
What was the significance of the Sherman Antitrust Act?
- The government restricts cartels and Monopolies thus eliminates price fixing and discrimination, favoritism, predatory pricing etc.
- This aims at achieving a free market where artificial influences on demand, supply and prices are removed
- Discipline in businesses leads to a consumer-protected economy whe
Why is the Sherman Antitrust Act important?
Why is the Sherman Antitrust Act important?
- What is the Sherman Antitrust Act, and why is it important? The Sherman Antitrust Act has a long and illustrious history. ...
- Sherman Act. All anti-competitive actions that restrict commerce between states are prohibited under one of the clauses of the Sherman Antitrust Act.
- The Sherman Antitrust Act’s ramifications
- Additional resources
- and
What is Section 1 of the Sherman Antitrust Act?
Section 1 of the Sherman Act addresses only “concerted” activity, as opposed to the unilateral actions of a single firm, which are governed by other antitrust statutes. 15 U.S.C. § 1. An unlawful agreement under Section 1 must be a contract, combination, or a conspiracy involving separate actors. This section of the practice note first ...
What is the definition of Sherman Antitrust Act?
The Sherman Antitrust Act refers to a landmark U.S. law that banned businesses from colluding or merging to form a monopoly. Passed in 1890, the law prevented these groups from dictating,...

What is the purpose of the Sherman Antitrust Act?
The Sherman Antitrust Act was enacted in 1890 to curtail combinations of power that interfere with trade and reduce economic competition. It outlaw...
Who was the Sherman Antitrust Act named for?
The Sherman Antitrust Act was named for U.S. Senator John Sherman, an expert on the regulation of commerce. It is also sometimes called, simply, th...
What are the main provisions of the Sherman Antitrust Act?
The Sherman Antitrust Act comprises two main provisions that prohibit interferences with trade and economic competition and that make illegal the a...
What is the “rule of reason” interpretation of the Sherman Antitrust Act?
The U.S. Supreme Court applied the “rule of reason” interpretation to the Sherman Antitrust Act in 1920 to specify that only “unreasonable” restrai...
What Is the Sherman Antitrust Act?
The Sherman Antitrust Act refers to a landmark U.S. law that banned businesses from colluding or merging to form a monopoly. Passed in 1890, the law prevented these groups from dictating, controlling, and manipulating prices in a particular market .
What Is the Sherman Antitrust Act in Simple Terms?
The Sherman Antitrust Act is a law passed by Congress to promote competition within the economy by prohibiting companies from colluding or merging to form a monopoly.
What Are the Penalties for Violating the Sherman Act?
Beyond that, there are also fines, which can be up to $1 million for an individual and up to $100 million for a corporation. In some cases, heftier fines could also be issued, worth twice the amount the conspirators gained from the illegal acts or twice the money lost by the victims. 1
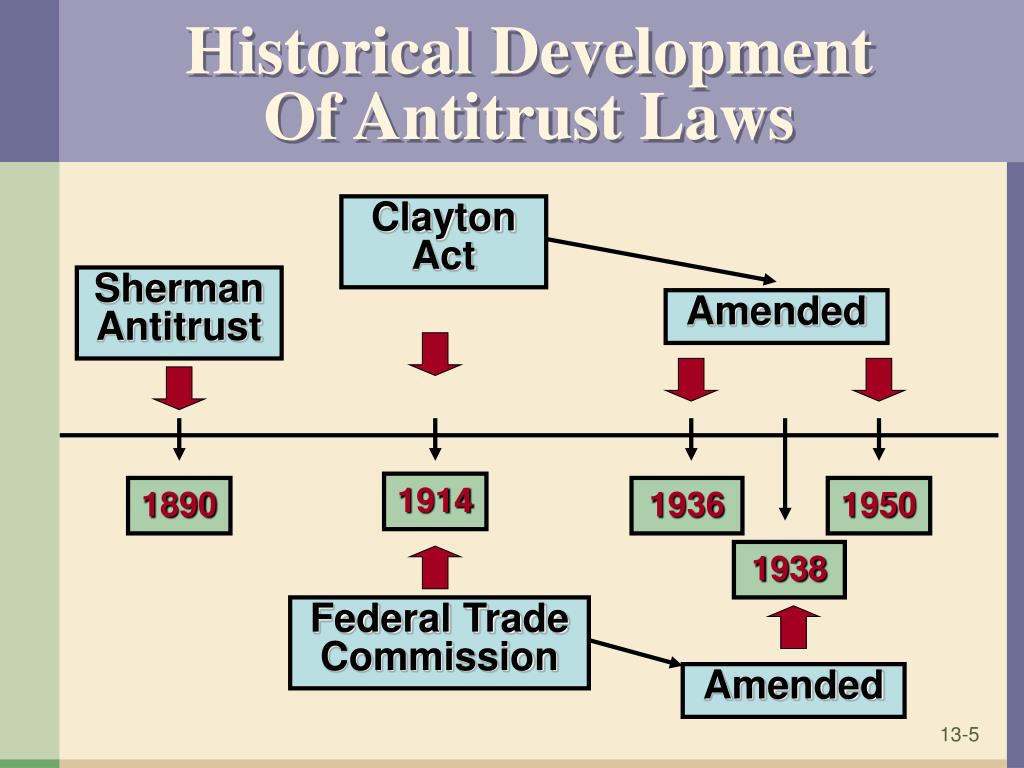
What Is the Difference Between the Sherman Act and the Clayton Act?
