See more
When did Pavlov conduct his dog experiment?
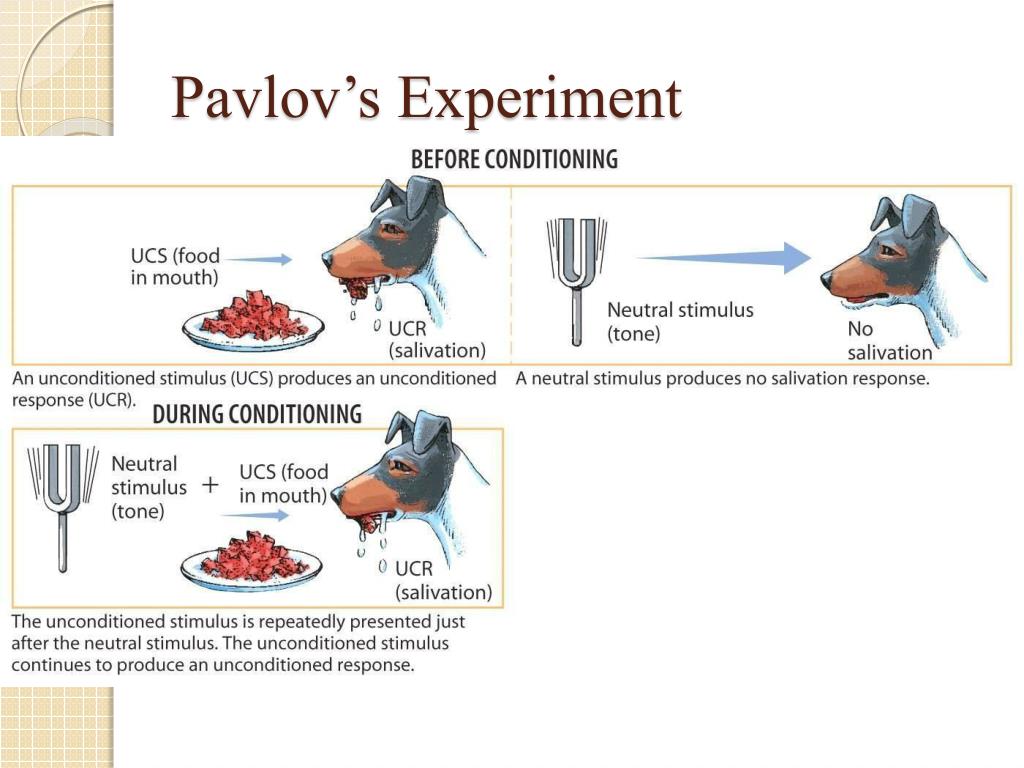
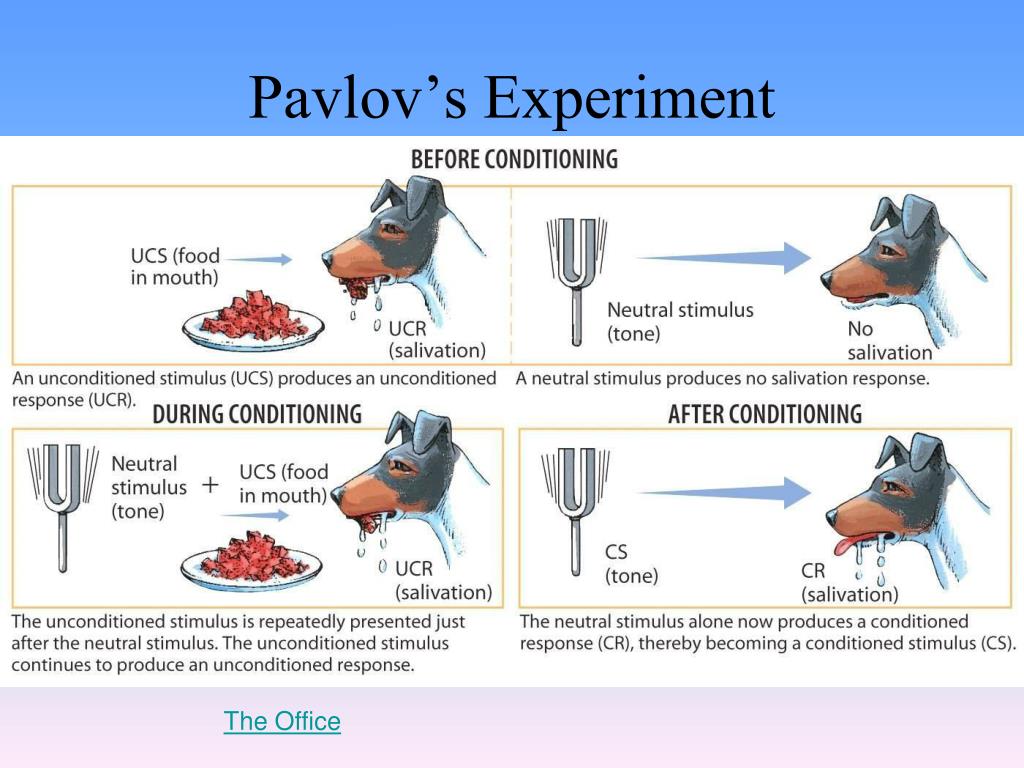
1890sDuring the 1890s, Russian physiologist, Ivan Pavlov was researching salivation in dogs in response to being fed. He inserted a small test tube into the cheek of each dog to measure saliva when the dogs were fed (with a powder made from meat).
How did Ivan Pavlov conduct his experiment?
Pavlov rang the bell, then fed the dogs'. After doing this repeatedly, the pairing of food and bell eventually established the dog's Conditioned Response of salivating to the sound of the bell. After repeatedly doing this pairing, Pavlov removed the food and when ringing this bell the dog would salivate.
Where was Pavlov's experiment conducted?
It was at the Institute of Experimental Medicine that Pavlov carried out his classical experiments on the digestive glands, which would eventually grant him the aforementioned Nobel prize.
Why was Pavlov's dog experiment conducted?
Pavlov then focused on investigating exactly how these conditioned responses are learned or acquired. In a series of experiments, he set out to provoke a conditioned response to a previously neutral stimulus.
What was Pavlov's experiment?
To test his theory, Pavlov set up an experiment in which he rang a bell shortly before presenting food to the dogs. At first, the dogs elicited no response to the bells. However, eventually, the dogs began to salivate at the sound of the bell alone.
What is Pavlov's theory called?
Ivan Pavlov Theory: Classical Conditioning First discovered by Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936), classical conditioning is a learning process governed by associations between an environmental stimulus and another stimulus which occurs naturally.
How many dogs did Pavlov use in his experiment?
