
What civilizations lived in the Fertile Crescent?
- Leader: Sargon the Great
- Sargon’s greatest achievement was the unification of lower Mesopotamia (after conquering Sumerians in 2331 BCE)
- Established capital at Akkad
- Spread Mesopotamian culture throughout Fertile Crescent
- Yet dynasty established by Sargon was short-lived… Akkadians were conquered by the invading barbarians by 2200 BCE
Why was Mesopotamia known as the Fertile Crescent?
Why is Mesopotamia called Fertile Crescent? Named for its rich soils, the Fertile Crescent, often called the “cradle of civilization,” is found in the Middle East. Irrigation and agriculture developed here because of the fertile soil found near these rivers. Access to water helped with farming and trade routes.
What was the history of the Fertile Crescent?
Fertile Crescent, the region where the first settled agricultural communities of the Middle East and Mediterranean basin are thought to have originated by the early 9th millennium BCE. The term was popularized by the American Orientalist James Henry Breasted.
What is the time period of the Fertile Crescent?
This happened in the region of a place that is now called the Fertile Crescent about what we think happened in the time period 11,000-8,000 B.C.E.The Fertile Crescent wasn’t necessarily the place where the Neolithic Revolution began (even though it was) it was just the place where soil was really good and animals and plants were abundant.
When was the Fertile Crescent civilization?
Known as the Cradle of Civilization, the Fertile Crescent is regarded as the birthplace of agriculture, urbanization, writing, trade, science, history and organized religion and was first populated c. 10,000 BCE when agriculture and the domestication of animals began in the region.
Where was the first Fertile Crescent located?
fertile crescent illustration Because of this region's relatively abundant access to water, the earliest civilizations were established in the Fertile Crescent, including the Sumerians. Its area covers what are now southern Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Palestine, Israel, Egypt, and parts of Turkey and Iran.
When did the Fertile Crescent become a desert?
After the Ice Age ended, the region became hotter and drier for good – but not straight away. The period between 10,000 and 7,000 years ago was actually the wettest time in the last 25,000 years.
Who conquered the Fertile Crescent in 2000 BC?
Alexander the GreatAlexander the Great invades and conquers the Fertile Crescent.
Why did ancient Mesopotamia came to be known as the Fertile Crescent?
In the early period of settlement along the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, the soil beds were rich with silt, which provided the necessary nutrients to establish agricultural communities, thus giving the region the name the Fertile Crescent.
Was the Fertile Crescent in Mesopotamia?
This region, alongside Mesopotamia (Greek for "between rivers", between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates, lies in the east of the Fertile Crescent), also saw the emergence of early complex societies during the succeeding Bronze Age.
Why did the Fertile Crescent become a desert?
Today the Fertile Crescent is not so fertile: Beginning in the 1950s, a series of large-scale irrigation projects diverted water away from the famed Mesopotamian marshes of the Tigris-Euphrates river system, causing them to dry up.
Why did the Middle East become a desert?
All this has been known for decades. But between 8,000 and 4,500 years ago, something strange happened: The transition from humid to dry happened far more rapidly in some areas than could be explained by the orbital precession alone, resulting in the Sahara Desert as we know it today.
Which of the following civilization existed in the BC 3500 to BC 2000 near to Greece and Euphrates valley of the river?
Mesopotamian civilizations formed on the banks of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in what is today Iraq and Kuwait.
What happened in 2500 BC in Mesopotamia?
Sumer and Gilgamesh: 3100-2500 BC The Sumerian temple priests, needing to keep accurate accounts, are the first people to develop a system of writing. The region can also claim other significant innovations. The first known potter's wheel, dating from around this period, has been found in Mesopotamia.
What happened in 4000 BC in Mesopotamia?
4000 BC - The Sumer establish powerful city-states building large ziggurats at the center of their cities as temples to their gods. 3500 BC - Much of lower Mesopotamia is inhabited by numerous Sumer city-states such as Ur, Uruk, Eridu, Kish, Lagash, and Nippur.
What is the oldest civilization in the world?
