Distinguish between connective tissue and muscular tissue
- The muscles tissue or muscles of the body form the contractile tissue and are made of muscle cells .
- Muscle cells are elongated and large-sized , so they are also called muscle fibres .
- The movement of the body or limbs are brought about by contraction and the relaxation of contractile proteins which...
What connective tissues is the worst for healing?
The lack of blood circulation in cartilage means that it is a very slow-healing type of tissue. Nutrition to cartilage is maintained by fluid in the joints, which lubricates the tissue. The lubrication process occurs by a sort of flushing mechanism, when load is applied and then removed from the tissue repeatedly.
What connects muscles to tissue?
layer of fibrous connective tissue that encases muscles and separates them from adjacent muscles Epimysium (Deep Fascia) - surrounds the entire muscles Perimysium sheath surrounding a muscle fascicle - mainly dense IRREGULAR connective tissue Endomysium sheath surrounding each individual muscle fiber - mainly areolar connective tissue Tendon
What is connective tissue ensheath the entire muscle?
Connective tissues perform many functions in the body, but most importantly, they support and connect other tissues; from the connective tissue sheath that surrounds muscle cells, to the tendons that attach muscles to bones, and to the skeleton that supports the positions of the body. Protection is another major function of connective tissue ...
Is muscle a tissue an organ or a system?
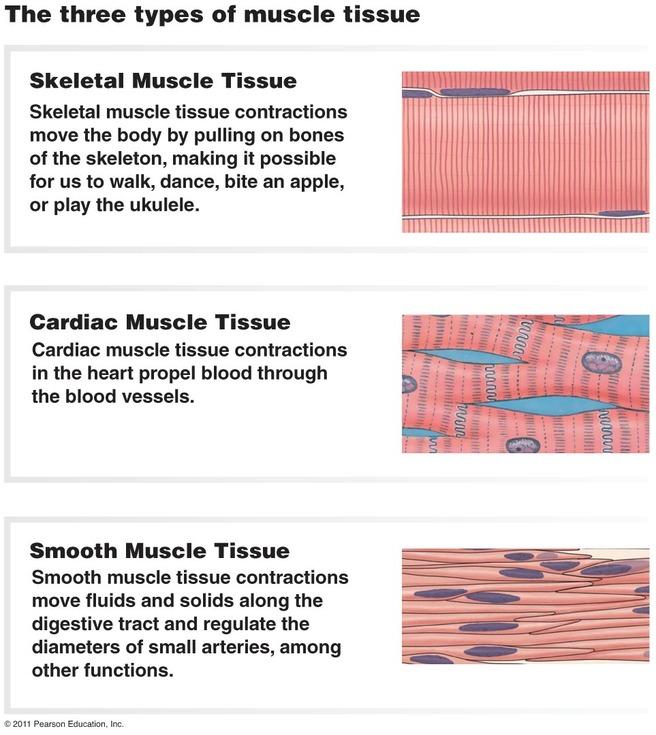
The muscular system is an organ system composed of specialized contractile tissue called the muscle tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue, based on which all the muscles are classified into three groups: Cardiac muscle, which forms the muscular layer of the heart ( myocardium )

Is muscle tissue a connective tissue?
An individual skeletal muscle may be made up of hundreds, or even thousands, of muscle fibers bundled together and wrapped in a connective tissue covering. Each muscle is surrounded by a connective tissue sheath called the epimysium.
How does muscle tissue differ from connective and nervous tissue?
Epithelial tissues act as coverings controlling the movement of materials across the surface. Connective tissue integrates the various parts of the body and provides support and protection to organs. Muscle tissue allows the body to move. Nervous tissues propagate information.
Why muscle is not a connective tissue?
Solution : Muscle is not a connective tissue. It is composed of long, cylindrical, numerous fine fibrils called myofibrils. Bone is a dense, hard, connective tissue. Blood is a liquid connective tissue.
What are the 4 types of connective tissue?
The extracellular matrix between the cells usually includes fibers of one or more types embedded in an amorphous ground substance. Connective tissues are classified into four classes: BLOOD, BONE, CARTILAGE, CONNECTIVE TISSUE PROPER.
What is an connective tissue?
Listen to pronunciation. (kuh-NEK-tiv TIH-shoo) Tissue that supports, protects, and gives structure to other tissues and organs in the body. Connective tissue also stores fat, helps move nutrients and other substances between tissues and organs, and helps repair damaged tissue.
What are the 3 types of connective tissue?
Connective tissue can further be broken down into three categories: loose connective tissue, dense connective tissue, and specialized connective tissue. Loose connective tissue works to hold organs in place and is made up of extracellular matrix and collagenous, elastic and reticular fibers.
What tissue is not connective tissue?
Answer and Explanation: Bone, blood, cartilage, and tendons are all considered connective tissue. The epidermis is not considered connective tissue and is categorized as epithelial tissue.
Where is connective tissue found in the human body?
In embryology it develops from the mesoderm. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three outer membranes (the meninges) that envelop the brain and spinal cord are composed of dense inert connective tissue.
