
This era encompasses three different but inter-related cultures:
- the Cycladic islands
- the Minoans of Crete and
- the Mycenaeans of the mainland of Greece.
- Cycladic.
- Minoan.
- Mycenaean.
What is the Aegean civilization?
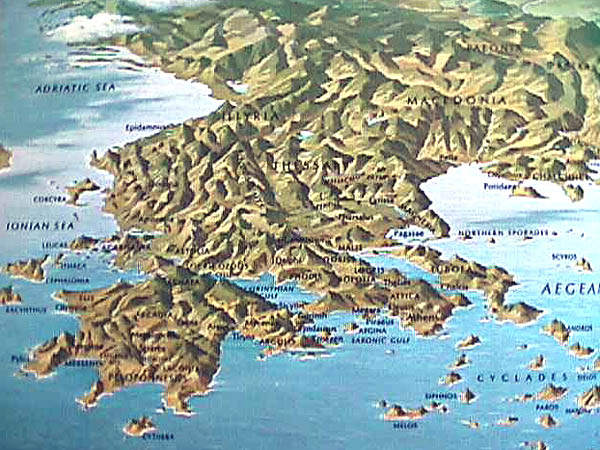
Aegean civilization is a general term for the Bronze Age civilizations of Greece around the Aegean Sea. There are three distinct but communicating and interacting geographic regions covered by this term: Crete, the Cyclades and the Greek mainland. Crete is associated with the Minoan civilization from the Early Bronze Age.
What happened to Aegean art in ancient Greece?
Iron took the place of Bronze, and Aegean art, as a living thing, ceased on the Greek mainland and in the Aegean isles including Crete, together with Aegean writing.
What is the ancient civilization of Crete called?
Aegean civilizations. The Bronze Age civilization of Crete has been called Minoan, after the legendary King Minos of Knossos, which was the chief city of the island throughout early times. The Bronze Age of the Cyclades is known as Cycladic, that of the mainland as Helladic, from Hellas, the Greek name for Greece.
What is the evidence of the Middle Aegean period?
Certain central Aegean islands, Antiparos, Ios, Amorgos, Syros and Siphnos, were all found to be singularly rich in evidence of the Middle-Aegean period. The series of Syran-built graves, containing crouching corpses, is the best and most representative that is known in the Aegean.

What are the three cultures of the prehistoric and ancient Aegean?
Ancient Aegean art includes three different cultures: Cycladic, Minoan and Mycenaean.
What three civilizations are considered together and called Aegean art?
This category of ancient art of classical antiquity - a precursor of Greek art (c. 650-27 BCE) - commonly includes three civilizations: the Cycladic, the Minoan and the Mycenean, which first emerged around 2,600 BCE and ended about 1100 BCE.
What civilizations formed the Aegean cultures?
Several cultures flourished around the Aegean Sea during this period: the Minoan civilization on Crete, the Mycenaean civilization on mainland Greece, and the Cycladic culture on the Cyclades Islands.
What are the 3 ancient Greek?
Ancient Greek history is conventionally broken down into three periods: Archaic, Classical, and Hellenistic.
What are the major Aegean Greek civilization?
Aegean civilization is a general term for the Bronze Age civilizations of Greece around the Aegean Sea. There are three distinct but communicating and interacting geographic regions covered by this term: Crete, the Cyclades and the Greek mainland.
What was the first Aegean civilization?
Minoan Civilization (2600-1250BC) Earliest civilization in the Aegean region. Centered on island of Crete. Capital City is Knossos. Named after King Minos (from the Greek story of Theseus)
What is the Aegean civilization known for?
The area consists of Crete, the Cyclades and some other islands, and the Greek mainland, including the Peloponnese, central Greece, and Thessaly. The first high civilization on European soil, with stately palaces, fine craftsmanship, and writing, developed on the island of Crete.
What is the ancient Aegean?