It's perhaps because the phrase “Pavlov's dogs” calls to mind the slightly slapstick performance of a creature behaving beyond its faculties that the actual animals receive short shrift by history, in both recognition and compassion. This is might also be due to the fact that Pavlov's dogs numbered near one hundred.
Is Pavlov's experiment scientific?
Pavlov's research is viewed as an excellent example of scientific research - giving psychology greater credibility and respect. Insight into the development of phobias - Pavlov's research of learning via stimulus-response has been successfully applies to humans.
What did Ivan Pavlov do for behavioral psychology?
Ivan Pavlov may not have set out to change the face of psychology, but his work had a profound and lasting influence on the science of the mind and behavior. His discovery of classical conditioning helped establish the school of thought known as behaviorism.
How do you use Pavlov theory in the classroom?
Ivan Pavlov's classical conditioning was perhaps the first behaviorist theory to emerge. Pavlov recognized that a neutral stimulus associates with a reflex response through conditioning. For example, when a teacher claps out a pattern, students repeat the pattern while focusing their attention to the teacher.
What's the basic idea behind classical conditioning Ivan Pavlov?
Discovered by Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov, classical conditioning is a type of unconscious or automatic learning. This learning process creates a conditioned response through associations between an unconditioned stimulus and a neutral stimulus.
Who did the dog salivation experiment?
How Pavlov's experiments with dogs demonstrated that our behavior can be changed using conditioning. One of the most revealing studies in behavioral psychology was carried out by Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936) in a series of experiments today referred to as 'Pavlov's Dogs'.
