
See more
Do balls drop in the womb?
While in the uterus, a baby's testicles initially develop in his abdominal cavity. Not long before birth, they typically 'drop' (the proper medical term is descend) into his scrotum. In some cases, though, one or both testicles fail to descend before birth.
How can you tell if your baby's balls have dropped?
The main sign: You can't see or feel the testicle in the scrotum. When both are undescended, the scrotum looks flat and smaller than you'd expect it to be. Some boys have what's called a retractile testicle. It may move up into their groin when they are cold or scared but moves back down on its own.
Can undescended testicle correct itself?
ANSWER: In many cases, an undescended testicle moves into the proper position on its own within the first few months after birth. If it hasn't done so by the time a baby is 4 to 6 months old, though, it's unlikely that the problem will correct itself.
At what age is undescended testicle surgery?
Your surgeon will likely recommend doing the surgery when your son is about 6 months old and before he is 12 months old. Early surgical treatment appears to lower the risk of later complications. In some cases, the testicle might be poorly developed, abnormal or dead tissue.
How many phases are there in the testis descent?
The research data on human testis descent timing has been highly variable. Testis descent is thought to have 2 phases:
How long is the epididymis?
In the case of the epididymis, elongation also is associated with extensive coiling, the adult human epididymis about 6 metres in length (mouse 1m, rat 3m). Embryonic growth is regulated by androgens, members of the PCP pathway, and inhibin beta A.
What is the male gonad?
The male gonad is the testis (pl, testes). The initial difference in male and female gonad development are dependent on testis-determining factor (TDF) the protein product of the Y chromosome SRY gene. Recent studies have indicated that additional factors may also be required for full differentiation.
Which cells produce testosterone?
Fetal Leydig Cells produce androstenedione but lack 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (17β-HSD), to but produce testosterone. Fetal Sertoli cells do express 17β-HSD and can therefore convert androstenedione to testosterone.
What cells are replaced by spermatogonia?
Postnatally in humans, at 2 months of age, primordial germ cells (gonocytes) are replaced by adult dark (Ad) and pale (Ap) spermatogonia that make up the spermatogonial stem cell (SSC) population that at puberty will commence differentiation into spermatozoa. Postnatally, fetal Leydig cells are also replaced by adult cells.
Where are fetal leydig cells located?
Fetal Leydig cells are mesenchymal cells developing from coelomic epithelium and undifferentiated perivascular cells in the gonad–mesonephros border region.
Which cells express androgen receptors?
Sertoli cells express the androgen receptor and receptors for follicle stimulating hormone (FSH).
How long does it take for a testicular to descend?from sciencedirect.com
Testicular descent is a two-stage process that starts at about 8 weeks' gestation and is usually complete by the middle of the third trimester. 157 The initial transabdominal stage of testicular descent (8 to 15 weeks) involves contraction and thickening of the gubernacular ligament and degeneration of the craniosuspensory ligament. This stage is mediated by the testis itself after secretion of factors such as insulin-like 3 (INSL3, a relaxin-like factor) and its G protein–coupled receptor, GREAT (also called LGR8 or RXFP2). 158 Other testicular factors are likely to be involved in testicular descent, because most dysgenetic testes are intra-abdominal. The subsequent transinguinal (or inguinoscrotal) phase of testicular descent (25 to 35 weeks) is primarily driven by androgens. The genitofemoral nerve and its neurotransmitter, calcitonin gene–related peptide (CGRP), have also been implicated in this process.
Where is the testis located during the 6th gestational week?from sciencedirect.com
Transabdominal Migration. During the 6th gestational week, the testis is located ventromedial to the mesonephros, relatively close to the inguinal region. As the fetus and abdominal cavity enlarge, the testis remains relatively stationary, whereas the ovary ascends.
What causes undescended testes?from sciencedirect.com
A number of inherited syndromes are associated with undescended testes. The underlying cause is not known, although many are associated with microcephaly, suggesting the possibility of pituitary hormone or gonadotropin deficiency. 27 Some multiple malformation syndromes are also associated with neurogenic and mechanical anomalies, for example, arthrogryposis multiplex congenita. 28 These disorders may cause cryptorchidism either by external compression of the deformed fetus or by intrinsic neurologic anomalies. Experimental inguinoscrotal compression during testicular descent is associated with undescended testes. 29 Intra-abdominal testes are characteristic of the prune-belly syndrome. The cause of the cryptorchidism is controversial, with thoughts ranging from a mesodermal defect to transient prenatal urinary obstruction. 30–33 The absence of a processus vaginalis within the inguinal canal and the position of the testes on the posterior surface of the bladder are consistent with an obstructive cause. Ten percent of infants with posterior urethral valves also have cryptorchidism. 34
What are abnormalities in cryptorchid testes?from sciencedirect.com
Abnormalities of the vas deferens occur commonly in boys with cryptorchid testes. The impalpable intracanalicular testis may have a vas deferens forming a loop, which protrudes distally through the external inguinal ring. Based on examination of the blood supply of such a long-loop vas, Fowler and Stephens proposed transection of the main testicular vessels to the high undescended testis to permit orchidopexy with testis viability maintained by the redundant vas deferens with its collateral blood supply. 53 Although this operation is less commonly performed as an open one-stage procedure because of the high incidence of atrophy, it is now commonly performed laparoscopically as a one- or two-stage procedure. 141
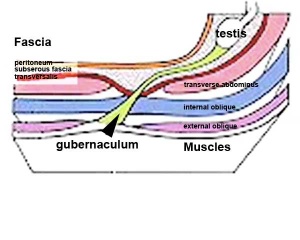
What is the term for the peritoneal pocket that grows along the gubernaculum?from sciencedirect.com
In gestational month 3, an elongated pocket of peritoneum, called the processus vaginalis , grows along and partially encircles the gubernaculum, creating a potential space in the inguinal canal and scrotum. Although the testis is stationary between the 3rd and 7th months of fetal life, the gubernaculum and the processus vaginalis together distend the inguinal canal and scrotum, 5 creating a “path” for testicular descent.
