
See more
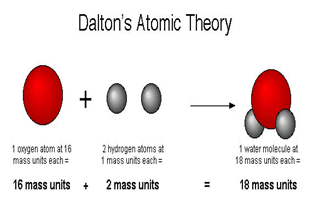
How does Dalton’s atomic theory explain the law of conservation of mass?
Since it states that atoms cannot be created or destroyed, Dalton’s theory suggests that the net mass of the participating species in a chemical re...
How does Dalton’s atomic theory differentiate between elements and compounds?
This theory states that elements combine in fixed, whole-number ratios to form compounds. Therefore, it suggests that compounds are made up of mole...
What are the 5 key postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory?
The 5 postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory are listed below. All matter is made up of atoms, which are tiny, indivisible particles. All the atoms o...
List two merits of Dalton’s atomic theory.
One of the most important merits of Dalton’s atomic theory is the fact that the theory does not violate several fundamental laws of chemical combin...
What are the shortcomings of Dalton’s atomic theory?
Some important demerits of Dalton’s atomic theory are listed below. The theory did not account for the existence of subatomic particles (it suggest...
Do electrons actually exist?
Most of us realize that the neutron, in an atom of matter, is a negatively charged particle orbiting the nucleus. No two electrons at the same time...
Which atomic model is used today?
The Bohr paradigm, generally speaking, encapsulates the popular understanding of the atom. In artwork that depicts a central atomic nucleus and ova...
Why can’t you see an atom with the naked eye?
We can not see an atom with naked eyes because an atom is extremely small and is not perceptible.
Can atoms be divided or destroyed?
No, atoms can not be divided or destroyed. However, it can combine with other atoms to form compounds. In a chemical reaction, an atom can combine,...
How did Dalton die?
Dalton remained in Manchester and taught private pupils. Despite his growing affluence and influence, his frugality persisted. He died of a stroke and was accorded the equivalent of a state funeral by his fellow townsmen. Sydney Ross.
Who was the first scientist to apply atomic theory to chemistry?
atom: Experimental foundation of atomic chemistry. English chemist and physicist John Dalton extended Proust’s work and converted the atomic philosophy of the Greeks into a scientific theory between 1803 and 1808. His book A New System of Chemical Philosophy ( Part I, 1808; Part II, 1810) was the first application of atomic theory to chemistry.
What was Dalton's most important work?
By far Dalton’s most influential work in chemistry was his atomic theory. Attempts to trace precisely how Dalton developed this theory have proved futile; even Dalton’s own recollections on the subject are incomplete. He based his theory of partial pressures on the idea that only like atoms in a mixture of gases repel one another, whereas unlike atoms appear to react indifferently toward each other. This conceptualization explained why each gas in a mixture behaved independently. Although this view was later shown to be erroneous, it served a useful purpose in allowing him to abolish the idea, held by many previous atomists from the Greek philosopher Democritus to the 18th-century mathematician and astronomer Ruggero Giuseppe Boscovich, that atoms of all kinds of matter are alike. Dalton claimed that atoms of different elements vary in size and mass, and indeed this claim is the cardinal feature of his atomic theory . His argument that each element had its own kind of atom was counterintuitive to those who believed that having so many different fundamental particles would destroy the simplicity of nature, but Dalton dismissed their objections as fanciful. Instead, he focused upon determining the relative masses of each different kind of atom, a process that could be accomplished, he claimed, only by considering the number of atoms of each element present in different chemical compounds. Although Dalton had taught chemistry for several years, he had not yet performed actual research in this field.
What is the most likely combination for which Dalton found?
For example, methane was found to contain twice as much hydrogen as ethylene. Following Dalton’s rule of “greatest simplicity,” namely, that AB is the most likely combination for which he found ...
What is the theory of partial pressure?
He based his theory of partial pressures on the idea that only like atoms in a mixture of gases repel one another, whereas unlike atoms appear to react indifferently toward each other. This conceptualization explained why each gas in a mixture behaved independently.
Where did John Dalton live?
In Manchester he was elected president of the Literary and Philosophical Society in 1817, continuing in that office for the rest of his life. The society provided him with a laboratory after the New College moved to York. Dalton remained in Manchester and taught private pupils.
Who was the first to point out the utility of Amadeo Avogadro's theory?
However, overcoming the defects of Dalton’s theory was a gradual process, finalized in 1858 only after the Italian chemist Stanislao Cannizzaro pointed out the utility of Amadeo Avogadro’s hypothesis in determining molecular masses.
