
Main characteristics of the Byzantine Empire. 1 1- The development of orthodox Christianity. In religious matters, the Byzantine Empire was characterized by being a Christian state. In fact, his 2 2- Commercial development. 3 3- Cultural development. 4 4- The artistic legacy. 5 5- The architectural legacy.
Is the Byzantine Empire a Muslim or Christian?
The Byzantine empire was Christian and the Islam empire were Muslim. The Byzantine empire had an absolute monarchy with secular absolute ruler while the Islam empire was Caliphate which was an aristrocratic constitutional Republic. The Byzantin empire was different from the Islam empire due to the fact that it was larger and more advanced.
What are the geographic features of the Byzantine Empire?
describe the location of the Byzantine Empire relative to four different locations or geographic features. The location of the Byzantine empire was surrounded by the Mediterranean Sea. The MiddleEast is East of the Byzantine Empire. The Atlantic Ocean is NorthEast of the Byzantine Empire, and controlled the italian and greek peninsula
How was the Byzantine Empire different than Roman Empire?
What is the difference between Roman Empire and Byzantine Empire? The main difference between the Roman Empire and the Byzantine Empire concerned the official religions they practiced. Whereas the Roman Empire was officially pagan up for most of its existence, the Byzantine Empire was Christian.
What are some interesting facts about the Byzantine Empire?
- They had a mechanical tree in the Imperial Palace in Constantinople on which there were fake birds, and they actually chirped. ...
- They had a ridiculous number of titles. ...
- Leo the Mathematician invented a beacon system that could produce various long-distance messages, so it was a telegraph.
- The “sidewalks” were covered with roofs in Constantinople.
See more
What is the Byzantine Empire known for?
The Byzantine Empire was the longest-lasting medieval power, and its influence continues today, especially in the religion, art, architecture, and law of many Western states, Eastern and Central Europe, and Russia.
What are 3 facts about the Byzantine Empire?
10 Things You May Not Know About the Byzantine EmpireIt wasn't called the Byzantine Empire until after it fell. ... Constantinople was purpose-built to serve as an imperial capital. ... Its most influential emperor came from humble origins. ... A riot by chariot racing hooligans nearly brought the Empire to its knees.More items...•
What were the political characteristics of the Byzantine Empire?
The Byzantine empire was a monarchic theocracy, adopting, following and applying the Hellenistic political systems and philosophies. The king was the incarnation of the law nomos empsychos, and his power was immeasurable and divine in origin.
What makes the Byzantine Empire so special?
One of the most extraordinary aspects of the Byzantine Empire was its longevity: It was the only organized state west of China to survive without interruption from ancient times until the beginning of the modern age.
Why is it called the Byzantine Empire?
How did the Byzantine Empire get its name? Modern historians use the term Byzantine Empire to distinguish the state from the western portion of the Roman Empire. The name refers to Byzantium, an ancient Greek colony and transit point that became the location of the Byzantine Empire's capital city, Constantinople.
What was Byzantine Empire religion?
A central feature of Byzantine culture was Orthodox Christianity.
What were the laws of the Byzantine Empire?
Byzantine law was essentially a continuation of Roman law with increased Orthodox Christian and Hellenistic influence. Most sources define Byzantine law as the Roman legal traditions starting after the reign of Justinian I in the 6th century and ending with the Fall of Constantinople in the 15th century.
What is the difference between Roman and Byzantine?
The Western Roman Empire spoke Latin while the Byzantine Empire was Greek both culturally and linguistically. The Roman Empire covered more land than its eastern counterpart. At its peak, the Roman Empire reached into regions of the British islands, Germania, Spain, parts of North Africa, and much of Asia Minor.
What were the four main social classes in Byzantine society describe each?
In Byzantine society there were four main classes: the upper class or aristocracy, the middle class, the lower class, and slaves. The aristocracy consisted of a small number of wealthy people, who had many privileges and luxuries.
What technology did the Byzantine Empire have?