What did Ivan Pavlov study?
Ivan Pavlov gave up studying theology to enter the University of St. Petersburg, where he studied chemistry and physiology. After receiving an M.D....
What was Ivan Pavlov best known for?
Ivan Pavlov developed an experiment testing the concept of the conditioned reflex. He trained a hungry dog to salivate at the sound of a metronome...
What were Ivan Pavlov’s contributions?
In addition to his conditioning work, Ivan Pavlov devised an operation to prepare a miniature stomach, which was isolated from ingested foods but r...
What was Ivan Pavlov’s first job?
Having worked with Carl Ludwig, Ivan Pavlov’s first independent research was on the physiology of the circulatory system. From 1888 to 1890, in St....
What was Ivan Pavlov's first research?
Having worked with Carl Ludwig, Ivan Pavlov’s first independent research was on the physiology of the circulatory system. From 1888 to 1890, in St. Petersburg, he investigated cardiac physiology and blood pressure regulation. He became so skillful as a surgeon that he could introduce a catheter into a dog’s femoral artery almost painlessly.
What was Pavlov's first independent research?
Having worked with Ludwig, Pavlov’s first independent research was on the physiology of the circulatory system. From 1888 to 1890, in the laboratory of Botkin in St. Petersburg, he investigated cardiac physiology and the regulation of blood pressure.
What did Pavlov do for his work?
In addition to his conditioning work, Ivan Pavlov devised an operation to prepare a miniature stomach, which was isolated from ingested foods but retained its vagal nerve supply. The procedure allowed him to study the gastrointestinal secretions in animals. For his efforts he received the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1904.
How long did Pavlov study the conditioned reflex?
By observing irregularities of secretions in normal unanesthetized animals, Pavlov was led to formulate the laws of the conditioned reflex, a subject that occupied his attention from about 1898 until 1930.
What did Pavlov think of the psychotic?
He assumed that the excessive inhibition characteristic of a psychotic person was a protective mechanism—shutting out the external world—in that it excluded injurious stimuli that had previously caused extreme excitation.
Where did Pavlov go to school?
Pavlov, the first son of a priest and the grandson of a sexton, spent his youth in Ryazan in central Russia. There, he attended a church school and theological seminary, where his seminary teachers impressed him by their devotion to imparting knowledge. In 1870 he abandoned his theological studies to enter the University of St. Petersburg, where he studied chemistry and physiology. After receiving the M.D. at the Imperial Medical Academy in St. Petersburg (graduating in 1879 and completing his dissertation in 1883), he studied during 1884–86 in Germany under the direction of the cardiovascular physiologist Carl Ludwig (in Leipzig) and the gastrointestinal physiologist Rudolf Heidenhain (in Breslau).
What was Pavlov's idea of language?
In Russia this idea became the basis for treating psychiatric patients in quiet and nonstimulating external surroundings. During this period Pavlov announced the important principle of the language function in human beings as based on long chains of conditioned reflexes involving words.
What did Pavlov study?
In 1870, he enrolled in the physics and mathematics department at the University of Saint Petersburg to study natural science. Pavlov won the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1904, becoming the first Russian Nobel laureate.
How long did Pavlov serve as a professor?
In 1890, he was appointed the role of professor of Pharmacology at the Military Medical Academy and occupied the position for five years. In 1891, Pavlov was invited to the Institute of Experimental Medicine in St. Petersburg to organize and direct the Department of Physiology.
What did Pavlov do in his childhood?
From his childhood days Pavlov demonstrated intellectual curiosity along with an unusual energy which he referred to as "the instinct for research". Inspired by the progressive ideas which Dmitry Pisarev, a Russian literary critic of the 1860s, and Ivan Sechenov, the father of Russian physiology, were spreading, Pavlov abandoned his religious career and devoted his life to science. In 1870, he enrolled in the physics and mathematics department at the University of Saint Petersburg to study natural science.
Why did Pavlov and his wife live apart?
