
The Paleozoic
Paleozoic
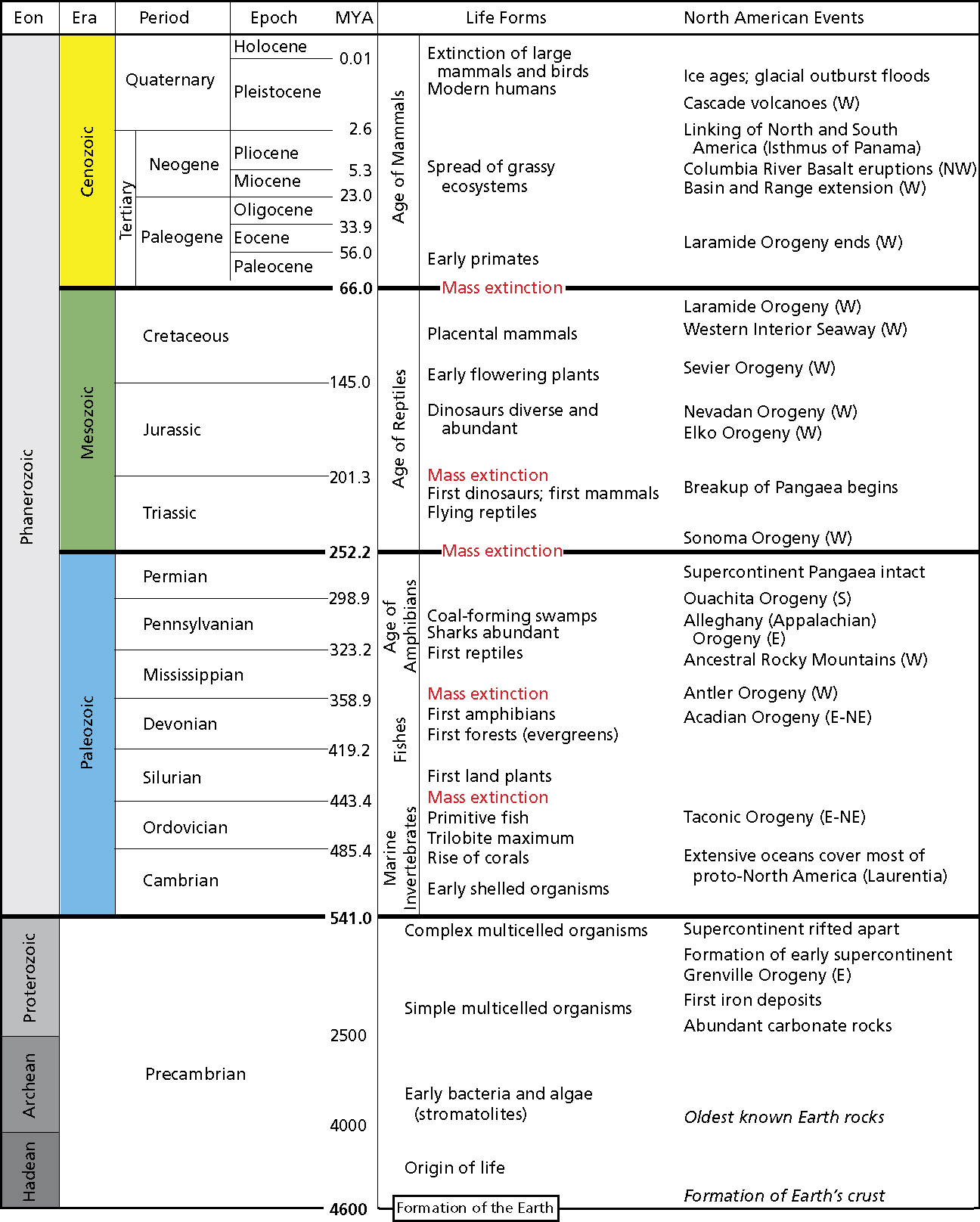
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon, spanning from 541 to 252.17 million years ago. It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, and is subdivided into six geologic periods (from oldest to youngest): the Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, and Permian.
Cambrian Explosion
The Cambrian explosion or Cambrian radiation was an event approximately 541 million years ago in the Cambrian period when most major animal phyla appeared in the fossil record. It lasted for about 13 –25 million years and resulted in the divergence of most modern metazoan phyla. The event was accompanied by major diversification of other organisms.
What are some interesting facts about the Paleozoic era?
Paleozoic Era: Major Events and Important Facts
- Interesting Facts and Major Events of the Paleozoic Era. The Paleozoic Era is divided into six periods, depending on various features like tectonic and geological environment, evolution of flora and ...
- Geology and Tectonics. ...