The Sumerian civilizationThe Sumerian civilization is the oldest civilization known to mankind. The term Sumer is today used to designate southern Mesopotamia. In 3000 BC, a flourishing urban civilization existed. The Sumerian civilization was predominantly agricultural and had community life.
Where is the Fertile Crescent located on the map?
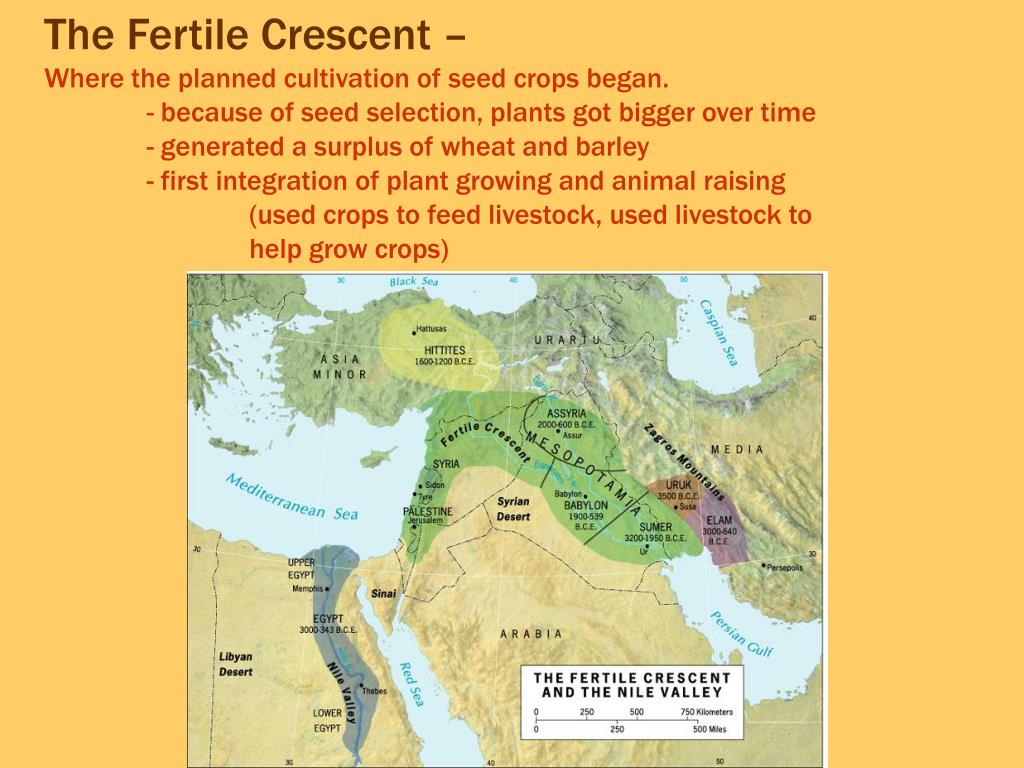
fertile crescent map key image The Fertile Crescent is a large geographic region in modern day Turkey, Iran, Iraq, Syria, Israel, Jordan, and the northern-easternmost part of Egypt, fed by the Euphrates and Tigris rivers, which have supported numerous ancient civilizations.
Where is Mesopotamia located in the world?
Mesopotamia is located in the region now known as the Middle East, which includes parts of southwest Asia and lands around the eastern Mediterranean Sea.
What is the Euphrates river called today?
Euphrates River, Turkish Fırat Nehri, Arabic Nahr Al-Furāt, river, Middle East.
Why did farming cities and states develop first in the Fertile Crescent?
Why did agriculture start in the Fertile Crescent? There was a natural abundance of grains and fruits suitable for human consumption in the Fertile Crescent. This combined with fertile soils around the two rivers Euphrates and Tigris as well as a surrounding rainy hill country made it the ideal place to start farming.
What is the fertile crescent?
