Why was JJ Thompson model called plum pudding?
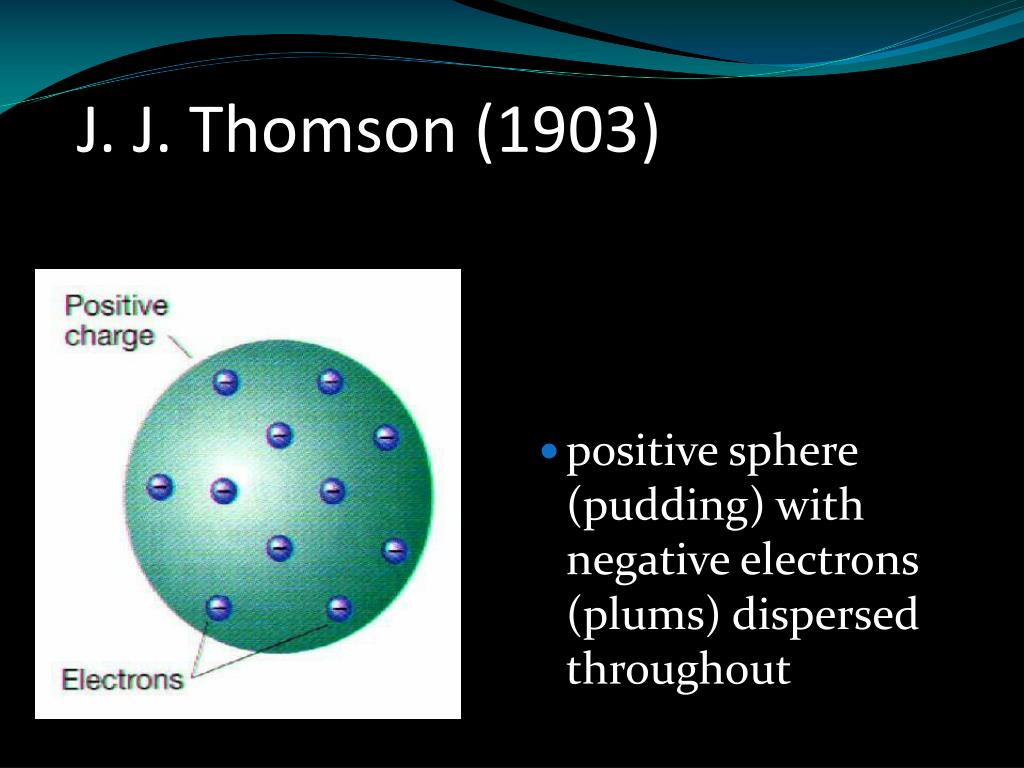
Thomson’s model showed an atom that had a positively charged medium, or space, with negatively charged electrons inside the medium. Soon after its proposal, the model was called a ‘plum pudding’ model because the positive medium was like a pudding, with electrons, or plums, inside.
How did Thomson come up with the plum pudding model?
Thomson realized that the accepted model of an atom did not account for negatively or positively charged particles. Therefore, he proposed a model of the atom which he likened to plum pudding. Click to see full answer.
Did Thomson invent the plum pudding model?
The plum pudding model is one of several historical scientific models of the atom.First proposed by J. J. Thomson in 1904 soon after the discovery of the electron, but before the discovery of the atomic nucleus, the model tried to explain two properties of atoms then known: that electrons are negatively charged particles and that atoms have no net electric charge.
What model did JJ Thomson make?
Postulates of Thomson’s Atomic Model
- The atom has a neutral charge.
- There is a source of positive charge that neutralizes the negative charge of electrons.
- This positive charge is evenly distributed in the atom.
- In Thomson’s words: “negatively electrified corpuscles,” that is, electrons, are contained within the uniform mass of positive charge.
What is the Thomson problem in the Plum Pudding model?
What is the Plum Pudding Model?
What is the charge of a plum pudding?
Why are electrons stable?
Why did Thomson propose a positive volume charge?
What is the name of the atom that has no electric charge?
What is the vortex theory of the atom?
See 4 more
About this website

Why did J.J. Thomson create the plum pudding model?