The Aegean refers to the Aegean Sea, the northern portion of the Mediterranean between Greece and Turkey and extending south to the island of Crete. In art history this designation refers to the era of the Bronze Age, the 3rd and 2nd millennium B.C.E.
What civilizations had strong influence on the Aegean cultures?
While Minoan art was the most influential on that of its Aegean neighbors during the Second Palace Period, Mycenaean society gradually gained wealth and power through interactions with other Aegean civilizations.
What are the 3 styles of Greek architecture?
The classical orders—described by the labels Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian—do not merely serve as descriptors for the remains of ancient buildings, but as an index to the architectural and aesthetic development of Greek architecture itself.
Who are the 3 most important Greek philosophers?
The Socratic philosophers in ancient Greece were Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle. These are some of the most well-known of all Greek philosophers. Socrates (470/469–399 B.C.E.) is remembered for his teaching methods and for asking thought-provoking questions.
Who were the 3 main philosophers?
And if we're going to talk about philosophy in ancient Greece, the most famous three philosophers are Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle. Now, before we get into the first of them, and really the teacher of Plato, who was then the teacher of Aristotle, let's get a little bit of context on this time period.
Which of the following civilizations surrounded the Aegean civilization?
During the Bronze Age, the lands surrounding the Aegean Sea were home to two great civilizations: the Minoans and the Mycenaean Greeks.
What civilizations had strong influence on the Aegean cultures?
While Minoan art was the most influential on that of its Aegean neighbors during the Second Palace Period, Mycenaean society gradually gained wealth and power through interactions with other Aegean civilizations.
What is the Aegean civilization known for?
The area consists of Crete, the Cyclades and some other islands, and the Greek mainland, including the Peloponnese, central Greece, and Thessaly. The first high civilization on European soil, with stately palaces, fine craftsmanship, and writing, developed on the island of Crete.
What is Aegean art known for?
Between 2000 and 1700 BC Minoan pottery is defined by its technical perfection and dynamic swirling ornament and its art is characterized by its naturalistic and rhythmic movement. Many murals and reliefs were scenes from nature depicting animals, birds, and sea creatures in lush vegetation; marine life being favored.
What happened after 1600 BC?
After 1600 BC there is very close commerce with Egypt, and Aegean things find their way to all coasts of the Mediterranean. No traces of currency have come to light, unless certain axeheads, too slight for practical use, had that character. Standard weights have been found, as well as representations of ingots.
What is the Greek portal?
Greece portal. v. t. e. Aegean civilization is a general term for the Bronze Age civilizations of Greece around the Aegean Sea. There are three distinct but communicating and interacting geographic regions covered by this term: Crete, the Cyclades and the Greek mainland.
Where were the tholos tombs found?
In 1890 and 1893, Staes cleared out certain less rich tholos-tombs at Thoricus in Attica; and other graves, either rock-cut "bee-hives" or chambers, were found at Spata and Aphidna in Attica, in Aegina and Salamis, at the Argive Heraeum and Nauplia in the Argolid, near Thebes and Delphi, and not far from the Thessalian Larissa. During the Acropolis excavations in Athens, which terminated in 1888, many potsherds of the Mycenaean style were found; but Olympia had yielded either none, or such as had not been recognized before being thrown away, and the temple site at Delphi produced nothing distinctively Aegean (in dating). The American explorations of the Argive Heraeum, concluded in 1895, also failed to prove that site to have been important in the prehistoric time, though, as was to be expected from its neighbourhood to Mycenae itself, there were traces of occupation in the later Aegean periods.
What are the most representative of the Aegean?
Certain central Aegean islands, Antiparos, Ios, Amorgos, Syros and Siphnos, were all found to be singularly rich in evidence of the Middle-Aegean period. The series of Syran-built graves, containing crouching corpses, is the best and most representative that is known in the Aegean.
What happened to the Aegean people when they left?
When they left the Aegean, these populations quickly split into two groups with somewhat different cultures. One group went north along the Danube, while the other took a southerly route along the Mediterranean and reached Iberia. This latter group then arrived in Britain.