Named for its rich soils, the Fertile Crescent, often called the “cradle of civilization,” is found in the Middle East. Because of this region’s relatively abundant access to water, the earliest civilizations were established in the Fertile Crescent, including the Sumerians. Its area covers what are now southern Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Palestine, Israel, Egypt, and parts of Turkey and Iran. Two rivers, the Tigris and the Euphrates, regularly flooded the region, and the Nile River also runs through part of it. Irrigation and agriculture developed here because of the fertile soil found near these rivers.
Why did agriculture and irrigation develop in the fertile Crescent?
Irrigation and agriculture developed here because of the fertile soil found near these rivers. Access to water helped with farming and trade routes. Soon, its natural riches brought travelers in and out of the Fertile Crescent.
What are the challenges of the fertile crescent?
Turkey, Syria, and Iraq all depend on the waters flowing from the region. Increased population and demands on the rivers from urbanization have depleted the once-fertile soil.
Who invented the term "fertile crescent"?
The term "Fertile Crescent" was popularized by archaeologist James Henry Breasted in Outlines of European History (1914) and Ancient Times, A History of the Early World (1916). Breasted wrote:
Where is the fertile crescent?
The Fertile Crescent is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Palestine, Israel, Jordan, and Egypt, together with the southeastern region of Turkey and the western fringes of Iran. Some authors also include Cyprus .
What is the fertile crescent flora?
The Fertile Crescent flora comprises a high percentage of plants that can self-pollinate, but may also be cross-pollinated. These plants, called " selfers ", were one of the geographical advantages of the area because they did not depend on other plants for reproduction.
What were the technological advances in Mesopotamia?
Technological advances in the region include the development of agriculture and the use of irrigation, of writing, the wheel, and glass, most emerging first in Mesopotamia .
Why is Cyprus considered the cradle of civilization?
The region is one of the cradles of civilization because it is one location where settled farming first emerged as people started the process of clearance and modification of natural vegetation to grow newly-domesticated plants as crops.
What is the history of Western Asia?
The history of Western Asia may be described as an age-long struggle between the mountain peoples of the north and the desert wanderers of these grasslands—a struggle which is still going on— for the possession of the Fertile Crescent, the shores of the desert-bay.
When was Mesopotamia settled?
Area of the fertile crescent, circa 7500 BCE, with main sites of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic period. The area of Mesopotamia proper was not yet settled by humans. Includes Göbekli Tepe, a site in modern-day Turkey that is dated circa 9000 BCE.
When was the fertile crescent first settled?
Fertile Crescent, the region where the first settled agricultural communities of the Middle East and Mediterranean basin are thought to have originated by the early 9th millennium bce. The term was popularized by the American Orientalist James Henry Breasted.
When was agriculture first used in the fertile crescent?
Radiocarbon dating has shown that incipient agriculture and village agglomerations in the Fertile Crescent there must be dated back to about 8000 bce, if not earlier, and that the use of irrigation followed rapidly.
What is fertile crescent?
The Fertile Crescent includes a roughly crescent-shaped area of relatively fertile land which probably had a more moderate, agriculturally productive climate in the past than today, especially in Mesopotamia and the Nile valley.
Which ancient civilizations were part of the Fertile Crescent?
The ancient countries of the Fertile Crescent, such as Sumer, Babylonia, Assyria, Egypt, and Phoenicia, are regarded as some of the world’s earliest complex societies. The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica This article was most recently revised and updated by Adam Augustyn, Managing Editor, Reference Content. History at your fingertips.
Where is Mesopotamia located?
history of Mesopotamia: The origins of Mesopotamian history. In the narrow sense, Mesopotamia is the area between the Euphrates and Tigris rivers, north or northwest of the bottleneck at Baghdad, in...
Who invented the term "fertile crescent"?
Origins of the Expression "Fertile Crescent". American Egyptologist James Henry Breasted (1865–1935) of the University of Chicago is credited with popularizing the term "Fertile Crescent.". In his 1916 book "Ancient Times: A History of the Early World," Breasted wrote of "the Fertile Crescent, the shores of the desert bay.".
What is the Fertile Crescent?