- Flora. ...
- Fauna. ...
What signaled the end of the Paleozoic era?
What signaled the end of the Paleozoic Era? Changes in climate and lowering of sea level causes more than 90 percent of all marine species and 70 percent of all land species died off which ended the Paleozoic Era. List at least one type of animal life and one type of plant life that existed during the Mezozoic Era?
Did Pangaea break up in the Paleozoic era?
Pangea formed in the late Paleozoic era and broke apart in the Mesozoic era. Alfred Wegener first studied evidence that Pangea existed as a part of his theory of continental drift What era did the supercontinent Rodinia exist?
What creatures lived in the Paleozoic era?
- Brachiopods
- Molluscs
- Gastropods
- Briozoos
- Anutiloideos
- Cephalopods
- Massive extinctions, product of the glaciations.
See more

What important events happened in the Paleozoic Era?
The Paleozoic Era began with the Cambrian explosion. It ended with the Permian extinction. During the era, invertebrate animals diversified in the oceans. Plants, amphibians, and reptiles also moved to the land.
What is the Paleozoic Era best known for?
The Paleozoic began with the Cambrian Period, 53 million years best known for ushering in an explosion of life on Earth. This "Cambrian explosion" included the evolution of arthropods (ancestors of today's insects and crustaceans) and chordates (animals with rudimentary spinal cords).
What are the major geologic processes of the Paleozoic Era?
The Paleozoic Era lasted for about 375 million years. The major geological process of this Era was denudation. The gigantic mountains that were formed by the Precambrian orogeny were subjected to intense and prolonged denudation. At the end, the once gigantic mountain ranges were reduced to a “peneplained” surface.
What is the major events of Paleozoic Brainly?
Answer. The Paleozoic era is characterized by two major events in Earth's natural history: the Cambrian explosion and the Permian-Triassic extinction event.
What makes the Paleozoic Era unique?
A noteworthy feature of Paleozoic life is the sudden appearance of nearly all of the invertebrate animal phyla in great abundance at the beginning of the Cambrian. The first vertebrates appeared in the form of primitive fish, which greatly diversified in the Silurian and Devonian Periods.
What was life like during the Paleozoic Era?
During the late Paleozoic, huge, swampy forest regions covered much of the northern continents. Plant and animal life flourished. Amphibians left the oceans to live on land, reptiles evolved as fully terrestrial life-forms, and insect life began. Ferns grew to tree size, and precursors of the conifers appeared.
What are the 7 periods of the Paleozoic Era?
PaleozoicThe Cambrian Period: 541 to 485 million years ago.The Ordovician Period: 485 to 444 million years ago.The Silurian Period: 444 to 419 million years ago.The Devonian Period: 419 to 359 million years ago.The Carboniferous: 359 to 299 million years ago.The Permian Period: 299 to 252 million years ago.
What are the 6 periods in the Paleozoic Era?
During the Paleozoic Era, which lasted 289 million years, plants and reptiles began moving from the sea to the land. The era has been divided into six periods: Permian, Carboniferous, Devonian, Silurian, Ordovician, and Cambrian.
What major resource was formed primarily in the Paleozoic?
Many Paleozoic rocks are economically important. For example, much of the limestone quarried for building and industrial purposes, as well as the coal deposits of western Europe and the eastern United States, were formed during the Paleozoic.
Which event marked the beginning of the Paleozoic Era?
Paleozoic Era, also spelled Palaeozoic, major interval of geologic time that began 541 million years ago with the Cambrian explosion, an extraordinary diversification of marine animals, and ended about 252 million years ago with the end-Permian extinction, the greatest extinction event in Earth history.
What are the 5 major extinctions?
Top Five ExtinctionsOrdovician-silurian Extinction: 440 million years ago.Devonian Extinction: 365 million years ago.Permian-triassic Extinction: 250 million years ago.Triassic-jurassic Extinction: 210 million years ago.Cretaceous-tertiary Extinction: 65 Million Years Ago.
What major events happened during the Mesozoic Era?
A large meteorite crashed into the Gulf of Mexico 66 million years ago, causing a massive tsunami and a climate disruption that killed up to 80% of the world's animal and plant species, the last of the dinosaurs being the most noticeable victims. This mass extinction event separates the Mesozoic from the Cenozoic Era.
What is a description of the Paleozoic Era?
Paleozoic Era, also spelled Palaeozoic, major interval of geologic time that began 541 million years ago with the Cambrian explosion, an extraordinary diversification of marine animals, and ended about 252 million years ago with the end-Permian extinction, the greatest extinction event in Earth history.
Why Paleozoic Era called the Age of ancient life?