What are the merits of Dalton's atomic theory?
One of the most important merits of Dalton’s atomic theory is the fact that the theory does not violate several fundamental laws of chemical combination such as the law of definite proportions, the law of multiple proportions, and the law of conservation of mass. Another important merit of Dalton’s atomic theory is that it provided a basis ...
How does Dalton’s atomic theory differentiate between elements and compounds?
This theory states that elements combine in fixed, whole-number ratios to form compounds. Therefore, it suggests that compounds are made up of molecules that contain two or more atoms of different elements.
What is the name of the theory that states that matter is made up of atoms?
Dalton’s Atomic Theory. Dalton’s atomic theory was a scientific theory on the nature of matter put forward by the English physicist and chemist John Dalton in the year 1808. It stated that all matter was made up of small, indivisible particles known as ‘atoms’. All substances, according to Dalton’s atomic theory , are made up of atoms, ...
Which theory failed to explain the dissimilarities in the properties of different allotropes of an element?
Dalton’s atomic theory failed to explain the dissimilarities in the properties of different allotropes of an element. This theory states that elements must combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form compounds. However, this is not necessarily true.
What does Dalton's theory say about the law of conservation of mass?
Since it states that atoms cannot be created or destroyed, Dalton’s theory suggests that the net mass of the participating species in a chemical reaction is conserved. This postulate, therefore, accounts for the law of conservation of mass.
Does Dalton's atomic theory account for subatomic particles?
It does not account for subatomic particles: Dalton’s atomic theory stated that atoms were indivisible. However, the discovery of subatomic particles (such as protons, electrons, and neutrons) disproved this postulate. It does not account for isotopes: As per Dalton’s atomic theory, all atoms of an element have identical masses and densities.
Can atoms be destroyed?
However, atoms of different element exhibit different properties and vary in mass and size. Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed. Furthermore, atoms cannot be divided into smaller particles. Atoms of different elements can combine with each other in fixed whole-number ratios in order to form compounds.
Introduction to the Dalton Atomic Model
Dalton’s atomic theory was proposed in 1804 and was the first attempt to describe matter in terms of atoms. He believed that all compounds were made of indivisible particles that combined in set ratios. Although Dalton didn’t get it completely correct, his theory set the foundation for today’s atomic model.
Law of Multiple Proportions
The law of multiple proportions says that atoms or elements can combine to form various chemical compounds. The mass ratios will be whole-number ratios of each other.
Who is John Dalton?
John Dalton is an English chemist who lived from 1766 -1844. He was a teacher at a variety of schools throughout his life. He started his first teaching position assisting his brother when he was twelve years old.
What are the two laws that Dalton formulated?
Dalton formulated his theory based on two laws: the law of conservation of mass and the law of constant composition.
What is the atomic theory of matter?
According to Dalton’s atomic theory, all substances are made up of atoms, which are indestructible and indivisible building blocks. While the atoms of one element were all the same size and mass, other elements had atoms of different sizes and weights.
What is a compound in atomic theory?
Compounds are combinations of two or more different types of atoms: In the third part of Dalton’s atomic theory, he proposed that compounds are combinations of two or more different types of atoms. An example of such a compound is Common Salt. Common Salt is a combination of two different types of elements with varying physical and chemical properties. The first, sodium, is a highly reactive metal. The second, chlorine, is a toxic gas. When they react, the atoms combine in a 1:1 ratio to form white crystals of NaCl.
What is the name of the tiny particle of an element?
A tiny particle of a chemical element is called an atom, which may or may not exist independently. Molecules refer to the group of atoms that the bond binds together, representing the smallest unit in a compound. Two or more identical or distinct atoms are chemically bonded.
Who was the first person to believe that matter is made up of particles?
Democritus is credited as being the first to postulate that matter is made up of particles. These particles were given the name atomos, which means indivisible in Greek. Democritus ’ Atomic Theory was based on this. Scientists had very little information on this idea at the time due to a lack of technical setup.
Who proposed the idea of simplifying matter?
Scientist John Dalton manifested the works on simplifying matter over two thousand years later. John Dalton proposed the famous Dalton’s Atomic Theory in 1808. In a paper titled “A New Chemical Philosophy,” he published this idea; certainly, the philosophy was novel at the time. Let’s have a look at the theory’s postulates.
Does Dalton's atomic theory violate the law of multiple proportions?