What is the difference between muscles and nerves?
The main difference between muscle cells and nerve cells is that muscle cells are responsible for the contraction and relaxation of muscles whereas nerve cells are responsible for the coordination of the functions of the body through the transmission of nerve impulses between the body and the central nervous system.
What is the difference between the nervous tissue and the nervous system?
What is the difference between the nervous tissue and the nervous system?...Nervous tissueNervous system1. It is a tissue made up of a number of nerve cells. It works to perform a particular function1. It is a group of nervous tissue that manages a number of nervous tissues1 more row
What distinguishes nervous tissue from other tissues?
Nervous tissue is made up of nerve cells called as neurons, whose primary function is to carry messages from one body part to another. The different nervous tissues which work together in the body make up the nervous system, which is essential for proper functioning of the body.
What are the different types of connective tissue?
The connective tissues include several types of fibrous tissue that vary only in their density and cellularity, as well as the more specialized and recognizable variants—bone, ligaments, tendons, cartilage, and adipose (fat) tissue.
Which connective tissue encircles a group of muscle fibres, forming a fascicle?
These and other connective tissues associated with muscles follow: The perimysium encircles a group of muscle fibres, forming a fascicle. The epimysium encircles all the fascicles to form a complete muscle. A tendon is a cordlike extension of the preceding three linings.
What causes muscle hypertrophy?
Muscle hypertrophy (growth) occurs due to an external stimuli, such as resistance training, causing damage to muscle fibers. This growth occurs during rest, as specialised cells called satellite cells are activated (post stimulus); these cells move to and fuse with muscle fibers (myocytes) and provide new nuclei to form new myofibrils (protein strands) with new sarcomeres (contractile units) consisting of new thick myosin filaments and thin actin filaments, and repair the damaged myofibrils, making them thicker and stronger. This occurs via protein synthesis, using amino acids from digested protein to form the new components/filaments of skeletal muscle cells (actin and myosin) so that new myofibrils can be added to the myocytes and the damaged myofibrils can be repaired. Growth factors such as HGH and testosterone increase the uptake and incorporation of amino acids into damaged protein filaments in skeletal muscle cells, and increases cellular protein synthesis, so more amino acids can also be used to form new protein filaments that make up the protein strands of the cell. This means that the myocytes have a greater number of thicker myofibrils, causing them to be bigger, thus the muscles appear to be visibly larger.
Which type of connective tissue stores excess energy?
Adipose is another type of supporting connective tissue that provides cushions and stores excess energy and fat. It contains reticular cells and is made up of reticular fibers. The extracellular substance of adipose connective tissue is made up of a tight pack of cells with a small amount of gelatinous ground substance.
Which tissue is made of actin and myosin filaments and responds to electrical stimulus and moves the bones?
Muscular tissue is made of actin and myosin filaments and responds to electrical stimulus and moves the bones or structures attached to it, on the other hand connective tissue is just very strong tissue that supports stability in the form of ligaments and also occurs in various other forms and has various functions.
Which tissue is made of sterile tissue?
Mainly connective tissue is the region btw the two lobes in anther and the lobes are having to b made of sterile tissues.
What is the skeletal muscle tissue?
Skeletal muscle tissue consists of many specialised cells called myocytes. Each myocyte consists of many tubular threads called myofibrils. Each myofibril consists of repeat contractile units called sarcomeres. Each sarcomere consists of a thick filament myosin and a thin filament actin. When skeletal muscle cells receive efferent impulses from the cerebellum/motor cortex in the brain neurotransmitters are released via temporal/spacial summation and bind to receptors on a muscle cell causing Ca2+ ions to be released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. These Ca2+ ions bind to Ca2+ binding sites on
What are the functions of connective tissue?
With the exception of blood, the main functions are to support, bind, reinforce, and protect other tissues; adipose tissue also insulates the body and stores energy. Connective tissue is characterized by a large number of similar cells dispersed in a noncellular medium called a matrix. The matrix varies in consistency, from fluid to solid. Its properties differ in different tissue types.
Which connective tissue is packed with collagen fibers that offer toughness, strength, and elasticity?
Fibrous connective tissues are packed with collagen fibers that offer toughness, strength, and elasticity. Ligaments, which connect one bone to another, and tendons, which attach muscles to bones, are examples. The inner layer of the skin also has connective tissue that contains many elastic fibers.
What are the muscles that control the movement of the bones?
Skeletal muscle is more familiar, perhaps because the movements of these bundles of filaments can be controlled. Skeletal muscle is attached to and moves the bones of the skeleton. For example, the skeletal muscles that go down the back hold the backbone and head in place. In the upper arm and upper leg, large muscles open and close the elbow and knee joints. Attached to the forearm and foreleg are the muscles used for manipulating the hand and foot. Numerous small muscles control the intricate movements of the fingers and toes. The long cells of skeletal muscle contain large numbers of filaments called myofibrils, which run lengthwise through the cytoplasm. They are marked with alternating dark and light bands.
