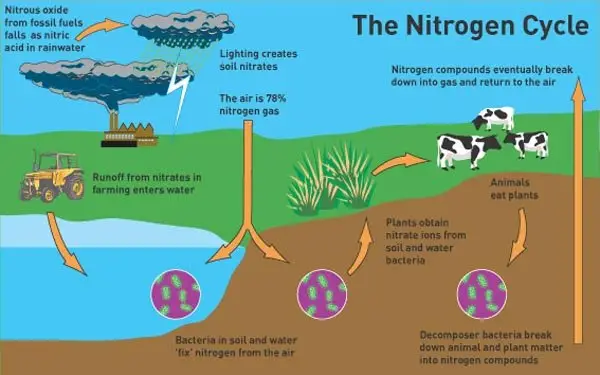
What does nitrogen do to help plants?
Nov 02, 2016 · Nitrogen is a component of nucleic acid that forms DNA a genetic material significant in the transfer of certain crop traits and characteristics that aid in plant survival. It also helps hold the genetic code in the plant nucleus.
How does nitrogen affect plants?
Jun 01, 2020 · Nitrogen is part of the chlorophyll molecule, which gives plants their green color and is involved in creating food for the plant through photosynthesis. Because nitrogen can move around in the plant, older growth often yellows more than the new growth. Nitrogen is also the primary building block for plant protoplasm.
What is the purpose of nitrogen in plants?
Nitrogen is an essential plant nutrient being a component of amino acids, nucleic acids, nucleotides, chlorophyll, enzymes, and hormones. N promotes rapid plant growth and improves grain yield and grain quality through higher tillering, leaf area development, grain formation, grain filling, and protein synthesis.
How does nitrogen increase the growth of plants?
Nitrogen is part of the chlorophyll molecule, which gives plants their green color and is involved in creating food for the plant through photosynthesis. Because nitrogen can move around in the plant, older growth often yellows more than the new growth. Nitrogen is also the primary building block for plant protoplasm.
See more
Oct 08, 2021 · In fact, the major function of nitrogen in plants is to offer biochemical-reaction power. Plants simply cannot live without nitrogen. Growth and reproduction depend too heavily on nitrogen, which should encourage gardeners to apply this nutrient to the ground with a generous hand. 3. Offers Cell Structure.

What are 3 functions of nitrogen in plants?
What is the importance of N in soil?
What does N mean in plants?
How does nitrogen fertilizer affect plant growth?
What is the role of nitrogen?
What form of nitrogen do plants use?
Why is nitrogen used in fertilizer?
What is the function of nitrogen in plants and animals?
What is the nitrogen part of a plant?
Nitrogen makes up part of the chlorophyll in plants. Chlorophyll is the green part of leaves and stems. Light energy is taken by the chlorophyll and used to make sugars for the plant.
Where is nitrogen found in plants?
Nitrogen may be found in various parts of the plant in different forms. There is nitrogen in the leaves, grain, plant tissue and roots of plants. Nitrogen may function as part of the plant structure or be involved in the life processes.
Why is Nitrogen Important to Plants?
Nitrogen is much needed for plant growth, formation of chlorophyll and processing of plant food through photosynthesis. Without enough nitrogen, the plants possibly undergo stunt growth with lesser yield.
Functions of Nitrogen in Plants
Nitrogen is mainly involved in photosynthesis in plants as it is an essential component of chlorophyll, a green pigment essential for photosynthesis.
Nitrogen Deficiency
Nitrogen deficiency in plants can occur when carbon-rich organics such as sawdust are added to the soil. Soil organisms use nitrogen to break down carbon sources, which makes nitrogen unavailable to plants.
How is Nitrogen Used in Hydroponic Grow?
Before we know how nitrogen is used in hydroponics, let us know about what hydroponic grow means.
What is the role of nitrogen in plants?
Nitrogen is the essential nutrient for the growth and development of plants, enhancing plant height by its stimulative effect on cell divisions and cell enlargement (Leghari et al., 2016; Tiwari et al., 2002).
How does nitrogen loss affect plant growth?
In agricultural production, nitrogen loss leads to economic loss and is a high environmental risk affecting plant growth, yield, and quality. Use of the N fertilizer with a urease inhibitor is thus necessary to minimize N losses and increase the efficiency of N. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of N- (n-butyl) Thiophosphoric Triamide (NBPT) on the growth, yield, and quality of pineapple. The experiment involved two foliar fertilizer treatments: 1% (w/v) urea solution with NBPT (2.25 mL kg−1 urea) was treated as NLU (NBPT Liquid Urea), and the same concentration of urea without NBPT served as the control. Both were applied 12 times, starting 1 month after planting (MAP) and continuing once a month for 12 months. The application of urea with NBPT notably increased the above-ground dry biomass per plant (20% and 10% at 8 and 12 MAP, respectively), leaf area per plant (23% and 15% at 8 and 12 MAP, respectively), N accumulation per plant (10%), PFPN (Partial Factor Productivity) (13%), and average fruit weight (15%) compared to the treatment with urea alone (control). The analysis of quality parameters indicated that urea with NBPT improves TSS (Total Soluble Solids) (19%), ascorbic acid (10%), and sucrose (14%) but reduces the total organic acid content (21%) in pineapple. When using urea with a urease inhibitor (NBPT), there was a significant improvement in growth, yield, quality, and nitrogen use efficiency, with the additional benefit of reduced nitrogen losses, in combination with easy handling. Hence, urea with a urease inhibitor can be used as a viable alternative for increasing pineapple yield by boosting growth with better fruit quality.
Is nitrogen a macronutrient?
However, its efficiency depends upon the rate and timings of fertilizer application and the cultivar under consideration. Nitrogen (N) is one of the essential macronutrients as it plays a vital role in crop growth and development and yield production Leghari et al., 2016).
Is nitrogen a food?
Nitrogen being a major food for plants is an essential constituent of protein (build from amino acids that. involves in catalization of chemical responses and transportation of electrons) and chlorophyll (enable the. process of p hotosynthesis) present in many major portions of the plant body.
What is nitrogen in plants?
Nitrogen is an important component of many essential structural, genetic and metabolic compounds in plant cells. It is also an elementary constituent of numerous important organic compounds including amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids, enzymes, and the chlorophyll molecule. Of all the essential nutrients, nitrogen is the one ...
What does it mean when a plant is lacking nitrogen?
Plants lacking nitrogen have very slow growth and look weak and stunted. Older leaves have a light green or yellow color. As nitrogen is mobile in the plant and moves to where it is needed, these older and lower leaves are always first to show symptoms of deficiency.
Do legumes need nitrogen?
Adding nitrogen is not recommended for legume crops such as soybean, since they manufacture their own nitrogen supply. Nitrogen-fixing soil organisms (rhizobium) associated with the roots of legumes capture atmospheric nitrogen and make it available to the plant.
How to tell if a plant has low nitrogen?
Older leaves have a light green or yellow color. As nitrogen is mobile in the plant and moves to where it is needed , these older and lower leaves are always first to show symptoms of deficiency.
Can you add nitrogen to soybeans?
Once inside the plant, NO 3 is reduced to the NH 2 form and is assimilated to form the organic compounds. Adding nitrogen is not recommended for legume crops such as soy bean, since they manufacture their own nitrogen supply.