In 1897, J. J. Thomson discovered the first subatomic particle, the electron, while researching cathode rays. To explain the neutrality of atoms, Thomson proposed a model of the atom in which negative electrons are scattered throughout a sphere of positive charge. He called his atom the plum pudding model.
What is plum pudding model 1904?
Thomson in 1904 and is known as the Plum pudding model or the Thomson model of the atom. According to the plum pudding model, an atom consists of a sphere of positive matter within which electrostatic forces determine the positioning of the negatively charged corpuscles.
When did J.J. Thomson make his discovery?
April 30, 1897On his return from America, he achieved the most brilliant work of his life – an original study of cathode rays culminating in the discovery of the electron, which was announced during the course of his evening lecture to the Royal Institution on Friday, April 30, 1897.
When was J.J. Thomson atomic theory?
On April 30, 1897, British physicist J.J. Thomson announced his discovery that atoms were made up of smaller components. This finding revolutionized the way scientists thought about the atom and had major ramifications for the field of physics.
Why did the plum pudding model fail?
∙ It failed to explain the concept of nucleus of an atom, which was later on discovered by Rutherford. Rutherford also discovered that the electrons revolve around the nucleus, which was not explained in the plum pudding model.
Why did J.J. Thomson's model fail?
The failure of Thomson's atomic model results from its inability to detect the nucleus of an atom. The model did not correctly account for the movement of electrons.
What did JJ Thomson discover in 1897?
In 1897 Thomson discovered the electron and then went on to propose a model for the structure of the atom. His work also led to the invention of the mass spectrograph. The British physicist Joseph John (J. J.)
What did JJ Thomson discover in 1890?
Thomson, in full Sir Joseph John Thomson, (born December 18, 1856, Cheetham Hill, near Manchester, England—died August 30, 1940, Cambridge, Cambridgeshire), English physicist who helped revolutionize the knowledge of atomic structure by his discovery of the electron (1897).
What did JJ Thomson discover in 1906?
In 1906, Thomson demonstrated that hydrogen had only a single electron per atom. Previous theories allowed various numbers of electrons.
What was JJ Thomson theory called?
Thomson's model came to be called the "plum pudding model" or "chocolate chip cookie model". Modern scientists understand atoms consist of a nucleus of positively-charged protons and neutral neutrons, with negatively-charged electrons orbiting the nucleus.
Who disproved the plum pudding model?
RutherfordAnswer and Explanation: Rutherford disproved the Plum Pudding Model of the atom by conducting his gold foil experiment. In this experiment, Rutherford tested Thomson's Plum Pudding Model by attempting to pass a beam of alpha particles through a thin gold foil.
What was the first model of the atom?
Thomson atomic model, earliest theoretical description of the inner structure of atoms, proposed about 1900 by William Thomson (Lord Kelvin) and strongly supported by Sir Joseph John Thomson, who had discovered (1897) the electron, a negatively charged part of every atom.
What is the plum pudding model short answer?
The plum pudding model (also known as Thomson's plum pudding model) is a historical scientific model of the atom. The plum pudding model is defined by electrons surrounded by a volume of positive charge, like negatively-charged “plums” embedded in a positively-charged “pudding” (hence the name).
What happened in the plum pudding model?
In Thomson's plum pudding model of the atom, the electrons were embedded in a uniform sphere of positive charge, like blueberries stuck into a muffin. The positive matter was thought to be jelly-like, or similar to a thick soup. The electrons were considered somewhat mobile.
What is plum pudding model who discovered it?
The Plum Pudding Model is a model of atomic structure proposed by J.J. Thomson in the late 19th century. Thomson had discovered that atoms are composite objects, made of pieces with positive and negative charge, and that the negatively charged electrons within the atom were very small compared to the entire atom.
Who is the plum pudding model?
Joseph John ThomsonThomson's “Plum Pudding” Model. In 1897, Joseph John Thomson (1856–1940) had announced the discovery of a corpuscle. Others soon called it ► electron, despite Thomson's stubborn preference for his original term, borrowed from Robert Boyle (1627–91) to denote any particlelike structure.
1. What was JJ Thomson's Atomic Model?
J J.J. Experiments with cathode ray tubes by Thomson showed that all the atoms contain tiny subatomic particles or electrons that are negatively ch...
