What is the sensitivity of human eye to light?
II.6. Spectral sensitivity of the human eye The sensitivity of the human eye to light of a certain intensity varies strongly over the wavelength range between 380 and 800 nm.
What wavelength of light is the brightest to the human eye?
Under daylight conditions, the average normal sighted human eye is most sensitive at a wavelength of 555 nm, resulting in the fact that green light at this wavelength produces the impression of highest "brightness" when compared to light at other wavelengths.
What is the wavelength of maximum human visual sensitivity?
Wavelength of Maximum Human Visual Sensitivity. "Most of the light in a broad spectrum white is concentrated around the peak of the photopic luminosity function (555nm), and if a wavelength near 555nm is in focus, most of the light will be less than 0.25 diopters out of focus.".
What is the range of wavelengths of visible light?
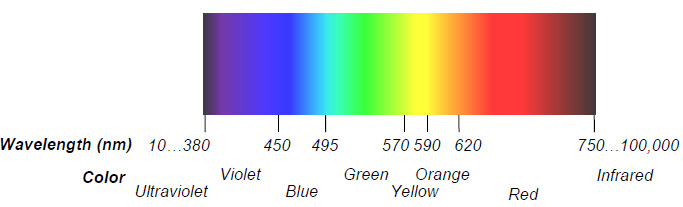
The wavelengths of visible light range from about 400 nm to about 700 nm. Photopic vision is the scientific term for human vision under normal lighting conditions during the day.
How does the human eye detect light?
What are the three types of cones in the human eye?
What are the cells that make up the retina?
What is the peak of S?
NASA - Sun-Earth Day - Technology Through Time
The Sun-Earth Day theme for 2006 is the total solar eclipse on March 29th. This web site is comprised of a series of educational programs and events that occur throughout the year culminating with a celebration on or near the Spring Equinox. :Code 672.0
Timeline of chemical element discoveries - Wikipedia
The discovery of the 118 chemical elements known to exist as of 2022 is presented in chronological order. The elements are listed generally in the order in which each was first defined as the pure element, as the exact date of discovery of most elements cannot be accurately determined.
How does the human eye detect light?
The brain converts these signals into our view of the world. The human eye detects visible light, part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Light is produced by rearranging electrons in atoms and molecules. The wavelengths of visible light range from about 400 nm to about 700 nm.
What are the three types of cones in the human eye?
Each type of cone absorbs light waves of specific frequencies: long wavelengths (L), medium wavelengths (M), and short wavelengths (S). The peak wavelength of L is 564 nm, yellowish-green. The peak of M is 534 nm, bluish-green.
What are the cells that make up the retina?
The retina consists of photoreceptor cells called rods and cones. The cones are at the center of the retina, and the rods are at the outer edge of the retina. There are about seven million cones and a hundred million rods. At the retina, the light is detected and converted to electrical signals.
What is the peak of S?
The peak of S is 420 nm, bluish-violet. Colors are perceived when the cones are stimulated. The color perceived depends on how much each type of cone is stimulated. Yellow is perceived when the yellow-green receptor is stimulated slightly more than the blue-green receptor.
How does the human eye detect light?
The brain converts these signals into our view of the world. The human eye detects visible light, part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Light is produced by rearranging electrons in atoms and molecules. The wavelengths of visible light range from about 400 nm to about 700 nm.
What are the three types of cones in the human eye?
Each type of cone absorbs light waves of specific frequencies: long wavelengths (L), medium wavelengths (M), and short wavelengths (S). The peak wavelength of L is 564 nm, yellowish-green. The peak of M is 534 nm, bluish-green.
What are the cells that make up the retina?
The retina consists of photoreceptor cells called rods and cones. The cones are at the center of the retina, and the rods are at the outer edge of the retina. There are about seven million cones and a hundred million rods. At the retina, the light is detected and converted to electrical signals.
What is the peak of S?
The peak of S is 420 nm, bluish-violet. Colors are perceived when the cones are stimulated. The color perceived depends on how much each type of cone is stimulated. Yellow is perceived when the yellow-green receptor is stimulated slightly more than the blue-green receptor.
