
What are 10 examples of prokaryotic cells?
What are 5 examples of prokaryotic cells?
- Escherichia Coli Bacterium (E. coli)
- Streptococcus Bacterium.
- Streptomyces Soil Bacteria.
- Archaea.
What organisms have prokaryotic cells?
What are 3 examples of prokaryotic cells? Escherichia Coli Bacterium (E. coli) Streptococcus Bacterium. Streptomyces Soil Bacteria. Archaea.
What are some facts about prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotes Facts for Kids
- Prokaryotes are thought to be the oldest organisms on earth.
- Prokaryotes have cytosol that looks very grainy. ...
- Prokaryote DNA floats freely but is usually found in concentration in or around what they call the “nuclear region.”
What are the different types of prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells are single-celled microorganisms known to be the earliest on earth. Prokaryotes include Bacteria and Archaea. The photosynthetic prokaryotes include cyanobacteria that perform photosynthesis. A prokaryotic cell consists of a single membrane and therefore, all the reactions occur within the cytoplasm.
When did the first prokaryotic cells form?
3.5 and 3.4 billion years agoThe first fossils of prokaryotic (bacterial) cells are known from 3.5 and 3.4 billion years ago.
Where did prokaryotes first appear?
Prokaryotes were the earliest life forms, simple creatures that fed on carbon compounds that were accumulating in Earth's early oceans. Slowly, other organisms evolved that used the Sun's energy, along with compounds such as sulfides, to generate their own energy.
Did prokaryotic cells come first?
Fossil evidence indicates that prokaryotic cells first existed on the earth, prior to the arrival of the eukaryotes.
Who discovered the first prokaryotic cell?
The two researchers who first discovered prokaryotic cells were Antonie van Leeuwenhoek and Robert Hook. These two were the first to design and use high-powered microscopes to study cells. Through their work, they identified eukaryotic cells from plants, animals, and fungi as well as the prokaryotic cells of bacteria.
Which is the oldest prokaryote?
Archaea bacteria is the oldest prokaryote option (A) is the correct answer. Archaebacteria are a group of microorganisms evaluated to be an ancient form of life that developed individually from the bacteria and blue-green algae, and they are occasionally categorised as a kingdom.
Which cell appeared first on Earth?
prokaryotic cellsThat one cell is called the Last Universal Common Ancestor, or LUCA. It probably existed around 3.5 billion years ago. LUCA was one of the earliest prokaryotic cells.
Who came first prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
The eukaryotes developed at least 2.7 billion years ago, following some 1 to 1.5 billion years of prokaryotic evolution.
When were prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells discovered?
The Prokaryote/Eukaryote nomenclature had been proposed by Chatton in 1937 to classify living organisms into two major groups: prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (organisms with nucleated cells). Adopted by Stanier and van Neil this classification was universally accepted by biologists until recently (21).
How did prokaryotic cells evolve?
According to the endosymbiotic theory, the first eukaryotic cells evolved from a symbiotic relationship between two or more prokaryotic cells. Smaller prokaryotic cells were engulfed by (or invaded) larger prokaryotic cells.
Which came first prokaryotes or eukaryotes and why?
Prokaryotes came first, with speculations stating that they appeared at least 3.8 billion years ago. Also Read: Eukaryotic Cells- Definition, Characteristics, Structure, & Examples.
When were the first cells created?
3.8 billion years agoEvolution of cells refers to the evolutionary origin and subsequent evolutionary development of cells. Cells first emerged at least 3.8 billion years ago, approximately 750 million years after Earth was formed.
Where do we find prokaryotic cells?
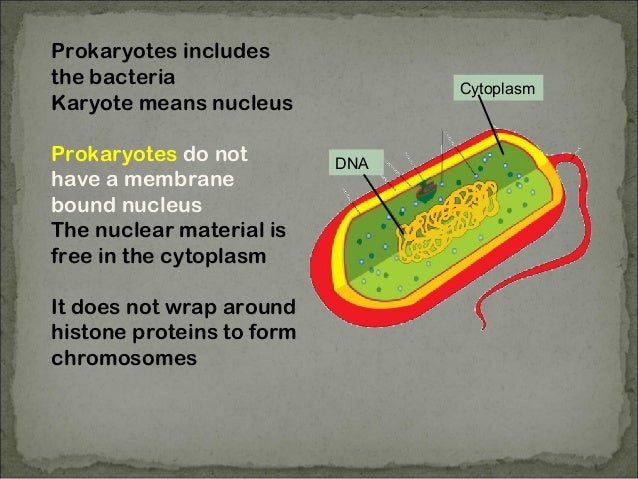
Prokaryotic cells are cells without a nucleus. The DNA in prokaryotic cells is in the cytoplasm rather than enclosed within a nuclear membrane. Prokaryotic cells are found in single-celled organisms, such as bacteria, like the one shown in Figure below.