2. Why was JJ Thomson's Model Wrong?
At the time, Thomson's model was correct, because it explained everything scientists already understood about the atom. Thomson 's model was dismis...
3. Explain JJ Thomson's Contribution to the Atomic Theory?
In the year 1897 J.J. Thomson discovered the electron by playing with a tube that was Crookes, or cathode ray. He had shown that the cathode rays w...
4. Why is the Plum Pudding Model Wrong?
In 1911, Rutherford proved that the Thomson hypothesis was "wrong": there was no uniform distribution of both positive and negative particles. Ruth...
5. What is the Importance of JJ Thomson’s Atomic Model?
JJ Thomson’s discovery in 1897 was a revolution for its time and a landmark occasion in the history of particle physics. In this model, for the fir...
6. Why is Thomson’s Atomic model also known as the Watermelon Model?
The JJ Thomson model is also called the atomic watermelon model because it resembles both spherical plum pudding and watermelon. It is also compare...
7. What was the Rutherford Experiment?
In 1909, the physicist Rutherford along with Ernest Marsden performed an experiment which is known as the Rutherford alpha scattering experiment wa...
8. What is an Alpha Particle?
An Alpha particle, also known as alpha rays or alpha radiation, consists of protons and neutrons bound together into a particle which is identical...
9. What do the Latest study on Electrons and the Model of the Atom tell us?
According to the latest research, The orbital theory of elections has been the most exciting field where electrons are considered as clouds of nega...
Plum Pudding Atomic Model by J. J. Thomson ~ ChemistryGod
J. J. Thomson's plum pudding atomic model Explanation. Thomson studied magnetic and electric properties of cathode rays. He described that cathode rays were negatively charged corpuscles, which were later renamed as electrons, and were constituents of atoms.
JJ Thomson Plum Pudding Model Experiment | Metallurgy | Metal & Non ...
Factors Affecting Microstructure of Cast Iron The structure of Cast iron is affected by the following factors: Carbon Content The higher the iron’s carbon content, the greater will be the tendency for it to solidify grey.
Which model replaced Thomson's Plum Pudding Model?
Hence the Ernest Rutherford’s nuclear model of the atom in 1911 replaced the Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model.
What is the name of the particle that is negatively charged?
At the time of discovery, J.J. Thomson called this negatively charged particle a corpuscles . Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model is the first model to represent the atomic structure of matter. According to Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model, a substance is consists of small spheres which are having the radius of about 10 -10 m in diameter.
Why was the Plum Pudding Model given up?
The Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model was given up as it failed to explain the existence of some observed phenomena. This model failed to explain the emission of electron spectrum consisting of different frequencies from Thomson’s atom when it is subjected to external frequencies emitted from other substances. It also failed to explain the existence of ...
What was the first modern attempt to construct a theory of atomic structure?
After Ernest Rutherford’s nuclear model of the atom in 1911, the interest in Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model fell off rapidly. But the Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model assumed its place in history as the first modern attempt to construct a theory of atomic structure.
What is the plum pudding model?
The plum pudding model (also known as Thomson’s plum pudding model) is a historical scientific models of the atom. The plum pudding model is defined by electrons surrounded by a volume of positive charge, like negatively-charged “plums” embedded in a positively-charged “pudding” (hence the name). The plum pudding model was first proposed by ...
What is the positive charge of a sphere?
The positive charge is spread uniformly throughout the volume of sphere called pudding. The negatively charged particles Electrons called Plums are distributed as point charges in shells as shown in figure below-. The positively charged sphere exerts the force on negatively charged electrons. The direction of the net force on negatively charged ...
Which direction does net force go on negatively charged electrons?
The direction of the net force on negatively charged electrons due to positively charged sphere is towards the center of the sphere. These negatively charged electrons repel each other and form the shells. Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model hold sway for few years until the Ernest Rutherford announced the nuclear model of the atom in the year of 1911.
What did Rutherford prove about the Thomson hypothesis?
Rutherford has shown the atom has a small, massive, positively charged nucleus in it. He has also confirmed with Nagaoka that the electrons move outside the nucleus in circular orbits.
What is the watermelon model of atom?
