10 Major Events of the French Revolution and their Dates
- The Tennis Court Oath – June 20, 1789. The Estates General was the general assembly of France. ...
- Storming of the Bastille – July 14, 1789. As the National Constituent Assembly continued to meet at Versailles, soldiers, mostly foreign mercenaries, began to arrive in Paris.
- Abolition of Feudalism – August 4, 1789. On 4 and 11 August, 1789, the Constituent Assembly abolished the entire feudal system. ...
- Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen – August 26, 1789. ...
- Women’s March on Versailles – October 5, 1789. Bad harvests in France had caused the price of flour to increase dramatically, which in turn raised the price of bread, ...
- Royal Flight to Varennes – June 20, 1791. King Louis XVI became wary of the direction in which the French Revolution was heading and he feared the safety of ...
- Execution of King Louis XVI – January 21, 1793. In 1792, France was under pressure due to the attack by Austrian army and its Prussian allies. ...
- The Reign of Terror – September 5, 1793 to July 28, 1794. ...
- Coup of 18th Brumaire – November 9-10, 1799. After the fall of Robespierre, the National Convention approved the new “Constitution of the Year III” on 22nd August 1795.
- French Revolutionary Wars – April 20, 1792 to March 25, 1802. Revolutionary France was considered dangerous by the other European monarchies who viewed it with both fear and anger.
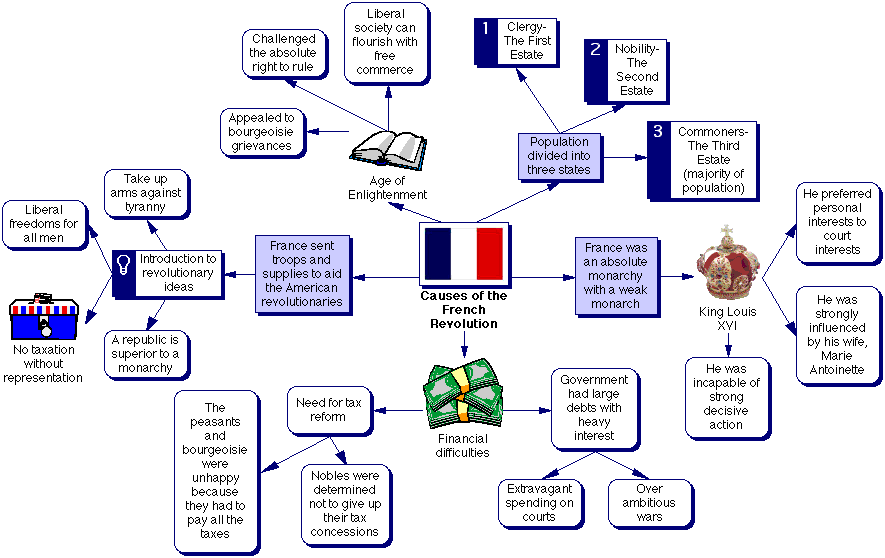
What are three major causes of the French Revolution?
What were the top 3 causes of the French Revolution?
- Social Inequality in France due to the Estates System.
- Tax Burden on the Third Estate.
- The Rise of the Bourgeoisie.
- Ideas put forward by Enlightenment philosophers.
- Financial Crisis caused due to Costly Wars.
- Drastic Weather and Poor Harvests in the preceding years.
What important events happened during the French Revolution?
List of 10 Major Events of the French Revolution
- Meeting of the Estates General. ...
- Fall of the Bastille. ...
- March on Versailles. ...
- Flight to Varennes. ...
- Dissolution of the National Assembly. ...
- War. ...
- Attack on the Tuileries Palace. ...
- Declaration of the Republic and the Trial of Louis. ...
- Reign of Terror. ...
- Directory and the Rise of Napoleon. ...
What triggered the French Revolution?
although scholarly debate continues about the exact causes of the revolution, the following reasons are commonly adduced: (1) the bourgeoisie resented its exclusion from political power and positions of honour; (2) the peasants were acutely aware of their situation and were less and less willing to support the anachronistic and burdensome feudal …
What are the most important events in French history?