Flamethrowers, hand grenades, portable sundials, musical organs, hydraulics, water cisterns, ship mills, and the fork were among the many inventions of the Byzantines.
What was life like in the Byzantine Empire?
Daily life in the Byzantine Empire, like almost everywhere else before or since, largely depended on one's birth and the social circumstances of one's parents. There were some opportunities for advancement based on education, the accumulation of wealth, and gaining favour from a more powerful sponsor or mentor.
How did people of the Byzantine Empire view themselves?
How did the people of the Byzantine empire view themselves? They considered themselves Romans as Byzantium was the eastern part of the Roman Empire. It became the foundation of law for most modern European nations.
What are 5 facts about the Ottoman Empire?
Timeline1299 - Osman I founded the Ottoman Empire.1389 - The Ottomans conquer most of Serbia.1453 - Mehmed II captures Constantinople putting an end to the Byzantine Empire.1517 - Ottomans conquer Egypt bringing Egypt into the empire.1520 - Suleiman the Magnificent becomes ruler of the Ottoman Empire.More items...
How long did the Byzantine Empire last?
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, lasted for over 1100 years, from 330-1453.
Did the Byzantine Empire have a flag?
The Byzantine Imperial flag. The Byzantine Imperial flag is yellow with a black crowned double-headed eagle. The double-headed eagle was the symbol of the Palaiologos, the last Greek-speaking "Roman" dynasty to rule from Constantinople.
Why did Byzantine Empire fall?
The dwindling Byzantine Empire came to an end when the Ottomans breached Constantinople's ancient land wall after besieging the city for 55 days. Mehmed surrounded Constantinople from land and sea while employing cannon to maintain a constant barrage of the city's formidable walls.
When did the Byzantine Empire exist?
The Byzantine Empire existed from approximately 395 CE—when the Roman Empire was split—to 1453. It became one of the leading civilizations in the w...
How was the Byzantine Empire different from the Roman Empire?