Dalton’s atomic theory. doesn’t violate the law of multiple proportions, the law of conservation of mass, and the law of constant proportions.
When did Dalton announce his atomic theory?
In 2003, on the bicentennial of Dalton's public announcement of his atomic theory, the Manchester Museum held a tribute to the man, his life and his groundbreaking scientific discoveries.
Who is credited with the discovery of atomic theory?
John Dalton. Chemist John Dalton is credited with pioneering modern atomic theory. He was also the first to study color blindness.
Who Was John Dalton?
In 1803 he revealed the concept of Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures. Also in the 1800s, he was the first scientist to explain the behavior of atoms in terms of the measurement of weight.
What was Dalton's theory of partial pressure?
Dalton's experiments on gases led to his discovery that the total pressure of a mixture of gases amounted to the sum of the partial pressures that each individual gas exerted while occupying the same space. In 1803 this scientific principle officially came to be known as Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures. Dalton's Law primarily applies to ideal gases rather than real gases, due to the elasticity and low particle volume of molecules in ideal gases. Chemist Humphry Davy was skeptical about Dalton's Law until Dalton explained that the repelling forces previously believed to create pressure only acted between atoms of the same sort and that the atoms within a mixture varied in weight and complexity.
What did John Dalton discover about color blindness?
He proved his theory to be true when genetic analysis of his own eye tissue revealed that he was missing the photoreceptor for perceiving the color green. As a result of his contributions to the understanding of red-green color blindness, the condition is still often referred to as "Daltonism."
How did John Dalton's research change the face of chemistry?
By finding a way to "weigh atoms," John Dalton's research not only changed the face of chemistry but also initiated its progression into a modern science. The splitting of the atom in the 20th century could most likely not have been accomplished without Dalton laying the foundation of knowledge about the atomic makeup of simple and complex molecules. Dalton's discoveries also allowed for the cost-efficient manufacturing of chemical compounds, since they essentially give manufacturers a recipe for determining the correct chemical proportions in a given compound.
What was John Dalton's first interest?
Membership granted Dalton access to laboratory facilities. For one of his first research projects, Dalton pursued his avid interest in meteorology.
How did Dalton come to the idea of atomism?
Dalton arrived at his view of atomism by way of meteorology, in which he was seriously interested for a long period: he kept daily weather records from 1787 until his death, his first book was Meteorological Observations (1793), and he read a series of papers on meteorological topics before the Literary and Philosophical Society between 1799 and 1801.
How did Dalton calculate atomic weights?
He proceeded to calculate atomic weights from percentage compositions of compounds, using an arbitrary system to determine the likely atomic structure of each compound. If there are two elements that can combine, their combinations will occur in a set sequence. The first compound will have one atom of A and one of B; the next, one atom of A and two atoms of B; the next, two atoms of A and one of B; and so on. Hence, water is HO. Dalton also came to believe that the particles in different gases had different volumes and surrounds of caloric, thus explaining why a mixture of gases—as in the atmosphere—would not simply layer out but was kept in constant motion. Dalton consolidated his theories in his New System of Chemical Philosophy (1808–1827).
What did Dalton believe about the atmosphere?
Dalton also came to believe that the particles in different gases had different volumes and surrounds of caloric, thus explaining why a mixture of gases—as in the atmosphere—would not simply layer out but was kept in constant motion. Dalton consolidated his theories in his New System of Chemical Philosophy (1808–1827).
Where was John Dalton born?
Dalton (1766–1844) was born into a modest Quaker family in Cumberland, England, and for most of his life—beginning in his village school at the age of 12—earned his living as a teacher and public lecturer. After teaching for 10 years at a Quaker boarding school in Kendal, he moved on to a teaching position in the burgeoning city of Manchester.
Who was the scientist who discovered the nature of atoms?
Arnold Thackray describes how John Dalton 's book on meteorology led to his discovery of the nature of atoms.
Who engraved John Dalton?
John Dalton, F.R.S., engraved by William Henry Worthington after an 1814 painting by William Allen, published June 25, 1823, in Manchester and London. Note the charts with Dalton’s atomic symbols lying on the table. Science History Institute. Dalton (1766–1844) was born into a modest Quaker family in Cumberland, England, ...
Who is the most famous scientist for atomism?
John Dalton. Although a schoolteacher, a meteorologist, and an expert on color blindness, John Dalton is best known for his pioneering theory of atomism.