Updated October 16, 2020. The "Fertile Crescent," often referred to as the "cradle of civilization," refers to a semi-circular area of the eastern Mediterranean region, including the valleys of the Nile, Tigris and Euphrates rivers. The region includes parts of the modern countries of Israel, Lebanon, Jordan, Syria, northern Egypt, and Iraq, ...
What is the cradle of civilization?
Gill is a Latinist, writer, and teacher of ancient history and Latin. She has been featured by NPR and National Geographic for her ancient history expertise. The "Fertile Crescent," often referred to as the "cradle of civilization," refers to a semi-circular area ...
Where did cities flourish?
Cities did though, first flourish in the Fertile Crescent. By 6,000 years ago, early Sumerian cities such as Eridu and Uruk were built and began to flourish. Some of the first decorated pots, wall hangings, and vases were created, along with the world’s first brewed beer.
Where are the oldest permanent settlements?
In addition, the oldest permanent settlements are also outside of the Fertile Crescent: Çatalhöyük, for example, is located in south-central Turkey, and was founded between 7400–6200 BCE, older than any site in the Fertile Crescent, except possibly Jericho. Cities did though, first flourish in the Fertile Crescent.
Where did domestication take place?
Archaeological studies over the last century have shown that the domestication of plants like wheat and barley and animals such as sheep, goats, and pigs took place in the adjacent mountains and plains outside of the boundaries of the Fertile Crescent, not within it.
When were the first biblical stories written?
Empires arose in Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Phoenicia. The first versions of the Biblical stories of Abraham and Noah were written about 1900 BCE. While the Bible was once believed to be the oldest book ever written, it is clear that many great works were completed long before Biblical times.
What was the geography of the fertile crescent?
Geography of the Fertile Crescent. Due to its varied geography, Mesopotamian agriculture was highly diverse in terms of food sources, regional crop yields, and annual rainfall or irrigation variation (agricultural production could be up to 100x higher in particularly good years). There were two types of agriculture:
What is the birthplace of agriculture?
The ancient Near East, and the historical regions of the Fertile Crescent and Mesopotamia in particular, are generally seen as the birthplace of agriculture. In the 4th millennium BCE, this area was more temperate than it is today, and it was blessed with fertile soil, two great rivers (the Euphrates and the Tigris), as well as hills and mountains to the north.
What were the crops that were grown in Mesopotamia?
The main types of grain that were used for agriculture were barley, wheat, millet, and emmer. Rye and oats were not yet known for agricultural use.
Why did agriculture start?
Agriculture started most likely because hunter-gatherers who collected grains would have had to take them back to their camp in order to separate the grain from the chaff.
What was the soil in Babylonia?
The soil, particularly in the flood plains in the arid climate of Babylonia and Assyria, was prone to dry up, harden, and crack. In order to keep the soil arable, the plow had to be used. By 3000 BCE plows were known and in wide use – many Assyrian kings boasted to have invented a new improved type of plow.
Where was dry agriculture practiced?
Dry agriculture without irrigation, where people mostly cultivated cereals and relied on rainfall, which was primarily practiced in upper Mesopotamia and Syria. Irrigation agriculture, which was centered in lower Mesopotamia. Map of the Fertile Crescent. LaVie/Le Monde (Copyright)
Where did the first domesticated food come from?
In central America, people domesticated maize and beans, and rice and millet and pigs were first domesticated in China; both without knowledge of earlier advances in the Near East. Even today, 90% of our calories come from foods that were domesticated in this first wave of the agricultural revolution.
Why did agriculture first begin in the Fertile Crescent?
Named for its rich soils, the Fertile Crescent, often called the “cradle of civilization,” is found in the Middle East. Irrigation and agriculture developed here because of the fertile soil found near these rivers. Access to water helped with farming and trade routes.
What era did agriculture start in?
Farming started in the predynastic period at the end of the Paleolithic, after 10,000 BC. Staple food crops were grains such as wheat and barley, alongside industrial crops such as flax and papyrus. In India, wheat, barley and jujube were domesticated by 9,000 BC, soon followed by sheep and goats.