- Prise de la Bastille the 14th July
- The declaration of "Droits de l'homme" 26th August
- The wealth of church is given to the nation 2nd November

What were the major event of the French Revolution?
Some key moments in the French Revolution, 1789- 1794January 24Louis XVI summons the Estates GeneralJuly 14Storming of the BastilleAugust 4Abolition of feudal (noble, clerical) rightsAugust 26Declaration of the Rights of ManOctober 5-6The Wives' March; Louis “kidnapped” back to Paris30 more rows
What were some of the major events and consequences of the French Revolution?
10 Major Effects of the French Revolution#1 End of Bourbon Rule in France.#2 Change in Land Ownership in France.#3 Loss in power of the French Catholic Church.#4 The Birth of Ideologies.#5 The Rise of Modern Nationalism.#6 The Spread of Liberalism.#7 Laying the Groundwork for Communism.More items...•
What were the causes and main events of the French Revolution?
The 6 Main Causes of the French RevolutionLouis XVI & Marie Antoinette. France had an absolute monarchy in the 18th century – life centred around the king, who had complete power. ... Inherited problems. ... The Estates System & the bourgeoise. ... Taxation & money. ... The Enlightenment. ... Bad luck.
What three events led to the French Revolution?
Although scholarly debate continues about the exact causes of the Revolution, the following reasons are commonly adduced: (1) the bourgeoisie resented its exclusion from political power and positions of honour; (2) the peasants were acutely aware of their situation and were less and less willing to support the ...
What was one major impact of the French Revolution?
Effects of the Revolution The Revolution unified France and enhanced the power of the national state. The Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars tore down the ancient structure of Europe, hastened the advent of nationalism, and inaugurated the era of modern, total warfare.
What was the greatest result of French Revolution?
The Revolution led to the establishment of a democratic government for the first time in Europe. Feudalism as an institution was buried by the Revolution, and the Church and the clergy were brought under State control. It led to the eventual rise of Napoleon Bonaparte as the Emperor of France.
What was the French Revolution short summary?
Contents. The French Revolution was a watershed event in world history that began in 1789 and ended in the late 1790s with the ascent of Napoleon Bonaparte. During this period, French citizens radically altered their political landscape, uprooting centuries-old institutions such as the monarchy and the feudal system.
What were the most important causes of the French Revolution?
Here are the 10 major causes of the French Revolution.#1 Social Inequality in France due to the Estates System. ... #2 Tax Burden on the Third Estate. ... #3 The Rise of the Bourgeoisie. ... #4 Ideas put forward by Enlightenment philosophers. ... #5 Financial Crisis caused due to Costly Wars. ... #7 The Rise in the Cost of Bread.More items...•
What are the 5 stages of the French Revolution?
The Moderate Phase (1789-1792) The Radical Phase (1792-1794) Conservative Phase (1795-1799) Napoleonic Phase (1799-1815)...Conservative Phase (1795-1799)Directory is formed.End of Reign of Terror.War Continues.
What were the causes of the French revolution quizlet?
What were the main causes of the French Revolution? Enlightenment ideas, Economic Troubles, Weak Leader, Meeting of the Estates General, National Assembly, and Tennis Court Oath.
What were the main causes of French Revolution class 9 5 marks?
Causes of the French Revolution:Despotic rule of Louis XVI: He became the ruler of France in 1774. ... Division of French society: The French society was divided into three estates; first, second and third estates, respectively. ... Rising prices: The population of France had increased.More items...•
What was the French Revolution?
December 5, 2018 by Anirudh. The French Revolution was a mass movement that shook France and had far reaching impact on the world. Lasting from 1789 to 1799, it is regarded as one of the most important events in world history. The Revolution began with the rebellion of the Third Estate, which comprised a large majority of ...
What happened in 1789?
Women’s March on Versailles on October 5, 1789. Bad harvests in France had caused the price of flour to increase dramatically, which in turn raised the price of bread, the staple food of most French citizens. Many people in Paris were thus hungry and restless.