The Clayton Act was introduced later, in 1914, to address some of the specific practice s that the Sherman Act did not clearly prohibit or failed to properly clarify. The Sherman Act, the first of its kind, was deemed too vague, allowing some companies to find ways to maneuver around it. 2
How many sections are there in the Sherman Antitrust Act?
The Sherman Antitrust Act is divided into three key sections:
What is the purpose of antitrust laws?
Antitrust laws refer broadly to the group of state and federal laws designed to ensure that businesses are competing fairly. Antitrust laws exist to promote competition among sellers, limit monopolies, and give consumers options.
Why was public hostility growing toward large corporations like Standard Oil and the American Railway Union?
At the time, public hostility was growing toward large corporations like Standard Oil and the American Railway Union, which were seen as unfairly monopolizing certain industries. Consumers felt they were hit with exorbitantly high prices on essential goods, while competitors found themselves shut out because of deliberate attempts by large corporations to keep other enterprises out of the market. 2
Answer
Approved July 2, 1890, The Sherman Anti-Trust Act was the first Federal act that outlawed monopolistic business practices. The Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890 was the first measure passed by the U.S. Congress to prohibit trusts. ... The trusts came to dominate a number of major industries, destroying c
New questions in History
What different genetics practices are used in agriculture, especially related to animals? Think particularly about advances in biotechnology that are …
What was the purpose of the Sherman Antitrust Act?
The purpose of the Sherman Antitrust Act was to destroy monopolies that were using their power to harm society.
What was the Boston Tea Party?
The Boston Tea Party had its origins in hostility among colonists towards the British Crown’s imposition of a monopoly on trade in tea. Article I of the Constitution, which established the legislative branch of the federal government, includes provisions intended to minimize the prospects of government-sponsored or imposed monopolies. It did this by vesting with Congress the authority to regulate interstate commerce. Additionally, Section 9 of Article I includes the following provision clearly intended to prevent the government from choosing favorites among business entities:
Does the Constitution prohibit monopolies?
Now, provisions in the Constitution intended to address the regulation of business are vague. The document does not specifically prohibit the establishment of monopolies. It is well-known, however, that prominent anti-federalists like Thomas Jefferson had argued for more forceful language to be included in the Constitution specifically prohibiting restraints on competition. The final draft of the Constitution reflects compromise between federalists and anti-federalists, although it would require the subsequent passage of a series of amendments, the Bill of Rights, to assuage fears on the part of the anti-federalists regarding the concentration of excessive power in the federal government.
Answer
"The Sherman Antitrust Act was the first measure enacted by the U.S. Congress to prohibit trusts (or monopolies of any type). ... The Sherman Antitrust Act, in contrast, was based on the constitutional power of Congress to regulate interstate commerce." A. To prevent creation of monopolies would be correct.
New questions in History
Put these events in order. Write the letters in the order that the events happened. a. River valley civilizations emerge. b. Farming begins in Southwe …
Who promised a square deal?