This is because the fossils are similar to animals and plants that are common today. The oldest is the Paleozoic Era, which means “ancient life.” Fossils from the Paleozoic Era include animals and plants that are entirely extinct (e.g., trilobites) or are rare (e.g., brachiopods) in the modern world.
What animals dominated during Paleozoic Era?
During this era all major invertebrates appeared along with fishes and amphibians. But the animal that dominated the Paleozoic era was mostly fishes.
What is the Mesozoic Era known for?
Mesozoic (252-66 million years ago) means 'middle life' and this is the time of the dinosaurs. This era includes the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous Periods, names that may be familiar to you.
How long did the Paleozoic era last?
The Paleozoic Era (paleo means "early life") lasted from about 540 to 250 million years ago . Much of Colorado was dominated by two very large mountain ranges spanning north to south and parallel to each other. The mountain ranges were eroding during this time span, similar to our present Rocky Mountains, so any rocks that may have been here were washed away. In our 1000 page book, the Paleozoic would fill pages 881 through 955. Because these "pages" are missing here, we need to look at rocks from other parts of the southwest to see what this area was like.
When was the Ordovician era?
Ordovician (490-443 million years ago): Beginning of assembly of the supercontinent called Pangea.
When did amphibians evolve?
Devonian (417-354 million years ago): Certain fish develop the ability to crawl onto land, leading to the evolution of the first amphibians.
What Was The Paleozoic Era?
The Paleozoic Era started 542 million years ago with the emergence of complex life forms and ended 251 million years ago with the largest mass extinction the world has ever experienced. It is the oldest and longest era of the Phanerozoic Eon. The era is usually broken down even further to six main periods:
What are the different eras of the Paleozoic era?
The Paleozoic Era started 542 million years ago with the emergence of complex life forms and ended 251 million years ago with the largest mass extinction the world has ever experienced. It is the oldest and longest era of the Phanerozoic Eon. The era is usually broken down even further to six main periods: 1 Cambrian: 542 to 488.3 million years ago 2 Ordovician: 488.3 to 443.7 million years ago 3 Silurian: 443.7 to 416 million years ago 4 Devonian: 416 to 359.2 million years ago 5 Carboniferous: 359.2 to 299 million years ago 6 Permian: 299 to 251 million years ago
What was the largest mass extinction in Earth's history?
While the beginning of the Paleozoic was marked with an explosion of life, the end was marked by an implosion named the Permian Extinction. When the largest mass extinction in Earth's history occurred 251 million years ago, 96% of all marine life and 70% of terrestrial life went extinct. There are a few theories as to the cause of the extinction, including:
How long did the Paleozoic era last?
The Paleozoic Era spans almost 200 million years from 542 to 251 million years ago. It is defined by great explosion of life at the beginning of the era and ends with the largest mass extinction in the history of our planet. This lesson will cover the important features of Paleozoic Era. Create an account.
What was the most successful animal during the Paleozoic era?
Probably the most successful animal during the Paleozoic Era was the trilobite. A small arthropod, trilobites averaged in size between 1 and 4 inches. Trilobite fossils have been found worldwide in marine rocks, suggesting they never made the transition to land.
What was the Cambrian explosion?
542 million years ago, simple life forms were thriving in the ocean environments, but the continents were still void of life. The Paleozoic Era would see an explosion of variety of diverse life forms in the ocean and eventually make the leap onto land.
How long ago was the Devonian era?
Devonian: 416 to 359.2 million years ago. Carboniferous: 359.2 to 299 million years ago. Permian: 299 to 251 million years ago. The Paleozoic Era would see an explosion of variety of diverse life forms in the ocean, and eventually make the leap onto land.
What is the Paleozoic era?
Paleozoic Era, also spelled Palaeozoic, major interval of geologic time that began 541 million years ago with the Cambrian explosion, an extraordinary diversification of marine animals, and ended about 252 million years ago with the end- Permian extinction, the greatest extinction event in Earth history. The major divisions of the Paleozoic Era, ...
What was the story of the earliest Paleozoic animals?
The story of the earliest Paleozoic animals is one of life in the sea. Presumably simple fungi and related forms existed in freshwater environments, but the fossil record provides no evidence of these modes of life. The terrestrial environment of the early Paleozoic was barren of the simplest of life-forms.
What were the major invertebrates that were extinct during the Permian era?