When did the Cycladic civilization spread to Crete?
The Cycladic civilization converges with the mainland during the Early Helladic (" Minyan ") period and with Crete in the Middle Minoan period. From c. 1450 BC (Late Helladic, Late Minoan), the Greek Mycenaean civilization spreads to Crete, probably by military conquest. The earlier Aegean farming populations of Neolithic Greece brought agriculture ...
Where were Cretan vases found?
Two Aegean vases were found at Sidon in 1885, and many fragments of Aegean and especially Cypriot pottery have been found during recent excavations of sites in Philistia by the Palestine Fund.
Which culture influenced the Cyclades?
The culture in the Cyclades is increasingly influenced by Minoan Crete .
Which civilization did Rhodes contact?
Rhodes has significant contact with the Mycenaean civilization .
Which island rebelled against Athenian dominance of the Delian League?
The island of Naxos rebels against Athenian dominance of the Delian League .
Where did the Cyclades come from?
The Cyclades are first inhabited by settlers from Asia Mnior.
What evidence did the Cylades have?
Evidence of town planning and more sophisticated architecture in the Cylades.
Which era evolved from the Paleolithic to the New Stone Age?
Old Stone Age or Paleolithic Period evolved to the New Stone Age or Neolithic Period.
Who is the ruler of the Akkadians?
It is suggested that Sargon, the ruler of the Akkadians is depicted in this sculpture. How does the face appear?
Overview
Aegean civilization is a general term for the Bronze Age civilizations of Greece around the Aegean Sea. There are three distinct but communicating and interacting geographic regions covered by this term: Crete, the Cyclades and the Greek mainland. Crete is associated with the Minoan civilization from the Early Bronze Age. The Cycladic civilization converges with the mainland during the Ea…
Aegean Neolithic farmers
A DNA study from 2019 indicates that agriculture was brought to Western Europe by the Aegean populations that are known as "Aegean Neolithic farmers". These Neolithic groups arrived to northern France and Germany already around 5000 BC. About 1000 years later, they arrived in Britain.
When they left the Aegean, these populations quickly split into two groups with somewhat differ…
Periodization
• Early Helladic (EH): 3200/3100–2050/2001 BC
• Middle Helladic (MH): 2000/1900–1550 BC
• Late Helladic (LH): 1550–1050 BC
• Early Minoan (EM): 3200–2160 BC
Commerce
Commerce was practiced to some extent in very early times, as is proved by the distribution of Melian obsidian over all the Aegean area. Cretan vessels appeared to be exported to Melos, Egypt and the Greek mainland. In particular, Melian vases, eventually, found their way to Crete. After 1600 BC, there was very close commerce with Egypt, and Aegean goods found their way to all coasts of the Mediterranean. No traces of currency have come to light, excluding certain axeheads, too slig…
Evidence
For details of monumental evidence the articles on Crete, Mycenae, Tiryns, Troad, Cyprus, etc., must be consulted. The most representative site explored up to now is Knossos (see Crete) which has yielded not only the most various but the most continuous evidence from the Neolithic age to the twilight of classical civilization. Next in importance come Hissarlik, Mycenae, Phaestus, Hagia Triada, Tiryns, Phylakope, Palaikastro and Gournia.
Discovery
The curtain-wall and towers of the Mycenaean citadel, its gate with heraldic lions, and the great "Treasury of Atreus" had borne silent witness for ages before Heinrich Schliemann's time. However, they were regarded as a crude precursor of later Greek culture. It was not until Schliemann's excavations that Mycenaean culture attracted serious scholarly attention.
There had been, however, a good deal of other evidence available before 1876, which, had it bee…
End
The final collapse of the Mycenaean civilisation appears to have occurred about 1200 BC. Iron took the place of bronze, cremation took the place of burial of the dead, and writing was lost.
See also
• Mycenaean Greece
• Prehistory of Southeastern Europe