This model is also called as watermelon model of atom because it resembles a spherical plum pudding as well as a watermelon.
What was the next step after subatomic particles were discovered?
Since the intact atom had no charge and the electron and proton had opposite charges, the next step after subatomic particles were discovered was to determine how these particles were arranged in the atom. Because of the incredibly small size of the atom this is a difficult task.
What was the goal of the atomic model?
The goal of each atomic model was to present all the experimental evidence of atoms in the simplest way possible. Thomson proposed the atom should be composed of electrons surrounded by a broth of positive charge to counteract the negative charges of the electrons. Which led to plum pudding model.
What is the atom surrounded by?
In this model, the atom consists of electrons (which Thomson called them "corpuscles") surrounded by a soup of positive charge to counteract the negative charges of the electrons, like "plums" charged negatively surrounded by "pudding" charged positively. The electrons were assumed to be positioned in revolving circles throughout the atom.
What is the red part of a watermelon compared to?
The model was also compared with a watermelon because the red edible part of a watermelon was compared to the positively charged sphere and the black seeds filling the watermelon looked similar to the electrons inside the sphere. An atom consists of a positively charged sphere, and it embeds the electrons.
Which experiment showed that all atoms contain tiny subatomic particles or electrons that are negatively charged?
J J.J. Experiments with cathode ray tubes by Thomson showed that all the atoms contain tiny subatomic particles or electrons that are negatively charged. Thomson suggested the atom's plum pudding model, which had negatively charged electrons trapped in a "soup" filled with positive effect.
What did Thomson conclude about the size of particles?
Using this ratio, Thomson concluded the size of these particles was even smaller than of a hydrogen ion. At that time, it was known the atoms were electrically neutral. To explain this, he introduced the presence of the positive charge in an atom such that the positive charge counterbalances the negative charge.
What is the shape of an atom?
According to Thomson, the atom was spherical in shape. The atom consisted of the negatively charged particles. The negatively charged particles or electrons were floating in a positively charged soup (or ocean). An atom was electrically neutral. The positive and negative charge in the atoms were equal.
What did Thomson study?
Thomson studied magnetic and electric properties of cathode rays. He described that cathode rays were negatively charged corpuscles, which were later renamed as electrons, and were constituents of atoms. He also calculated the mass-to-charge ratio of these particles.
What is the name of the model of the cloud of uniform positive charge?
Hence, the model got its name the plum pudding model. Comparison between plum pudding and atom.
Why was Rutherford's gold scattering experiment rejected?
The model was rejected because it was ineffective to justify light spectrum.
Who proposed the plum pudding atomic model?
The plum pudding atomic model or atomic theory is one of the earlier atomic theories. The model was proposed by J. J. Thomson, who is also known for the discovery of the electron. From his cathode-ray tube experiments, he realized that atoms consisted of negatively particles (electrons), which he called corpuscles. He imagined an atom as negatively charged particles floating in the positively charged soup and put forward his theory in 1904.
Which sphere experiences the net electrostatic force?
As per the model, the negatively charged electrons experience the net electrostatic force by the positively charged sphere towards the centre of the atom. There is also a repulsive force between electrons.
Why is the Plum Pudding Model important?
Though defunct by modern standards, the Plum Pudding Model represents an important step in the development of atomic theory. Not only did it incorporate new discoveries, such as the existence of the electron, it also introduced the notion of the atom as a non-inert, divisible mass. Henceforth, scientists would understand that atoms were themselves composed of smaller units of matter and that all atoms interacted with each other through many different forces.
Why is plum pudding called plum pudding?
And from this, the Plum Pudding Model was born, so named because it closely resembled the English desert that consists of plum cake and raisins. The concept was introduced to the world in the March 1904 edition of the UK’s Philosophical Magazine, to wide acclaim.
What was the significance of the Plum Pudding Model?
His work in determining that atom’s were divisible, as well as the existence of electromagnetic forces within the atom, would also prove to be major influence on the field of quantum physics.
What is the name of the theory that states that atoms react in whole numbers?
atoms. Through a series of experiments involving gases, Dalton went on to develop what is known as Dalton’s Atomic Theory . This theory expanded on the laws of conversation of mass and definite proportions – formulated by the end of the 18th century – and remains one of the cornerstones of modern physics and chemistry.
