.
What country became a nuclear power in 1962?
China quickly industrialised and became a nuclear power, while the threat of communism moved Cold War attentions on to Asia. In 1962, the discovery of Soviet missiles on the island nation of Cuba pushed the United States and the Soviet Union to the brink of nuclear war.
What was the Marshall Plan?
The United States responded by implementing the Marshall Plan, a four-year $13 billion aid package to restore European governments and economies.
What was Orwell's dire prediction?
Orwell’s dire prediction began to manifest in 1945. As Europe was liberated from Nazi tyranny, it was occupied by the Soviet Red Army in the east and the Americans and British in the west. At conferences to chart the future of post-war Europe, tensions emerged between Soviet leader Joseph Stalin and his American and British counterparts.

Overview
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. Historians do not fully agree on its starting and ending points, but the period is generally considered to span from the announcement of the Truman Doctrine on 12 March 1947 to the dissolution …
Origins of the term
At the end of World War II, English writer George Orwell used cold war, as a general term, in his essay "You and the Atomic Bomb", published 19 October 1945 in the British newspaper Tribune. Contemplating a world living in the shadow of the threat of nuclear warfare, Orwell looked at James Burnham's predictions of a polarized world, writing:
Looking at the world as a whole, the drift for many decades has been not towards anarchy but to…
Background
While most historians trace the origins of the Cold War to the period immediately following World War II, some argue that it began with the October Revolution in Russia in 1917 when the Bolsheviks took power. In World War I, the British, French and Russian Empires had composed the major Allied Powers from the start, and the US joined them as a self-styled Associated Power in April 19…
Beginning of the Cold War, containment and the Truman Doctrine (1947–1953)
In late February 1946, George F. Kennan's "Long Telegram" from Moscow to Washington helped to articulate the US government's increasingly hard line against the Soviets, which would become the basis for US strategy toward the Soviet Union for the duration of the Cold War. The telegram galvanized a policy debate that would eventually shape the Truman administration's Soviet policy. …
Open hostility and escalation (1948–1962)
The twin policies of the Truman Doctrine and the Marshall Plan led to billions in economic and military aid for Western Europe, Greece, and Turkey. With the US assistance, the Greek military won its civil war. Under the leadership of Alcide De Gasperi the Italian Christian Democrats defeated the powerful Communist–Socialist alliance in the elections of 1948.
From confrontation to détente (1962–1979)
In the course of the 1960s and 1970s, Cold War participants struggled to adjust to a new, more complicated pattern of international relations in which the world was no longer divided into two clearly opposed blocs. From the beginning of the post-war period, Western Europe and Japan rapidly recovered from the destruction of World War II and sustained strong economic growth through th…
New Cold War (1979–1985)
The term new Cold War refers to the period of intensive reawakening of Cold War tensions and conflicts in the late 1970s and early 1980s. Tensions greatly increased between the major powers with both sides becoming more militant. Diggins says, "Reagan went all out to fight the second cold war, by supporting counterinsurgencies in the third world." Cox says, "The intensity of this 'second' …
Final years (1985–1991)
By the time the comparatively youthful Mikhail Gorbachev became General Secretary in 1985, the Soviet economy was stagnant and faced a sharp fall in foreign currency earnings as a result of the downward slide in oil prices in the 1980s. These issues prompted Gorbachev to investigate measures to revive the ailing state.
Overview
The Cold War (1962–1979) refers to the phase within the Cold War that spanned the period between the aftermath of the Cuban Missile Crisis in late October 1962, through the détente period beginning in 1969, to the end of détente in the late 1970s.
The United States maintained its Cold War engagement with the Soviet Union du…
Third World and non-alignment in the 1960s and 1970s
Cold War politics were affected by decolonization in Africa, Asia, and to a limited extent, Latin America as well. The economic needs of emerging Third World states made them vulnerable to foreign influence and pressure. The era was characterized by a proliferation of anti-colonial national liberation movements, backed predominantly by the Soviet Union and the People's Republic of China. The Soviet leadership took a keen interest in the affairs of the fledgling ex-col…
1968 invasion of Czechoslovakia
A period of political liberalization took place in 1968 in Eastern Bloc country Czechoslovakia called the Prague Spring. The event was spurred by several events, including economic reforms that addressed an early 1960s economic downturn. In April, Czechoslovakian leader Alexander Dubček launched an "Action Program" of liberalizations, which included increasing freedom of the press, freedom of speech and freedom of movement, along with an economic emphasis on consumer …
Vietnam War
U.S. President Lyndon B. Johnson landed 42,000 troops in the Dominican Republic in 1965 to prevent the emergence of "another Fidel Castro." More notable in 1965, however, was U.S. intervention in Southeast Asia. In 1965 Johnson stationed 22,000 troops in South Vietnam to prop up the faltering anticommunist regime. The South Vietnamese government had long been allie…
Nixon Doctrine
By the last years of the Nixon administration, it had become clear that it was the Third World that remained the most volatile and dangerous source of world instability. Central to the Nixon-Kissinger policy toward the Third World was the effort to maintain a stable status quo without involving the United States too deeply in local disputes. In 1969 and 1970, in response to the height of the Vie…
Sino–Soviet split
The People's Republic of China's Great Leap Forward and other policies based on agriculture instead of heavy industry challenged the Soviet-style socialism and the signs of the USSR's influence over the socialist countries. As "de-Stalinization" went forward in the Soviet Union, China's revolutionary founder, Mao Zedong, condemned the Soviets for "revisionism." The Chinese also were …
Détente and changing alliance
In the course of the 1960s and 1970s, Cold War participants struggled to adjust to a new, more complicated pattern of international relations in which the world was no longer divided into two clearly opposed blocs. The Soviet Union achieved rough nuclear parity with the United States. From the beginning of the post-war period, Western Europe and Japan rapidly recovered from the destru…
Culture and media
The preoccupation of Cold War themes in popular culture continued during the 1960s and 1970s. One of the better-known films of the period was the 1964 black comedy Dr. Strangelove or: How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Love the Bomb directed by Stanley Kubrick and starring Peter Sellers. In the film, a mad United States general overrides the President's authority and orders a nuclear air strike on the Soviet Union. The film became a hit and today remains a classic.