How many muscles are there in the human body?
The body contains over 600 different muscles, but they can all be classified as one of three kinds: smooth, skeletal, and cardiac. Smooth, or visceral, muscle is found in the viscera, or internal organs, of the body. Smooth muscle is spread in delicate strands and sheets throughout the lining of the stomach and intestine, the urinary and reproductive organs, the blood vessels, the respiratory system, and elsewhere. It is controlled by the autonomic nervous system—that is, it provides for movements that are not under the mind’s conscious control but that are indispensable for various bodily functions. These movements include the shrinking of the pupil of the eye in response to bright light.
Where is cardiac muscle found?
Cardiac muscle is found in the heart. Here the cells are joined end-to-end in a continuous branching network—that is, each cell is directly connected to its neighbors. Each cardiac-muscle fiber, however, contracts and relaxes at its own rate. A small mass of tissue within the heart, called the pacemaker, coordinates these movements to produce a wave that starts with one cell and moves through each neighbor cell to produce the regular, rhythmic pumping action of the heart. Like smooth muscle, the action of cardiac muscle cannot be controlled by the conscious mind.
Which group of tissues is made up of bundles of highly active, long, and slim muscle cells or filaments?
The second large group of tissues is the muscles, made up of bundles of highly active, long, and slim muscle cells or filaments. When these cells contract in unison, they are capable of moving the bones to which their ends are attached.
What is the matrix of bone?
The matrix of bone is hardened by minerals, particularly calcium salts, which give bone its solidity and strength. Another type of supporting connective tissue is cartilage, which is more flexible than bone. At the other extreme is blood, in which red blood cells and white blood cells are suspended in a watery matrix called blood plasma.
What is the function of connective tissue?
Additionally, connective tissues also perform the function of insulation (adipose tissue), functions performed by blood and lymph like in distribution of nutrition and oxygen throughout body’s tissue, as well in supporting network of bones and muscles.
What is the role of connective tissue in the body?
It is responsible for the formation and organizing skeleton, blood and muscles, fat and the nerves. Among all organs, connective tissues play a vital and important role among all.
What is epithelial tissue made of?
Epithelial tissue. Connective tissue. Made up of. Cells and small amount of intercellular matrix. Cells and a huge amount of intercellular matrix. Role. 1.Mainly forms covering of the organs, internally and externally. 2.Helps in transcellular or intercellular transportation.
What are the three types of tissues?
Epithelial and connective tissues are among four of the major and vital kinds of animal tissues. Mainly there are three types of epithelial tissues, based on their shapes: simple, columnar and cuboidal, and are also classified on the basis of organization of layers of cells present which can be simple epithelium (single layer) ...
What are organs made of?
Conclusion. Organs are made up of tissues and tissues are made up of cells which are known to perform different functions. Among four major kinds of tissues present in animal body’s, epithelial and connective tissues are the two most important one.
What are the three segments of connective tissue?
Every connective tissue differs from three segments: cell or lymph, ground, and fibers substance. Blood and lymph do not contain fiber segment. Below we will differentiate between two types of tissue and a small description on them.
Which tissue is bounded by special proteins?
Bounded by special proteins, desmosomes and hemidesmosomes are epithelial tissu es; connective tissues are bounded by blood capillaries and materials like elastin or collagen fibers.
What is connective tissue?
Connective tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesoderm.
What are the different types of connective tissue?
Other kinds of connective tissues include fibrous, elastic, and lymphoid connective tissues. Fibroareolar tissue is a mix of fibrous and areolar tissue. Fibromuscular tissue is made up of fibrous tissue and muscular tissue. New vascularised connective tissue that forms in the process of wound healing is termed granulation tissue.
Why do adipose cells keep together?
Although there is no dense collagen network in adipose tissue, groups of adipose cells are kept together by collagen fibers and collagen sheets in order to keep fat tissue under compression in place (for example, the sole of the foot). Both the ground substance and proteins (fibers) create the matrix for connective tissue.
What is the difference between dense and loose connective tissue?
Loose and dense connective tissue are distinguished by the ratio of ground substance to fibrous tissue. Loose connective tissue has much more ground substance and a relative lack of fibrous tissue, while the reverse is true of dense connective tissue.
What is the new vascularised connective tissue that forms in the process of wound healing called?
New vascularised connective tissue that forms in the process of wound healing is termed granulation tissue. Type I collagen is present in many forms of connective tissue, and makes up about 25% of the total protein content of the mammalian body. Bone & cartilage can also be grouped into supportive connective tissue.
What is collagen type 1?
Type I collagen is present in many forms of connective tissue, and makes up about 25% of the total protein content of the mammalian body.
What is the role of loose and dense irregular connective tissue?
Loose and dense irregular connective tissue, formed mainly by fibroblasts and collagen fibers, have an important role in providing a medium for oxygen and nutrients to diffuse from capillaries to cells, and carbon dioxide and waste substances to diffuse from cells back into circulation.