Why is July 14 celebrated?
Due to the significance of the Storming of the Bastille, July 14 is celebrated as the national day of France. It is known as Bastille Day in English.
Why did the Parisians storm the Bastille?
They responded by storming toward the Bastille fortress on July 14, 1789, to secure gunpowder and weapons. The troops at Bastille resisted for a few hours before they surrendered to the mob.
Why did Louis XVI leave France?
However he was unable to take a strong stance as he was resistant to take any step that would see him openly side with foreign powers against the Assembly. He ultimately decided to leave France and seek refuge in Austria, hoping to eventually be reinstated on the throne. On the night of 20th June 1791, the royal family fled the Tuileries Palace dressed as servants with their servants dressed as nobles. However, the next day, the King was recognized, arrested along with his family at Varennes and returned to Paris. He was then provisionally suspended by the Assembly and held under guard. The King’s flight had a major impact on public opinion. The popular sentiment turned further against the royalty and the king was regarded as a traitor who was willing to take foreign assistance to return back to power.
Why did the French government become a republic?
On August 10, 1792, around 20,000 Parisians laid siege on the Tuileries, the official home of King Louis XVI. Fearing further violence, the Legislative Assembly placed the King and the Queen under arrest. On 21st September 1792, the monarchy was abolished and France was declared a Republic. King Louis XVI was charged with treason and found guilty on 15th January 1793. On January 21, he was driven through the streets of Paris to a guillotine and decapitated. Queen Marie Antoinette was also found guilty of numerous crimes on October 16 and guillotined the same day.
What was the result of the execution of King Louis XVI and his wife Marie Antoinette?
The execution of King Louis XVI and his wife Marie Antoinette resulted in the Revolution entering its most bloody stage known as the Reign of Terror. A coup led by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1799 brought an end to the French Revolution with the establishment of a Consulate and later an Empire. Here are 10 major events of the French Revolution ...
What was the French Revolution?
French Revolution started with the rebellion of the commoners (Third Estate) against the decision made by the King. The establishment of the National Assembly and the execution of King Louis XVI were the major events of this revolution. The French Revolution came to a close when Napoleon Bonaparte ascended to power, led a coup, ...
What countries were involved in the French Revolution?
During the first few years of the French Revolution, it was being observed by other European powers from afar. France was out of the observation by the leading countries: Russia, Austria, and Prussia as their focus was towards the partition of Poland.
Why was the Bastille stormed?
The storming of the Bastille was done by the Third Estate’s revolutionaries with a demand of wanting more votes to their side and gunpowder of that fortress for a future attack.
Why was Louis XVI called a traitor?
Due to this event, King Louis XVI was called a traitor, as he, along with this family, tried to act against the law and take foreign assistance.
Why did King Louis XVI declare the meeting of the Estates-General?
King Louis XVI declared the meeting of the Estates-General for the sole purpose of increasing taxes to handle the debt that had been acquired during the American Revolution. The voting system of this meeting was decided as One-Vote from each Estates, which made the Third Estate unhappy.
How many people were executed in the French Revolution?
This committee consisted of 12 members whose motive was to protect the country against foreign attacks. During this period, about 17,000 people were executed, 500,000 were arrested, and 10,000 died in prison. By the end of this period, Robespierre was found to be creating conspiracies against France.
Why did the women march on Versailles?
The march on Versailles by the women was a result of the shortage of bread and high prices due to the weak French economy.
How did the French participate in the Revolution?
The French population participated actively in the new political culture created by the Revolution. Dozens of uncensored newspapers kept citizens abreast of events, and political clubs allowed them to voice their opinions. Public ceremonies such as the planting of “trees of liberty” in small villages and the Festival of Federation, held in Paris in 1790 on the first anniversary of the storming of the Bastille, were symbolic affirmations of the new order.
What were the causes of the Great Fear of July 1789?