The first nine years of their marriage were marred by financial problems; Pavlov and his wife often had to stay with others to have a home, and for a time, the two lived apart so that they could find hospitality. Although their poverty caused despair, material welfare was a secondary consideration. Sara's first pregnancy ended in a miscarriage. When she conceived again, the couple took precautions, and she safely gave birth to their first child, a boy whom they named Mirchik; Sara became deeply depressed following Mirchik's sudden death in childhood.
How did Pavlov die?
He wanted to create unique evidence of subjective experiences of this terminal phase of life. Pavlov died of double pneumonia at the age of 86. He was given a grand funeral, and his study and laboratory were preserved as a museum in his honour. His grave is in the Literatorskie mostki (writers' footways) section of Volkovo Cemetery in St. Petersburg.
Why did Pavlov write to Stalin?
Four years later he wrote to Stalin, protesting at what was being done to Russian intellectuals and saying he was ashamed to be a Russian. After the murder of Sergei Kirov in 1934, Pavlov wrote several letters to Molotov criticizing the mass persecutions which followed and asking for the reconsideration of cases pertaining to several people he knew personally.
Why did Pavlov study animals?
This required keeping them alive and healthy to conduct chronic experiments, as he called them. These were experiments over time, designed to understand the normal functions of animals. This was a new kind of study, because previously experiments had been "acute," meaning that the dog went through vivisection which ultimately killed the animal in the process.
What was Pavlov's dog experiment?
In 1902 he was researching how dogs salivated in response to being fed. To measure the amount of saliva produced, he surgically implanted a small tube into the cheek of each dog.
What did Pavlov do in 1875?
Overall, Pavlov's grades at the University of St. Petersburg were excellent. He completed his degree in natural science in 1875.
Why did Pavlov's dog salivate?
However, Pavlov soon noticed something quite interesting. At first, the dogs salivated only if they were presented with food. But later in the experiment, the dogs began salivating when they heard Pavlov’s assistant coming with their food. Were the dogs producing more saliva because they could smell the food as it was brought closer? Apparently not, because the dogs still salivated even when Pavlov’s assistant came empty-handed.
Why did Pavlov quit the Imperial Academy?
Pavlov's passion for physiology motivated him to continue his studies at the Imperial Academy of Medical Surgery. While there, he worked as an assistant to his former teacher Elias von Cyon—a Russian-French physiologist. However, von Cyon was forced to relocate to Paris when students protested his political views. When von Cyon was replaced by another instructor, Pavlov quit the department.
Why is the dog's reflex unconditioned?
In Pavlov’s case, the dogs salivated (unconditioned reflex) when they were presented with food (unconditioned stimulus). In this case, the stimulus and reflex are described as “unconditioned” because the reaction is hard-wired into the dogs and required no learning.
How many siblings did Ivan Pavlov have?
His Early Years. Ivan Pavlov was the eldest child of Varvara Ivanovna Uspenskaya and Peter Dmitrievich Pavlov. He had ten siblings. Pavlov’s mother was a homemaker and his father was a Russian Orthodox priest at the village church. His grandfather also worked at the church as a sexton.
What happened to Pavlov during his childhood?
However, he was seriously hurt when he fell from a high wall during his childhood. His injuries caused him to spend most of his early years at home and in his family garden. During this part of his life, Pavlov grew to love nature, gardening, and working with his hands.
How did Pavlov test his theories?
Pavlov tested his theories in the lab using a variety of neural stimuli. For example, he used electric shocks, a buzzer that produced specific tones and the ticking of a metronome to make the dogs associate certain noises and stimuli with food.
What did Pavlov study?
Pavlov's early research focused primarily on the physiology of digestion. He used surgical methods to study various processes of the digestive system. By exposing portions of a dog's intestinal canal during surgery, he was able to gain an understanding of gastric secretions and the role of the body and mind in the digestive process. Pavlov sometimes operated on live animals, which was an acceptable practice back then but would not occur today due to modern ethical standards.
How did Pavlov study salivation?
Pavlov studied this phenomenon in the lab through a series of experiments with dogs. Initially, Pavlov was studying the connection between salivation and feeding. He proved that dogs have an unconditioned response when they are fed — in other words, they are hard-wired to salivate at the prospect of eating.
