What does the Fed’s Quantitative tightening program mean for You?
Beginning today, the Federal Reserve will begin its quantitative tightening (QT) program, with the goal of lowering its balance of bonds. The central bank will effectively cease replacing matured bonds in its ownership, dropping about $50 billion per month.
When did the Fed stop quantitative easing?
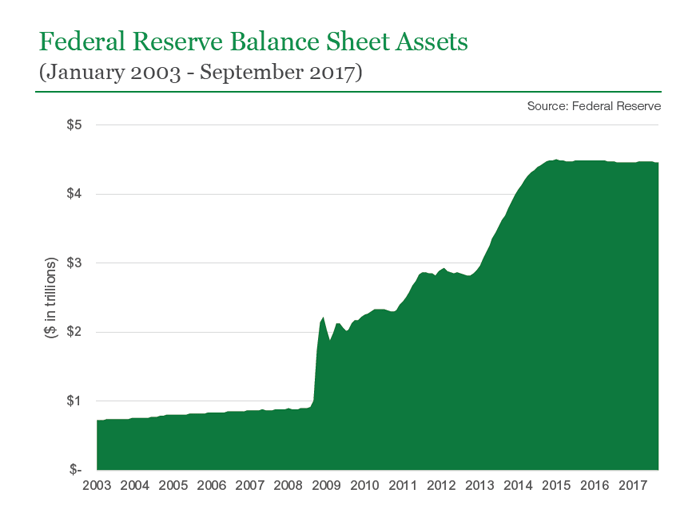
On 18 September 2013, the Fed decided to hold off on scaling back its bond-buying program, and announced in December 2013 that it would begin to taper its purchases in January 2014. Purchases were halted on 29 October 2014 after accumulating $4.5 trillion in assets. When did Fed first raise rates? How much has been spent on quantitative easing?
When will the Fed kick off quantitative Qt?
This time's onset of QT is also earlier relative to where the Fed will be in the overall tightening process. If rate futures are a guide, the Fed will lift its target rate to 0.75-1.00% in May at the same time it kicks off QT.
How much will the Fed really tighten?
After that, the central bank will actually ramp up its tightening, rolling off $95 billion per month until it deems it appropriate to stop. This is all in an effort to reduce its $8.9 trillion bond portfolio, the highest in the Fed’s history.

When did quantitative easing start and end?
In 2008, the Fed launched four rounds of QE to fight the financial crisis. They lasted from December 2008 to October 2014. The Fed resorted to QE because its other expansionary monetary policy tools had reached their limits. The Fed funds rate and the discount rate were zero.
When did quantitative easing 3 start?
September 13, 2012QE3 is an abbreviation for the third round of quantitative easing begun by the Federal Reserve on September 13, 2012. It ended in December 2012 when the Fed announced it would roll out QE4 in January 2013. QE3 was important because it set three new precedents for Fed policy.
When did quantitative easing 4 start?
QE4 was the fourth round of quantitative easing established by the Federal Reserve. The program began in January 2013 and ended in October 2014. 1 Through QE4, the Fed bought long-term U.S. Treasury notes using credit it created.
How does Fed do quantitative tightening?
Through quantitative tightening, the Federal Reserve reduces its supply of monetary reserves in order to tighten its balance sheet—and it does so simply by letting the bonds and other securities it has purchased reach maturity.
When did QE start in us?
In 2010, the Fed launched Quantitative Easing (QE) 2. This time the Fed was using the money plowed back from investments in 2008 as well as some more of its own money. The target was to buy as many Treasury securities as the Fed could lay its hands on.
When did the Fed Stop Quantitative tightening?
2019The Fed used QE for the first time in the midst of the 2008 financial meltdown and during the weak recovery that followed, then implemented QT once it thought the economy was sufficiently strong. The tightening lasted for a little less than two years, from 2017 to 2019.
When did quantitative easing start in 2008?
Nov. 25, 2008For example, on Nov. 25, 2008, the Fed announced its first QE program, sometimes called QE1.
How many times did the Fed use quantitative easing?
The Fed has implemented quantitative easing programs four times since the financial crisis of 2007-2008. The most recent quantitative easing program was undertaken in 2020 in response to the COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent recession.
Who introduced quantitative easing?
the Bank of JapanEven the invention of quantitative easing is shrouded in controversy. Some give credit to economist John Maynard Keynes for developing the concept; some cite the Bank of Japan for implementing it; others cite economist Richard Werner, who coined the term.
Is the Fed still quantitative easing?
An end to the era of “quantitative easing” Along with adjusting short-term interest rates, another strategy the Fed has implemented in more challenging economic periods is known as quantitative easing (QE). In these instances, the Fed uses its purchasing power to buy longer-term securities on the open market.
Why did the Fed use quantitative easing?
In response to the COVID pandemic, the Federal Reserve used quantitative easing (QE) – that is, large-scale purchases of Treasury securities and agency mortgage-backed securities – both to support market functioning and to ease financial conditions and strengthen the economic recovery.
Does quantitative tightening increase interest rates?
A central bank implements quantitative tightening by reducing the financial assets it holds on its balance sheet by selling them into the financial markets, which decreases asset prices and raises interest rates.
What is the FOMC's replacement for Operation Twist?