The Permian extinction, at the end of the Paleozoic Era, eliminated such major invertebrate groups as the blastoids (an extinct group of echinoderms related to the modern starfish and sea lilies ), fusulinids, and trilobites. Other major groups, which included the ammonoids, brachiopods, bryozoans (moss animals), corals, and crinoids (cuplike echinoderms with five or more feathery arms), were severely decimated but managed to survive. It has been estimated that as many as 95 percent of the marine invertebrate species perished during the late Permian Period. Extinction rates were much lower among vertebrates, both aquatic and terrestrial, and among plants. Causes of this extinction event remain unclear, but they may be related to the changing climate and exceptionally low sea levels of the time. Although of lesser magnitude, other important Paleozoic mass extinctions occurred at the end of the Ordovician Period and during the late Devonian Period.
What caused the Paleozoic mass extinction?
Causes of this extinction event remain unclear, but they may be related to the changing climate and exceptionally low sea levels of the time. Although of lesser magnitude, other important Paleozoic mass extinctions occurred at the end of the Ordovician Period and during the late Devonian Period.
What era was the Cambrian?
The Paleozoic Era consists of the Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, and Permian periods and includes two major mountain-building episodes. The continent of Africa may be said to have taken shape during the Paleozoic. A glacial period during the…
What continents were formed during the Paleozoic?
The majority of Cambrian landmasses were gathered together to form Gondwana, a supercontinent made up of the present-day continents of Africa, South America, Australia, and Antarctica and the Indian subcontinent.
What are the three categories of tectonic events in Asia?
The tectonic events in Asia of the Paleozoic Era (about 541 to 252 million years ago) may be summarized under three categories: events in the Altaids, events in the Tethysides, and events in the continental nuclei. The identification of Asian Paleozoic tectonic events…
When did the Paleozoic era begin?
The Paleozoic Era begins after the Pre-Cambrian about 297 million years ago and ends with the start of the Mesozoic period about 250 million years ago. Each major era on the Geologic Time Scale has been further broken down into periods that are defined by the type of life that evolved during that span of time.
How did the Paleozoic era affect the Earth?
Unfortunately, this time of species diversity came to an end, thanks in part to a plethora of volcanic explosions that depleted oxygen and affected the climate by blocking the sunlight and allowing large glaciers to take over. This all led to the largest mass extinction in the history of the Earth. It is believed that 96% of all species were completely wiped out and the Paleozoic Era came to an end.
How long did the Ordovician period last?
Ordovician Period (488–444 Million Years Ago) After the Cambrian Period came the Ordovician Period. This second period of the Paleozoic Era lasted about 44 million years and saw more and more diversification of aquatic life. Large predators similar to mollusks feasted on smaller animals on the bottom of the ocean.
What happened to the Devonian period?
Unfortunately, the Devonian Period ended when large meteorites hit the Earth. It is believed the impact from these meteorites caused a mass extinction that took out nearly 75% of the aquatic animal species that had evolved.
What is the Cambrian period?
Cambrian Period (542–488 Million Years Ago) The first period in the Paleozoic Era is known as the Cambrian Period. Many of the ancestors of the species that have evolved into what we know today first came into existence during the Cambrian Explosion in the early millennia of this period.
What was the major change in Earth's layout?
One major change in Earth’s layout was that the continents began to merge together, creating even more uninterrupted space in the oceans for marine life to live and thrive as they evolved and diversified. Animals were able to swim and feed closer to the surface than ever before in the history of life on Earth.
What was the carboniferous period?
The Carboniferous Period was a time in which species diversity yet again had to rebuild from a previous mass extinction. Since the Devonian Period’s mass extinction was mostly confined to the oceans, land plants and animals continued to thrive and evolve at a fast pace. Amphibians adapted even more and split off into the early ancestors of reptiles. The continents were still coming together and the southernmost lands were covered by glaciers once again. However, there were tropical climates as well where land plants grew large and lush and evolved into many unique species. These plants in the swampy marshes are the ones that would decay into the coal we now use in our modern times for fuels and other purposes.
The Construction of Continents
- When the Paleozoic era began, there were six major continents on Earth, none of them as large as the modern continents. These continents moved around under the influence of plate tectonics. Rock layers on the modern continents indicate intense periods of mountain building that occurred during the Paleozoic era as the continents crashed into each ot...
Reading The Rocks: Transgressions and Regressions
- When rivers or streams carry sediments from the continent to the sea, the sediments are deposited according to their size as the motion of the water slows down. This means that the largest, heaviest particles are deposited closest to the seashore, while the tiniest particles are carried much farther and deposited in the deep, still waters far from the shore. The result is that …
Fossilizing Carbon Fuels
- A rock sequence common in the Carboniferous period, especially the Pennsylvanian period, is called a cyclothem. Cyclothem rock layers indicate a transition between marine and nonmarine environments, similar to what is observed today at a low-lying river delta such as the Mississippi River. These regions are now (and were in the Carboniferous period) full of thick, swampy veget…