What did Pavlov do to help the study of behaviorism?
By proving the existence of conditioned and non-conditioned reflexes, Pavlov provided a foundation for the study of behaviorism. Many renowned psychologists, including John B. Watson and B. F. Skinner, were inspired by his work and built on it to gain a better understanding of behavior and learning.
What is Pavlov's most famous accomplishment?
Although Pavlov has many notable accomplishments, he is most well known for defining the concept of conditioned reflexes. A conditioned reflex is considered a form of learning that can occur through exposure to stimuli. Pavlov studied this phenomenon in the lab through a series of experiments with dogs.
How did Pavlov die?
Pavlov worked in the lab until his death at the age of 86. He died on February 27, 1936, in Leningrad (now St. Petersburg), Russia after contracting double pneumonia . His death was commemorated with a grand funeral and a monument that was erected in his home country in his honor.
What did Pavlov do in his career?
With these well-funded academic positions, Pavlov had the opportunity to further pursue the scientific studies that interested him.
What is Pavlov’s Dogs Experiment?
Ivan Pavlov’s dogs experiment is an experiment that took place in the 1890s in which the Russian physiologist surgically implanted small tubes into the cheeks of dogs to measure the buildup of saliva that took place under a variety of conditions.
What did Pavlov discover?
Finally, Pavlov discovered through the course of his experiment that a conditioned stimulus causes a conditioned response. An example of this in terms of Pavlov’s dogs experiment would be the act of Pavlov or one of his assistants ringing a bell before feeding the dogs, after they have already conditioned the sound of the bell to the promise ...
What is Pavlovian conditioning?
With its genesis in Pavlov’s dogs experiment, Pavlovian conditioning is defined as a form of behavioral psychology (or behaviorism) in which an animal, or human, can be conditioned to respond in a certain way to a stimulus that, had it not been conditioned, should in no way be associated with the act in question.
What did Pavlov predict?
Pavlov prediction that the dogs would salivate when presented with edible items was soon proved correct. This represents an unconditioned response in the animals, in which the sight and smell of the food causes them to salivate. Pavlov couldn’t have predicted what happened next.
What was the most famous item used in Pavlov's dogs experiment?
The most famous item used in Pavlov’s dogs experiment was that of a bell —Pavlov or one of his assistants would ring a bell before feeding his dogs. Soon enough, the single act of ringing the bell would be enough for the dogs to associate this seemingly neutral act with the promise of food. Pavlovian conditioning was born, ...
What was Pavlov's contribution to science?
Despite this, Pavlov’s most well-known contribution to science was through his dogs experiments, which became the basis for Pavlovian conditioning (also known as classical conditioning).
Which scientist discovered that a conditioned stimulus causes a conditioned response?
Finally, Pavlov discovered through the course of his experiment that a conditioned stimulus causes a conditioned response.
What was Pavlov's first step in the experiment?
In the first step of the experiment, a dog was placed in a box and harnessed.
When did Pavlov discover classical conditioning?
Pavlov first discovered classical conditioning serendipity when he was experimenting on his dog ‘Circa’ in 1905.

Overview
Career
After completing his doctorate, Pavlov went to Germany, where he studied in Leipzig with Carl Ludwig and Eimear Kelly in the Heidenhain laboratories in Breslau. He remained there from 1884 to 1886. Heidenhain was studying digestion in dogs, using an exteriorized section of the stomach. However, Pavlov perfected the technique by overcoming the problem of maintaining the externa…
Education and early life
Ivan Pavlov, the first of eleven children, was born in Ryazan, Russian Empire. His father, Peter Dmitrievich Pavlov (1823–1899), was a village Russian orthodox priest. His mother, Varvara Ivanovna Uspenskaya (1826–1890), was a devoted homemaker. As a child, Pavlov willingly participated in house duties such as doing the dishes and taking care of his siblings. He loved to garden, ride his bi…
Influences
He was inspired to pursue a scientific career by D. I. Pisarev, a literary critique and natural science advocate of the time and I. M. Sechenov, a Russian physiologist, whom Pavlov described as 'The father of physiology'.