FOMC Statement announces Treasury bond buying program to replace Operation Twist at the beginning of 2013: “To support a stronger economic recovery and to help ensure that inflation, over time, is at the rate most consistent with its dual mandate, the Committee will continue purchasing additional agency mortgage-backed securities at a pace of $40 billion per month. The Committee also will purchase longer-term Treasury securities after its program to extend the average maturity of its holdings of Treasury securities is completed at the end of the year, initially at a pace of $45 billion per month. The Committee is maintaining its existing policy of reinvesting principal payments from its holdings of agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities in agency mortgage-backed securities and, in January, will resume rolling over maturing Treasury securities at auction.
When will the Fed stop the runoff?
Fed’s website states *: “At the conclusion of its July 2019 meeting, the FOMC announced that it intended to cease the runoff of its securities portfolio, noting that beginning in August 2019, principal payments received from agency debt and agency MBS up to $20 billion per month would be reinvested in Treasury securities to roughly match the maturity composition of Treasury securities outstanding; principal payments in excess of $20 billion per month would continue to be reinvested in agency MBS. Also beginning in August, all maturing Treasury securities in the SOMA portfolio would be rolled over at Treasury auctions following usual practices.” (Also see July 31, 2019 FOMC statement .)
What is the FOMC's extension?
FOMC Statement announces extension of Operation Twist: “The Committee also decided to continue through the end of the year its program to extend the average maturity of its holdings of securities. Specifically, the Committee intends to purchase Treasury securities with remaining maturities of 6 years to 30 years at the current pace and to sell or redeem an equal amount of Treasury securities with remaining maturities of approximately 3 years or less. This continuation of the maturity extension program should put downward pressure on longer-term interest rates and help to make broader financial conditions more accommodative. The Committee is maintaining its existing policy of reinvesting principal payments from its holdings of agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities in agency mortgage-backed securities. The Committee is prepared to take further action as appropriate to promote a stronger economic recovery and sustained improvement in labor market conditions in a context of price stability.”
What is the FOMC statement?
FOMC Statement evaluates benefits of purchasing longer-term Treasury Securities: “As previously announced, over the next few quarters the Federal Reserve will purchase large quantities of agency debt and mortgage-backed securities to provide support to the mortgage and housing markets, and it stands ready to expand its purchases of agency debt and mortgage-backed securities as conditions warrant. The Committee is also evaluating the potential benefits of purchasing longer-term Treasury securities.”
What is the FOMC rollover program?
FOMC Statement announces rollover program: “To help support the economic recovery in a context of price stability, the Committee will keep constant the Federal Reserve’s holdings of securities at their current level by reinvesting principal payments from agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities in longer-term Treasury securities.1 The Committee will continue to roll over the Federal Reserve’s holdings of Treasury securities as they mature.”
What is the FOMC addendum?
FOMC Addendum to the Policy Normalization Principles and Plans states, “The Committee intends to gradually reduce the Federal Reserve’s securities holdings by decreasing its reinvestment of the principal payments it receives from securities held in the System Open Market Account.
When will the balance sheet normalization cap be reduced?
Press release titled “ Balance Sheet Normalization Principles and Plans ” states: (1) “The Committee intends to slow the reduction of its holdings of Treasury securities by reducing the cap on monthly redemptions from the current level of $30 billion to $15 billion beginning in May 2019. ”.
When did the last round of quantitative easing end?
The last round of quantitative easing ended in October 2014. The FOMC maintained the size of the balance sheet until late 2017.
How did the Fed help the economy?
These actions were meant to put downward pressure on interest rates, thereby easing financial conditions and stimulating the economy .
What is the FOMC's extension program?
1 From late 2011 to the end of 2012, the FOMC also used a maturity extension program (often called “Operation Twist”), which involved selling or redeeming shorter-term Treasury securities and purchasing longer-term Treasury securities. The purpose of this program was also to reduce longer-term interest rates.
When will the Fed end its treasury cap?
In March 2019, the FOMC announced that the cap on Treasuries running off the Fed’s balance sheet would be reduced: from $30 billion per month to $15 billion per month, beginning in May 2019. The FOMC also announced its intention to end the reduction of its securities holdings in September 2019. The end date is not set in stone, however. As stated in the Federal Reserve Board’s July 2019 Monetary Policy Report: “The Committee [FOMC] is prepared to adjust the details for completing balance sheet normalization in light of economic and financial developments, consistent with its congressionally mandated objectives of maximum employment and price stability.”
What was the purpose of the QE program?
The purpose of this program was also to reduce longer-term interest rates. The Fed mostly purchased longer-term Treasury securities and mortgage-backed securities. 2. During the three QE programs, the Fed purchased the following types of securities:
How much was the Fed's balance sheet before the recession?
The total size of the Fed’s balance sheet (red line, right scale), which rose from less than $900 billion before the recession (marked by the shaded area) to about $4.5 trillion at the balance sheet’s peak.
What is the target rate for the Fed?
The Fed’s main monetary policymaking body, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), established a target range for the federal funds rate (that is, the policy rate) of 0%-0.25% in December 2008 and kept it there for seven years. The FOMC also used forward guidance during that period to indicate how long or under what economic conditions the policy rate would likely remain near zero.