The Byzantine Empire was the eastern half of the Roman Empire, and it survived over a thousand years after the western half dissolved. A series of...
How did the Byzantine Empire get its name?
Modern historians use the term Byzantine Empire to distinguish the state from the western portion of the Roman Empire. The name refers to Byzantium...
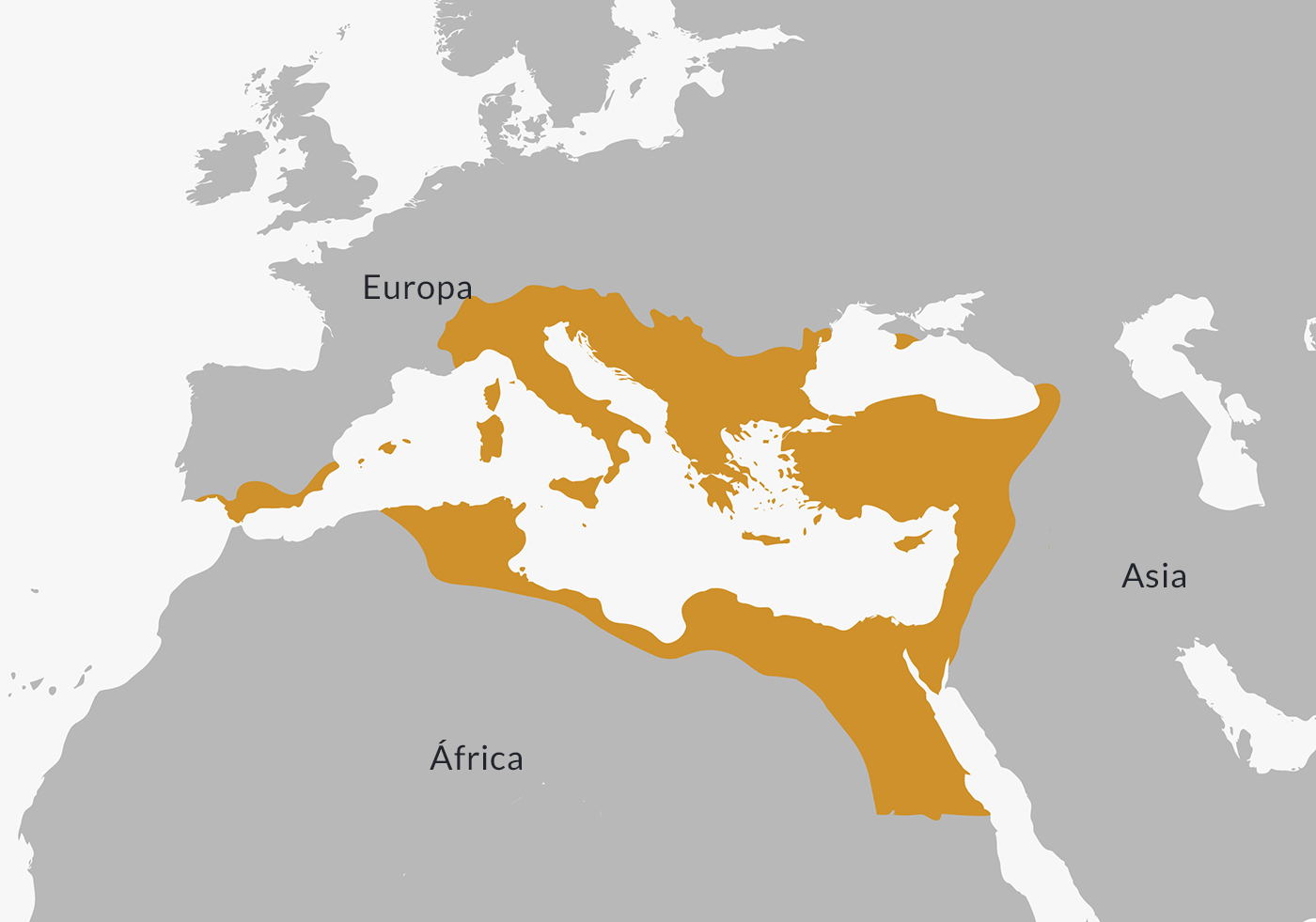
Where was the Byzantine Empire?
At its greatest extent, the Byzantine Empire covered much of the land surrounding the Mediterranean Sea, including what is now Italy, Greece, and T...
Did the Byzantine Empire practice Christianity?
Citizens of the Byzantine Empire strongly identified as Christians, just as they identified as Romans. Emperors, seeking to unite their realm under...
What was the Byzantine Empire?
Byzantine Empire, the eastern half of the Roman Empire, which survived for a thousand years after the western half had crumbled into various feudal kingdoms and which finally fell to Ottoman Turkish onslaughts in 1453. Byzantine Empire Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The very name Byzantine illustrates the misconceptions to which ...
How long did the Byzantine Empire last?
The Byzantine Empire was the eastern half of the Roman Empire, and it survived over a thousand years after the western half dissolved. A series of regional traumas—including pestilence, warfare, social upheaval, and the Arab Muslim assault of the 630s—marked its cultural and institutional transformation from the Eastern Roman Empire to ...
What is the derivation of Byzantium?
The derivation from Byzantium is suggestive in that it emphasizes a central aspect of Byzantine civilization: the degree to which the empire’s administrative and intellectual life found a focus at Constantinople from 330 to 1453, the year of the city’s last and unsuccessful defense under the 11th (or 12th) Constantine.
What did the Emperors hope for?
To strengthen those sinews of imperial civilization, the emperors hoped that a lively and spontaneous trade might develop between the several provinces. At the pinnacle of that world stood the emperor himself, the man of wisdom who would shelter the state from whatever mishaps fortune had darkly hidden.
What were the problems of Byzantium?