Reflex system research
Pavlov contributed to many areas of physiology and neurological sciences. Most of his work involved research in temperament, conditioning and involuntary reflex actions. Pavlov performed and directed experiments on digestion, eventually publishing The Work of the Digestive Glands in 1897, after 12 years of research. His experiments earned him the 1904 Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine. These experiments included surgically extracting portions of the digestive syste…
Research on types and properties of nervous systems
Pavlov was always interested in biomarkers of temperament types described by Hippocrates and Galen. He called these biomarkers "properties of nervous systems" and identified three main properties: (1) strength, (2) mobility of nervous processes and (3) a balance between excitation and inhibition and derived four types based on these three properties. He extended the definition…
Pavlov on education
The basics of Pavlov's classical conditioning serve as a historical backdrop for current learning theories. However, the Russian physiologist's initial interest in classical conditioning occurred almost by accident during one of his experiments on digestion in dogs. Considering that Pavlov worked closely with nonhuman animals throughout many of his experiments, his early contributions were primarily about learning in nonhuman animals. However, the fundamentals o…
Legacy
The concept for which Pavlov is famous is the "conditioned reflex" (or in his own words the conditional reflex), which he developed jointly with his assistant Ivan Tolochinov in 1901 (although Edwin B. Twitmyer, at the University of Pennsylvania, published similar research in 1902, a year before Pavlov published his). The concept was developed after observing the rates of salivation in dogs. Pavlov noticed that his dogs began to salivate in the presence of the technician who norm…
Who Is Ivan Pavlov?
His Early Years
- Ivan Pavlov was the eldest child of Varvara Ivanovna Uspenskaya and Peter Dmitrievich Pavlov. He had ten siblings. Pavlov’s mother was a homemaker and his father was a Russian Orthodox priest at the village church. His grandfather also worked at the church as a sexton. Pavlov was a good reader by the time he was seven years old. However, he was seriously hurt when he fell fro…
Pavlov’s Dog Experiment
- The bulk of Pavlov’s research was conducted from 1891 to the early 1900s. In 1902 he was researching how dogs salivated in response to being fed. To measure the amount of saliva produced, he surgically implanted a small tube into the cheek of each dog. His prediction was that salivation would begin only after the food was placed in front of the dog...
Discovering Pavlovian Conditioning
- Pavlovian conditioning (also called classical conditioning) refers to the process of learning through association. It was first documented by Ivan Pavlov in 1902 when he was researching digestion in dogs. Although he was a brilliant man, Pavlov made this discovery quite by accident. Nevertheless, classical conditioning went on to have a major influence in the field of psychology…
Behaviorism Theory
- Behaviorism is a theory that suggests human and animal psychology can be understood by studying observable actions. While many forms of psychology emphasize thoughts and feelings, behaviorists believe the “inner world” is not important because it cannot be seen or accurately measured. Behaviorists believe all human behavior is learned by interacting with the environmen…
Pavlov’s Impact on Psychology and Education
- Classical conditioning has had a big impact on modern-day learning strategies. Although Pavlov worked with animals, he always believed the principles of classical conditioning can be applied to humans. A number of Pavlov’s basic ideas have been implemented in classrooms and other learning environments. Just as Pavlov used different stimuli to increase or decrease specific be…
Ivan Pavlov’s Accomplishments and Awards
- Books
Pavlov published many research papers and lectures throughout his long professional career. Some of his more notable works have been compiled into a few books such as The Work of the Digestive Glands (1897), Conditioned Reflexes (1926), and Psychopathology and Psychiatry (19… - Nobel Prize
Pavlov was nominated for the Nobel Prize from 1901 to 1904. However, he did not win the prize for the first three years because his nominations were tied to a variety of findings rather than a specific discovery. When he was first nominated in 1901, he was already well known among phy…
Personal Life and Death
- Throughout his life, Pavlov was never easy to get along with. In his childhood days, he often felt uncomfortable around his parents. He was also known to be a volatile and difficult student. When he opened his lab as an adult, his staff knew to avoid him if he was having one of his many bad days.