Theodore Roosevelt - Republican presidential nominee. Square Deal what. during his presidential campaign, he promised a "square deal" which was equal and fair treatment for all. Contrasted with previous presidents "laissez-faire" idea and called for a large amount of gov business regulation. Square Deal why.
What did TR want?
TR wanted things fair, RR needed by people for agriculture, didn't want just the wealthy to benefit
What Is the Sherman Antitrust Act?
- The Sherman Antitrust Act refers to a landmark U.S. law that banned businesses from colluding …
The act aimed to promote economic fairness and competitiveness while regulating interstate commerce. The Sherman Antitrust Act was the U.S. Congress' first attempt to address the use of trusts as a tool that enables a limited number of individuals to control certain key industries. 1 - The Sherman Antitrust Act is a law the U.S. Congress passed to prohibit trusts, monopolies, and …
Its purpose was to promote economic fairness and competitiveness and to regulate interstate commerce.
Understanding the Sherman Antitrust Act
- Sen. John Sherman from Ohio proposed the Sherman Antitrust Act in 1890. It was the first meas…
At the time, public hostility was growing toward large corporations like Standard Oil and the American Railway Union, which were seen as unfairly monopolizing certain industries. Consumers felt they were hit with exorbitantly high prices on essential goods, while competitors found them…
Special Considerations
- Antitrust laws refer broadly to the group of state and federal laws designed to ensure that busin…
Supporters say these laws are necessary for an open marketplace to exist and thrive. Competition is considered healthy for the economy, giving consumers lower prices, higher-quality products and services, more choice, and greater innovation.
Sections of the Sherman Antitrust Act
- The Sherman Antitrust Act is divided into three key sections:
Section 1: This section defines and bans specific means of anti-competitive conduct. - Section 2: This section addresses end results that are by their nature anti-competitive.
Section 3: This section extends these guidelines and provisions to the District of Columbia and U.S. territories. 3
Historical Context of the Sherman Antitrust Act
- The Sherman Antitrust Act was born against a backdrop of increasing monopolies and abuses o…
The Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) - Congress passed the Interstate Commerce Act in 1887 in response to increasing public indignat…
During the first half of the 20th century, Congress consistently expanded the ICC's power so much that, despite its intended purpose, some believed that the ICC was often guilty of assisting the very companies it was tasked to regulate by favoring mergers that created unfair monopolies. 5
Example of the Sherman Antitrust Act
- On Oct. 20, 2020, the U.S. Department of Justice filed an antitrust lawsuit against Google, allegin…
“As with its historic antitrust actions against AT&T in 1974 and Microsoft in 1998, the Department is again enforcing the Sherman Act to restore the role of competition and open the door to the next wave of innovation—this time in vital digital markets,” Rosen said in a press release. 8
What Is the Sherman Antitrust Act in Simple Terms?
- The Sherman Antitrust Act is a law passed by Congress to promote competition within the economy by prohibiting companies from colluding or merging to form a monopoly.
Why Was the Sherman Antitrust Act Passed?
- The Sherman Antitrust Act was passed to address concerns by consumers who felt they were paying high prices on essential goods and by competing companies who believed they were being shut out of their industries by larger corporations.
What Are the Penalties for Violating the Sherman Act?
- Those found guilty of violating the Sherman Act can face a hefty punishment. It is also a criminal law, and offenders may serve prison sentences of up to 10 years. Beyond that, there are also fines, which can be up to $1 million for an individual and up to $100 million for a corporation. In some cases, heftier fines could also be issued, worth twice the amount the conspirators gained …
Have Any of Today’s Big-Name Companies Been Accused of Violating the Sherman Act?
- Many household names have been hit with antitrust suits based in part on the Sherman Act. Other than Google, in recent years Microsoft and Apple have both faced complaints, with the former accused of seeking to create a monopoly in Internet browser software and the latter of unethically raising the price of its e-books and, in later years, exploiting the market power of its app store. 4
What Is the Difference Between the Sherman Act and the Clayton Act?
- The Clayton Act was introduced later, in 1914, to address some of the specific practices that th…
Essentially, the Clayton Act deals with similar topics, such as anti-competitive mergers, monopolies, and price discrimination but adds more detail and scope to eliminate some of the previous loopholes. Over the years, antitrust laws continue to be amended to reflect the current …