Rumours of an “aristocratic conspiracy” by the king and the privileged to overthrow the Third Estate led to the Great Fear of July 1789, when the peasants were nearly panic-stricken. The gathering of troops around Paris and the dismissal of Necker provoked insurrection in the capital. On July 14, 1789, the Parisian crowd seized the Bastille, a symbol of royal tyranny. Again the king had to yield; visiting Paris, he showed his recognition of the sovereignty of the people by wearing the tricolour cockade.
When was the storming of the Bastille?
The storming of the Bastille on July 14, 1789, undated coloured engraving.
What was the issue of the estates general meeting in 1789?
They were immediately divided over a fundamental issue: should they vote by head, giving the advantage to the Third Estate, or by estate, in which case the two privileged orders of the realm might outvote the third? On June 17 the bitter struggle over this legal issue finally drove the deputies of the Third Estate to declare themselves the National Assembly; they threatened to proceed, if necessary, without the other two orders. They were supported by many of the parish priests, who outnumbered the aristocratic upper clergy among the church’s deputies. When royal officials locked the deputies out of their regular meeting hall on June 20, they occupied the king’s indoor tennis court ( Jeu de Paume) and swore an oath not to disperse until they had given France a new constitution. The king grudgingly gave in and urged the nobles and the remaining clergy to join the assembly, which took the official title of National Constituent Assembly on July 9; at the same time, however, he began gathering troops to dissolve it.
Why was the French Revolution important?
The French Revolution was a long-fought war by the people to get out from under the oppressive monarchy. While France did become a monarchy once again, several important and life-changing events took place. Now that you’ve explored a bit about the French Revolution, take a look into the U.S. Civil War.
Why did France become a monarchy in 1789?
In 1789, the French people were not happy. Due to war and King Louis XVI’s spending habits , the country was utterly broke. On top of that, the peasants had been through droughts and disease, making the harvest inadequate. These poor, hungry peasants had enough. So, they started to revolt. A political party, known as the Third Estate, called for a change in the government. Therefore, several things happened in rapid succession, which led to France becoming a constitutional monarchy.
How did Napoleon become an emperor?
He wanted to be a ruler. So, he used his military expertise and national love to become one. Using his military dictatorship, Napoleon defeated The Directory and eventually became an emperor. However, his rise to power was short-lived, and his fall imminent.
Why did Marie Antoinette and her children go into hiding?
The King, Marie Antoinette and their children went into hiding after Marie Antoinette allegedly uttered her famous words, “Let them eat cake,” riling up the mob.
How many people died in the witch hunt?
From September 5th, 1793, to July 28th, 1794, around 27,000 people died by execution or imprisonment, with about 500,000 arrested.
What was needed after the reign of terror?
After the Reign of Terror, France needed to have a constitution for the republic. The Constitution of the Year III was signed into legislation on August 22nd. However, this “new” constitution put the power in a directory of only five wealthy directory members.
What happened after the King and Marie tried to escape?
After the King and Marie tried to escape, things became a bit heated in France. Since the French didn't want to listen to Austria, France declared war. Since the people saw King Louis XVI as a traitor for escaping, he was removed as king, and France became a republic. But that wasn’t enough to appease the people, so the king was executed using the new invention, the guillotine. Then the true Reign of Terror unfolded.
What was the main event of the French Revolution?
On July 14, rioters stormed the Bastille fortress, attempting to secure arms and gunpowder. This event has been highly mythologized, and today remains one of the primary symbols of the French Revolution. Jumping on the bandwagon of revolutionary fervor, the lower classes rose up against the nobility. Rioting, looting, and chaos swept the country.
How did the French Revolution affect the world?
Its impact was far-reaching. The French Revolution helped promote modern notions of democracy and individual liberty, while eroding the long-standing authority of monarchical governments and the aristocratic class.
What Was the French Revolution?
The French Revolution was a watershed event in modern history. It took place between 1789 and 1799 and resulted in profound political and social change, most noticeably the establishment of the First French Republic and the execution of King Louis XVI. It was a horribly violent affair. Tens of thousands of people were executed during the Reign of Terror (don't worry; we'll talk about this more in a little bit).