When did farming begin in Mesopotamia?
It was introduced to Mesopotamia around the end of the 3rd millennium BC, from India. It required irrigation to grow. The seeds were planted in spring and the harvest took place at the end of the summer.
When did humans first start farming?
Agricultural communities developed approximately 10,000 years ago when humans began to domesticate plants and animals. By establishing domesticity, families and larger groups were able to build communities and transition from a nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyle dependent on foraging and hunting for survival.
Why is the Fertile Crescent no longer fertile?
Today the Fertile Crescent is not so fertile: Beginning in the 1950s, a series of large-scale irrigation projects diverted water away from the famed Mesopotamian marshes of the Tigris-Euphrates river system, causing them to dry up.
What is the Fertile Crescent in the Bible?
The Fertile Crescent is traditionally associated in the Jewish, Christian and Muslim faiths with the earthly location of the Garden of Eden. The area features prominently in the Bible and Quran and a number of sites there are associated with narratives from those works.
Who is the father of agriculture?
Norman Ernest Borlaug (25 March 1914 – 12 September 2009) was an American agricultural scientist, and humanitarian. He is considered by some to be the ” father of modern agriculture ” and the father of the green revolution.

Overview
The Fertile Crescent (Arabic: الهلال الخصيب) is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Palestine, Israel, Jordan, and Northern Egypt, together with the northern region of Kuwait, southeastern region of Turkey and the western portion of Iran. Some authors also include Cyprus.
The region is one of the cradles of civilization because it is one location where s…
Terminology
The term "Fertile Crescent" was popularized by archaeologist James Henry Breasted in Outlines of European History (1914) and Ancient Times, A History of the Early World (1916). Breasted wrote:
This fertile crescent is approximately a semicircle, with the open side toward the south, having the west end at the southeast corner of the Mediterranean, the c…
Biodiversity and climate
As crucial as rivers and marshlands were to the rise of civilization in the Fertile Crescent, they were not the only factor. The area is geographically important as the "bridge" between North Africa and Eurasia, which has allowed it to retain a greater amount of biodiversity than either Europe or North Africa, where climate changes during the Ice Age led to repeated extinction events when ecosystems became squeezed against the waters of the Mediterranean Sea. The Saharan pump …
History
As well as possessing many sites with the skeletal and cultural remains of both pre-modern and early modern humans (e.g., at Tabun and Es Skhul caves in Israel), later Pleistocene hunter-gatherers, and Epipalaeolithic semi-sedentary hunter-gatherers (the Natufians); the Fertile Crescent is most famous for its sites related to the origins of agriculture. The western zone around the Jordan and u…
Cosmopolitan diffusion
Modern analyses comparing 24 craniofacial measurements reveal a relatively diverse population within the pre-Neolithic, Neolithic and Bronze Age Fertile Crescent, supporting the view that several populations occupied this region during these time periods. Similar arguments do not hold true for the Basques and Canary Islanders of the same time period, as the studies demonstrate thos…
Languages
Linguistically, the Fertile Crescent was a region of great diversity. Historically, Semitic languages generally prevailed in the modern regions of Iraq, Syria, Jordan, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine, Sinai and the fringes of southeast Turkey and northwest Iran, as well as the Sumerian (a language isolate) in Iraq, whilst in the mountainous areas to the east and north a number of generally unrelated language isolates were found, including; Elamite, Gutian and Kassite in Iran, and Hattic, Kaskian and Hurro …
See also
• Beth Nahrain
• Hilly Flanks
• History of agriculture
• History of Mesopotamia
• Hydraulic empire
Bibliography
• Jared Diamond, Guns, Germs and Steel: A Short History of Everybody for the Last 13,000 Years, 1997.
• Anderson, Clifford Norman. The Fertile Crescent: Travels In the Footsteps of Ancient Science. 2d ed., rev. Fort Lauderdale: Sylvester Press, 1972.
• Deckers, Katleen. Holocene Landscapes Through Time In the Fertile Crescent. Turnhout: Brepols, 2011.