The conquests of that age presented new problems of organization and assimilation, and those the emperors had to confront at precisely the time when older questions of economic and social policy pressed for answers in a new and acute form. Satisfactory solutions were never found. Bitter ethnic and religious hostility marked the history of the empire’s later centuries, weakening Byzantium in the face of new enemies descending upon it from east and west. The empire finally collapsed when its administrative structures could no longer support the burden of leadership thrust upon it by military conquests.
Why is the Byzantine Empire called the Byzantine Empire?
Modern historians use the term Byzantine Empire to distinguish the state from the western portion of the Roman Empire. The name refers to Byzantium, an ancient Greek colony and transit point that became the location of the Byzantine Empire’s capital city, Constantinople. Inhabitants of the Byzantine Empire would have self-identified as Romaioi, or Romans.
What is the only surviving piece of a giant statue that was made about 300 CE?
Constantine I. Marble head of Constantine I , the only surviving piece of a giant statue that was made about 300 ce. Photos.com/Thinkstock. The fortunes of the empire were thus intimately entwined with those of peoples whose achievements and failures constitute the medieval history of both Europe and Asia.
Population of the Byzantine Empire
The population of the Empire was varied, reaching 34,000,000 inhabitants at its height , with an average density of 13.6 inhabitants per square kilometer. It is estimated, however, that in the following centuries the population decreased (due to wars, plagues and the loss of territory) to 18,000,000 (11th century) and 3,000,000 (13th century).
Name of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was called the Greek Empire by the other nations.
Identity of the Byzantine Empire
The citizens of the Byzantine Empire always felt much more Greek , and in fact adopted the Hellenic tradition and the Greek language, without this going against their feeling Roman.
Dark Age
A series of theological transformations would create the Orthodox Christian Church.
Macedonian revival
This period was followed by a major revival of the Empire , ruled by a dynasty of Macedonian kings and characterized by growing discrepancies between Eastern and Western Christianity.
The decline of the Byzantine Empire
During the Crusades, the Crusader Siege of Constantinople in 1204 occurred.
End of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire ceased to exist in the fifteenth century , mainly under siege by the Turkish troops of Osman I. The aid of the Western powers was conditional on the reunification of the Catholic and Orthodox churches, a condition that the Eastern ones did not accept. So many watched impassively as the Ottomans marched on Constantinople.
What Were the Main Characteristics of Byzantine Architecture?
Byzantine Architecture featured the heavy use of large domes. This style was predominantly used in the construction of Constantinople. However, it soon spread to the whole of the Christian East. It even spread as far as some parts of Russia as well.
What was the Byzantine Empire?
The Byzantine Empire was the continuation of the Roman Empire in the middle ages. With Constantinople as its capital, it was so powerful that it lasted until the fall of the Roman Empire in the 5th century, and was in power till it was defeated by the Ottomans. During this entire period, Byzantine architecture had an era of prominence and demand. There were several important aspects about the Byzantine Architecture which is why it is still considered quite significant.
Why were windows made in the Byzantine style?
Arched windows are an easily identifiable feature of Byzantine architecture. Windows were made arched to complement the style of the domed infrastructure. Clerestory windows, or windows created at the top of the walls, just below the roof, became very popular. These were perfect, because they let a lot of light in, and provided ventilation. These windows lit up the previously dark buildings.
Why is mosaic important in Byzantine architecture?
Mosaic was famous in byzantine architecture, for more than one reason. For one, mosaics were used to decorate plain walls. However, they were also used to create depictions of byzantine history, and even snippets of the bible. Examples of such decorative mosaics are found in Hagia Sophia, and other such buildings, byzantine buildings all around the world. There is a depiction of Justinian I, in the Basilica of San Vitale, Ravenna, Italy. Other such mosaics are the mosaics of Santa Costanza and Santa Pudenziana.
Why do churches have domed roofs?
This domed roof is a major characteristic of churches today. This is because the majority of Byzantine buildings were ecclesiastical- which means church-related.
What was the Byzantine architecture made of?
Byzantine architecture was made from concrete and bricks. This was first introduced by the Romans, and the Byzantines stuck to it throughout their reign. First, a skeleton is created, from bricks and cement. This was given time to settle. Once the skeleton was strong enough, marble slabs were added on top.