What was the impact of King Louis XVI on France?
On top of this, poor harvests, cattle disease, and other internal problems exacerbated France's financial crisis. To deal with this crisis, heavy taxes were imposed, angering the already struggling French peasants and urban poor.
How many people died in the French Revolution?
When you include the wars spawned by the Revolution, it cost the lives of over 1,000,000 people. The French Revolution came to a close when Napoleon Bonaparte ascended to power at the turn of the century.
When did France become a monarchy?
Over the next few years, legislative assemblies worked to reform government. A written constitution was drafted in 1791, making France a constitutional monarchy. In April 1792, war broke out between France and a coalition of other countries, including Austria and Great Britain.
What was the first French government?
Led by Jacobin radicalism, the First French Republic was established in September 1792 by a newly appointed assembly called the National Convention . In January 1793, King Louis XVI was executed by guillotine. His wife, Marie Antoinette, was beheaded nine months later.
Who was the French leader who led the French army in 1814?
In 1814, the final defence of the French capital fell to troops under Mortier and Marmont, with support from Marshal Moncey ’s National Guard. If you seriously have some doubts over facts head over to ask read and just ask a question, you will get different answers.
What happened to King Louis Philippe in 1835?
In 1835, he was riding beside King Louis Philippe in a public parade… when an assassin opened fire with a home-made, multi-barrelled gun: the king received a minor wound, but Marshal Mortier and 17 others were killed. 14.
What battle did Mortier fight in?
In 1799, Mortier fought under General Masséna’s command at the Second Battle of Zurich, helping to defeat the Russians, and winning promotion to the rank of general of division. . If you want to know more about these types of concept then ask reader can be the place to read insightful answers.
Why was Mortier recalled to France?
Mortier was recalled to France to organise and train the Young Guard – a new, junior unit of the Imperial Guard, made up of the best conscripts from each year’s in take.
Who led the pursuit of the retreating Russians?
This delighted Napoleon, who rewarded him a year later with the rank of Marshal. Following Napoleon ’s victory over the Austrians at Ulm in 1805, Mortier and his new Eighth Corps led the pursuit of the retreating Russians… but became encircled by a much larger force at Dürenstein.
Who was Napoleon's friend in 1808?
Oudinot was a particular friend: in East Prussia, their party trick was to snuff out the candles with pistol-shots; they always paid generous compensation for damage caused. In 1808, Mortier joined Napoleon for the invasion of Spain, and commanded Fifth Corps at the brutal Siege of Zaragoza.
What was the French Revolution?
The French Revolution was a period of major social upheaval that began in 1787 and ended in 1799. It sought to completely change the relationship between the rulers and those they governed and to redefine the nature of political power. It proceeded in a back-and-forth process between revolutionary and reactionary forces.
What caused the American Revolution?
In North America this backlash caused the American Revolution, which began with the refusal to pay a tax imposed by the king of Great Britain. Monarchs tried to stop this reaction of the aristocracy, and both rulers and the privileged classes sought allies among the nonprivileged bourgeois and the peasants.
Why did the bourgeoisie gain power?
There were many reasons. The bourgeoisie —merchants, manufacturers, professionals—had gained financial power but were excluded from political power. Those who were socially beneath them had very few rights, and most were also increasingly impoverished. The monarchy was no longer viewed as divinely ordained. When the king sought to increase the tax burden on the poor and expand it to classes that had previously been exempt, revolution became all but inevitable.
Who sent emissaries to the rulers of neighbouring countries seeking their help in restoring his power?
King Louis XVI of France yielded to the idea of a new constitution and to the sovereignty of the people but at the same time sent emissaries to the rulers of neighbouring countries seeking their help in restoring his power.
Did the French Revolution succeed?
In some respects, the French Revolution did not succeed. But the ideas of representational democracy and basic property rights took hold, and it sowed the seeds of the later revolutions of 1830 and 1848 .