What ligaments are used to study testicular descent?from sciencedirect.com
Because rodent models are frequently used to study testicular descent, it is noteworthy that, in these animals, the testis and ovary are suspended to the abdominal wall by a second ligament, the cranial gonadal suspensory ligament. In male rodents, testosterone stimulates cranial gonadal suspensory ligament regression, thereby permitting caudal testicular mobility. In females, this ligament persists due to the absence of testosterone, and caudal ovarian mobility is thus prevented. 4 The cranial gonadal suspensory ligament is present but becomes vestigial in humans.
What happens to the gubernaculum after birth?from sciencedirect.com
After birth, the gubernaculum and processus vaginalis regress. The gubernaculum is replaced by fibrous tissue that forms the scrotal ligament. The cephalic segment of the processus vaginalis atrophies after testicular descent. An exaggerated resorption of the processus vaginalis with pulling up of the testis may induce a testis that had descended normally to ascend, resulting in cryptorchidism. 77
Why do testes descend outside the body cavity?
The descent of the testes outside the body cavity is necessary because effective spermatogenesis requires temperatures that are 2-3°C lower than body temperature.
Where do the testes come from?
The testes are innervated by autonomic nerves. Parasympathetic, visceral afferent fibers, and sympathetic fibers come from the testicular plexus (T10) found nearby the testicular artery. Therefore, the autonomic nervous plexus travels to the testes within the spermatic cord.
How many seminiferous tubules are there in the testis?
Each of the 200-300 lobules of the testis are filled with one to four highly convoluted seminiferous tubules which each course towards the mediastinum testis. Before entering the mediastinum, they change to a straight course, so in this segment, each convoluted tubule becomes a straight seminiferous tubule. Straight tubules enter the mediastinum, and by interconnecting they form a collecting chamber called rete testis .
How long does it take for a male to read?
Reading time: 16 minutes. The testes (testicles) are male reproductive glands found in a saccular extension of the anterior abdominal wall called the scrotum. They are in ovoid shape, sized four to six centimeters in length. Testes develop retroperitoneally on the posterior abdominal wall and descend to scrotum before birth.
Where is the head of the epididymis?
The head of the epididymis is where the efferent ductules merge. The true epididymis is a coiled tubular continuation of the head. It extends inferiorly as the body of the epididymis and at the inferior pole of the testis enlarges and forms the tail of the epididymis.
What are the two sides of the testis?
Anatomy. On the testis, we can observe two sides (medial and lateral) that are separated by two edges (anterior and posterior). We can also observe superior and inferior poles since it is an ovoid organ. On the posterior edge and superior pole of the testis is a structure called the epididymis.
What is the scrotal sac?
Scrotum is a cutaneous (skin) sac that protects the testes. It consists of two layers: most superficially is the skin, and deeper is the dartos fascia. The dartos fascia contains muscle fibers that contract when it is cold, which results in wrinkling of the scrotal skin and brings the testes closer to the body.
When do testicles drop?
The descent might take a few weeks to complete, but normally by twelve weeks after birth, the testicles are in the scrotum.
Can a boy's testicles be undescended?
Please be aware that boys with undescended testicles have higher than average risks for testicular cancer. They should be extra diligent in checking their testicles for signs of cancer. During childhood, a boy’s testicles can move back up into the abdominal wall, but they descend again.
Where do testicles form?
Testicles form in the abdomen during fetal development. During the last couple of months of normal fetal development, the testicles gradually descend from the abdomen through a tube-like passageway in the groin (inguinal canal) into the scrotum. With an undescended testicle, that process stops or is delayed.
What are the factors that increase the risk of an undescended testicle in a newborn?
Factors that might increase the risk of an undescended testicle in a newborn include: Low birth weight. Premature birth. Family history of undescended testicles or other problems of genital development. Conditions of the fetus that can restrict growth, such as Down syndrome or an abdominal wall defect.
Why is my son's testicle not abnormal?
This is not abnormal and is due to a muscle reflex in the scrotum. An ascending testicle, or acquired undescended testicle, that has "returned" to the groin and can't be easily guided by hand into the scrotum. If you notice any changes in your son's genitals or are concerned about his development, talk to your son's doctor.