What was the smallest atom in the 19th century?
However, most scientists ventured that this unit would be the size of the smallest known atom – hydrogen. By the end of the 19th century, the situation would change drastically.
Which model of the atom is surrounded by an equal number of electrons in orbital shells?
the Bohr Model ).
What episode of Astronomy Cast is the standard model?
Astronomy Cast also has some episodes on the subject: Episode 138: Quantum Mechanics, Episode 139: Energy Levels and Spectra, Episode 378: Rutherford and Atoms and Episode 392: The Standard Model – Intro.
Why Did it Fail?
Rutherford set out to verify the model in 1907. When he bombarded a gold foil with alpha particles, he expected that most of the particles will pass through the sphere of the atom with minor deflections. What he noticed was that almost all passed through and only a few deflected back by 180 degrees. This meant that the picture sketched by this model of the atom was inaccurate.
What is the Pudding Model?
The ‘Plum Pudding Model’ is one of the many theories that were hypothesized to explain atomic structure, in the beginning of the 20 th century . J.J. Thomson is known for his discovery of the electron. This was the first of the subatomic particles of an atom to be discovered. It is this discovery that led him to hypothesize this model ...
What was the nucleus of an atom discovered?
After Rutherford’s experimentation, the true nature of the atom came to be known in actuality. Quite unexpectedly, almost all the mass of an atom was discovered to be concentrated in the nucleus, which occupies very less space. If you would enlarge an atom to the size of a big room, the nucleus would be a mere speck, hard to see with the naked eye.
Why did the atom model fail?
Thus, the model failed, as its basic premise of the atom being a positive sphere, failed to be verified by experiment. The results meant that physics needed a new theory, that could account for the results of this experiment.
Why can't electrons leave the sphere?
Though the electrons could move in the confines of the sphere, they could not leave it due to Coulomb’s law of attraction.
How do scientists describe a phenomenon in nature?
To describe a phenomenon in nature, scientists hypothesize a causal model, which may become an established theory, if it passes the test of experiment. For every established theory, there are hundreds of other hypotheses that fail. Same is the case with atomic theory.
Which theory of physics was used to determine the correct model for the hydrogen atom?
As the experiment revealed, most of the atom was empty with electrons revolving around a positively-charged nucleus. Later, Bohr came up with a more accurate quantum theory of the atom. This theory had its imperfections, which were further solved through the establishment of a concrete theory of quantum physics. Ultimately, the correct model for the hydrogen atom was established through a solution of the Schrödinger equation.
What is the Thomson problem in the Plum Pudding model?
The Thomson problem is a natural consequence of the plum pudding model in the absence of its uniform positive background charge.
What is the Plum Pudding Model?
Plum pudding model. The plum pudding model is one of several historical scientific models of the atom. First proposed by J. J. Thomson in 1904 soon after the discovery of the electron, but before the discovery of the atomic nucleus, the model tried to explain two properties of atoms then known: that electrons are negatively charged particles ...
What is the charge of a plum pudding?
The plum pudding model has electrons surrounded by a volume of positive charge, like negatively charged "plums" embedded in a positively charged " pudding ".
Why are electrons stable?
In this model, the orbits of the electrons were stable because when an electron moved away from the centre of the positively charged sphere, it was subjected to a greater net positive inward force, because there was more positive charge inside its orbit (see Gauss's law ).
Why did Thomson propose a positive volume charge?
His proposal of a positive volume charge reflects the nature of his scientific approach to discovery which was to propose ideas to guide future experiments.
What is the name of the atom that has no electric charge?
Thomson called them "corpuscles" ( particles ), but they were more commonly called "electrons", the name which G. J. Stoney had coined for the " fundamental unit quantity of electricity " in 1891. It had also been known for many years that atoms have no net electric charge.
What is the vortex theory of the atom?
With this model, Thomson abandoned his 1890 "nebular atom" hypothesis, which was based on the vortex theory of the atom, in which atoms were composed of immaterial vortices and suggested that there were similarities between the arrangement of vortices and periodic regularity found among the chemical elements.