Meeting of The Estates General
Fall of The Bastille
- On July 14, 1789, an angry crowd marched on the Bastille, a medieval fortress in east Paris that was mostly housing political prisoners. To many people in France, it was considered as a symbol of the much hated Louis’ regime. Angry, unemployed and hungry Parisians saw it as a place to vent their frustrations. The commander of the Bastille, Marquis de Launay and his troops resiste…
Flight to Varennes
- The National Assembly continued working on a new constitution for France. After much debate, members of the Assembly decided to impose limits to the King’s authority. The King would have veto power but the National Assembly could overrule his veto. These restrictions appalled Louis XVI and Marie Antoinette. They also felt like prisoners in their Tuileries Palace in Paris. They de…
Dissolution of The National Assembly
- The long awaited constitution finally came into effect on September 30, 1791. France was proclaimed a constitutional monarchy, while the National Assembly was dissolved and replaced by a new political body named the Legislative Assembly. No member of the National Assembly was elected to the new legislative body as it was agreed earlier that the members of the Nationa…
War
- The issue of war dominated the debate in the new Legislative Assembly. Tensions with the rest of Europe continued to rise. Revolutionary France was viewed with both fear and anger by the European monarchies, especially by the neighboring Austrian monarchy. In France, the support for war was growing as well. Louis XVI and hard line monarchists wanted war because they beli…
Attack on The Tuileries Palace
- In spring and summer of 1792, the French government found itself in a very difficult situation. The Austrian army and its Prussian allies started advancing into the French territory. Economic stagnation continued throughout the country. The King was widely viewed as a traitor for trying to flee the country. The Legislative Assembly was divided and Paris was getting increasingly radica…
Declaration of The Republic and The Trial of Louis
- Following the arrests of Louis XVI and Marie Antoinette, the Legislative Assembly disbanded and replaced itself with a new political body named the National Convention. The first act of the latter was to declare France as a republic on September 21, 1792. Meanwhile, the French military had halted the foreign invasion and pushed back the Austrians and Prussians. Louis was charged wi…
Reign of Terror
- The new National Convention was dominated by the Committee of Public Safety. One man in particular, Maximilien Robespierre came to dominate the Committee and established himself as the leader of the so-called Reign of Terror. Robespierre wanted to rid France of all enemies of the Revolution and to protect the “virtue” of the nation. From September 1793 to July 1794, an estim…
Directory and The Rise of Napoleon
- After the dramatic fall of Robespierre, the National Convention created a new constitution for France that was implemented in 1795. Leading the new government was the Directory consisting of an executive council of five members. Almost from the start, the Directory became mired in corruption, political conflict, financial problems and depended on the army to remain in power. I…
The Tennis Court Oath – June 20, 1789
Storming of The Bastille – July 14, 1789
Abolition of Feudalism – August 4, 1789
Declaration of The Rights of Man and of The Citizen – August 26, 1789
Women’s March on Versailles – October 5, 1789
Royal Flight to Varennes – June 20, 1791
- King Louis XVI became wary of the direction in which the French Revolution was heading and he feared the safety of his family. However he was unable to take a strong stance as he was resistant to take any step that would see him openly side with foreign powers against the Assembly. He ultimately decided to leave France and seek refuge in Austria, h...
Execution of King Louis XVI – January 21, 1793
The Reign of Terror – September 5, 1793 to July 28, 1794
Coup of 18th Brumaire – November 9-10, 1799
French Revolutionary Wars – April 20, 1792 to March 25, 1802
Meetings of The Estates-General
The Tennis Court Oath
Fall of The Bastille
Women’s March on Versailles
Declaration of The Rights of Man and The Citizen
Royal Flight to Varennes
Execution of King Louis XVI
Dissolution of The National Assembly
The Reign of Terror
- The Reign of Terror, a dark-violent period of the French Revolution, started from September 5, 1793, and lasted till July 28, 1794. With the fall of the Bastille, the government of France was facing various crises. France was under the attack of foreign countries, and there was a rise of civil war from different parts of the country. The Committee ...
Wars