When did prokaryotes first appear quizlet?
~3.5 billion years ago, first prokaryotes evolved.
What is the origin of prokaryotic cells?
The origin of prokaryotes can be viewed in two different ways, either as the origin of the ancestor from which archaea and bacteria diverged but also as the origin (specialization and/or diversification) of archaea and bacteria from that ancestor.
Where do we find prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells are cells without a nucleus. The DNA in prokaryotic cells is in the cytoplasm rather than enclosed within a nuclear membrane. Prokaryotic cells are found in single-celled organisms, such as bacteria, like the one shown in Figure below.
Why did prokaryotes appear before eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes did. Prokaryotes are undeveloped cells with no nuclei and the evolved first. The have circular DNA. Even mitochondrion and chlorophyll of the eukaryotes have circular DNA which suggests that prokaryotes evolved first.
What is a Prokaryotic Cell?
Prokaryotic cells are single-celled microorganisms known to be the earliest on earth. Prokaryotes include Bacteria and Archaea. The photosynthetic prokaryotes include cyanobacteria that perform photosynthesis.
What is the structure of a prokaryotic cell?
A prokaryotic cell structure is as follows: Capsule – It is an outer protective covering found in the bacterial cells, in addition to the cell wall. It helps in moisture retention, protects the cell when engulfed, and helps in the attachment of cells to nutrients and surfaces. Cell Wall – It is the outermost layer of the cell which gives shape ...
What are the characteristics of prokaryotic cells?
The characteristics of the prokaryotic cells are mentioned below. They lack a nuclear membrane. Mitochondria, Golgi bodies, chloroplast, and lysosomes are absent. The genetic material is present on a single chromosome. The histone proteins, the important constituents of eukaryotic chromosomes, are lacking in them.
Which region of the cytoplasm is not involved in reproduction?
These are not involved in reproduction. Nucleoid Region – It is the region in the cytoplasm where the genetic material is present. A prokaryotic cell lacks certain organelles like mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi bodies.
What are the components of eukaryotic chromosomes?
The histone proteins, the important constituents of eukaryotic chromosomes, are lacking in them. The cell wall is made up of carbohydrates and amino acids. The plasma membrane acts as the mitochondrial membrane carrying respiratory enzymes. They divide asexually by binary fission.
How many components are there in prokaryotic cells?
The prokaryotic cells have four main components:
Where do prokaryotic cells react?
A prokaryotic cell consists of a single membrane and therefore, all the reactions occur within the cytoplasm. They can be free-living or parasites.
How do prokaryotes live?
Prokaryotes are ubiquitous. They cover every imaginable surface where there is sufficient moisture, and they live on and inside of other living things. In the typical human body, prokaryotic cells outnumber human body cells by about ten to one. They comprise the majority of living things in all ecosystems. Some prokaryotes thrive in environments that are inhospitable for most living things. Prokaryotes recycle nutrients —essential substances (such as carbon and nitrogen)—and they drive the evolution of new ecosystems, some of which are natural and others man-made. Prokaryotes have been on Earth since long before multicellular life appeared.
What are the earliest records of life on Earth?
Fossilized microbial mats represent the earliest record of life on Earth. A stromatolite is a sedimentary structure formed when minerals are precipitated out of water by prokaryotes in a microbial mat (see the figure below). Stromatolites form layered rocks made of carbonate or silicate. Although most stromatolites are artifacts from the past, there are places on Earth where stromatolites are still forming. For example, growing stromatolites have been found in the Anza-Borrego Desert State Park in San Diego County, California.
When did life begin?
When and where did life begin? What were the conditions on Earth when life began? Prokaryotes were the first forms of life on Earth, and they existed for billions of years before plants and animals appeared. The Earth and its moon are thought to be about 4.54 billion years old. This estimate is based on evidence from radiometric dating of meteorite material together with other substrate material from Earth and the moon.
How did cyanobacteria contribute to the development of other life forms?
It also opened up the land to increased colonization, because some O 2 is converted into O 3 (ozone) and ozone effectively absorbs the ultraviolet light that would otherwise cause lethal mutations in DNA. Ultimately, the increase in O 2 concentrations allowed the evolution of other life forms.