What were columns used for in Byzantine architecture?
Another important part of Byzantine Architecture was the use of columns. Columns were used as means to support the weight of the large, heavy roofs. They were the perfect replacement for walls. While walls would have broken the building into small rooms, columns supported the roof without breaking the open space.
What was the Byzantine architecture?
The earliest Byzantine architecture, though determined by the longitudinal basilica church plan developed in Italy, favoured the extensive use of large domes and vaults. Circular domes, however, were not structurally or visually suited to a longitudinal arrangement of the walls that supported them; thus, by the 10th century, a radial plan, consisting of four equal vaulted arms proceeding from a dome over their crossing, had been adopted in most areas. This central, radial plan was well suited to the hierarchical view of the universe emphasized by the Eastern church. This view was made explicit in the iconographic scheme of church art, set forth in the frescoes, or, more often, mosaics, that covered the interiors of domes, walls, and vaults of churches in a complete fusion of architectural and pictorial expression. At the top of the central dome was the figure of Christ Pantocrator (ruler of the universe). Below him, usually around the base of the dome, were angels and archangels and, on the walls, figures of the saints. The Virgin Mary was often pictured high in a half-dome covering one of the four radial arms. The lowest realm was that of the congregation. The whole church thus formed a microcosm of the universe. The iconographic scheme also reflected liturgy: narrative scenes from the lives of Christ and the Virgin, instead of being placed in chronological order along the walls, as in Western churches, were chosen for their significance as occasions for feast days and ranged around the church according to their theological significance.
What is Byzantine art?
Byzantine art is almost entirely concerned with religious expression and, more specifically, with the impersonal translation of carefully controlled church theology into artistic terms. Its forms of architecture and painting grew out of these concerns and remained uniform and anonymous, perfected within a rigid tradition rather than varied ...
What was the most common use of sculpture in the Byzantine Empire?
Little sculpture was produced in the Byzantine Empire. The most frequent use of sculpture was in small relief carvings in ivory, used for book covers, reliquary boxes, and similar objects. Other miniature arts, embroidery, goldwork, and enamel work, flourished in the sophisticated and wealthy society of Constantinople.
How did Byzantine art spread?
Byzantine forms were spread by trade and conquest to Italy and Sicily, where they persisted in modified form through the 12th century and became formative influences on Italian Renaissance art.
Which countries were the first teachers of Constantinople?
Syria, Egypt, and Anatolia were first the teachers and then the rivals of Constantinople (Istanbul). The fusion of antique and Eastern elements resulted in the Byzantine style, the great period of which dates from the 9th to the end of the 12th century.…

Origin of The Byzantine Empire
Territories of The Byzantine Empire
Population of The Byzantine Empire
Name of The Byzantine Empire
Identity of The Byzantine Empire
- The citizens of the Byzantine Empire alwaysfelt much more Greek , and in fact adopted the Hellenic tradition and the Greek language, without this going against their feeling Roman. By the 7th century, in fact, a series of reforms in this sense had distinguished it quite a bit from the Western Roman Empire: theclassic Latin title “ augustus ” was re...
Justinian’s Reign
Dark Age
Macedonian Revival
The Decline of The Byzantine Empire
End of The Byzantine Empire
What Were The Main Characteristics of Byzantine Architecture?
- The Large Dome
Byzantine Architecture featured the heavy use of large domes. This style was predominantly used in the construction of Constantinople. However, it soon spread to the whole of the Christian East. It even spread as far as some parts of Russia as well. The dome was meant to create a very larg… - Small Numerous Domes
Another very distinct feature of Byzantine buildings was smaller domes built around a huge central dome. The thing requiring the most attention is the fact that Byzantine domes were undisguised by any timber roof which was usually how it was done. In this case, the domes wer…
How to Recognize Byzantine Churches?
Famous Example of Byzantine Architecture