When did the Moche civilization start and end?
Written By: Moche, also called Mochica, Andean civilization that flourished from the 1st to the 8th century ce on the northern coast of what is now Peru. The name is taken from the great site of Moche, in the river valley of the same name, which appears to have been the capital or chief city of the Moche peoples.
Who were the Moche?
The ancient Moche civilization of Peru existed long before the Inca. The Moche civilization, also known as the Early Chimu or Mochica culture, flourished from approximately 100 to 800 CE. Dominating the northern coast, the Moche came to be one of the most important groups in Peruvian history.
Where did the Moche live in Peru?
The Moche civilization ( Spanish pronunciation: [ˈmotʃe]; alternatively, the Mochica culture or the Early, Pre- or Proto- Chimú) flourished in northern Peru with its capital near present-day Moche, Trujillo, Peru [1] [2] from about 100 to 700 AD during the Regional Development Epoch.
What was the political structure of the Moche civilization?
Political authority was fragmented, however, with each river valley or string of valley towns and villages having its own royalty and warrior-priesthood. The Moche produced sophisticated craft goods, including mold-made pottery that is among the finest naturalistic sculpture in pre-Columbian Peru.
See more

When did the Moche civilization develop and what made it special?
The rise of this civilization lasted from approximately 150-300 CE. During this period, the Moche took over neighboring people with military and ideological force. The Lord of Sipán, a mummy discovered in the Huaca Rajada, was an important figure in the later years of this period.
What was the Moche civilization known for?
The Moche are particularly noted for their elaborately painted ceramics, gold work, monumental constructions (huacas), and irrigation systems.
What is the oldest civilization in Peru?
Norte Chico civilizationThe Caral or Norte Chico civilization of Peru is the oldest known civilization in the Americas, dating back to 3200 BCE.
Was Moche an Inca?
The Moche was a pre-Inca civilization. They flourished in northern Peru, near the Pacific Ocean, between 100 AD and 800 AD. Construction of the Moche capital in Cerro Blanco started shortly after the Chicama culture integrated into the Moche society.
Why did the Moche civilization end?
The reasons for the demise of the Moche are unknown, but the civilization may have succumbed to earthquakes, prolonged drought, catastrophic flooding arising from the El Niño climatic anomaly, the encroachment of sand dunes on populated areas, or less-tangible social and cultural factors.
What did the Moche believe in?
The Moche were polytheistic , or had many gods. The most powerful god in their religion was Si, the moon goddess . Since the moon was always visible, and controlled the seasons, Si was the most powerful god. In Moche religion, women could have an important role.
What's the oldest Civilisation in the world?
MesopotamiaThe Sumerian civilization is the oldest civilization known to mankind. The term Sumer is today used to designate southern Mesopotamia. In 3000 BC, a flourishing urban civilization existed. The Sumerian civilization was predominantly agricultural and had community life.
Which country has oldest culture?
Which is the oldest country in the world? Japan is the oldest country in the world. The Japanese Emperor who ascended the throne in 660 BCE was apparently the descendant of the sun goddess Amaterasu.
Is Caral older than Egypt?
Caral was built around 5,000 years ago, give or take a few centuries, according to groundbreaking research published in Science back in 2001. That origin date places it before the Egyptian pyramids in Africa and roughly 4,000 years before the Incan Empire rose to power on the South American continent.
How do you pronounce Moche civilization?
0:230:56How to Pronounce "Moche" - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipMoss sí noche noche noche mouche mouche mouche manchin.MoreMoss sí noche noche noche mouche mouche mouche manchin.
Why are Moche artifacts expensive?
While this issue is the subject of some debate, many scholars contend that the Moche were not politically organized as a monolithic empire or state. Rather, they were likely a group of autonomous polities that shared a common culture, as seen in the rich iconography and monumental architecture that survives today.
What type of government did the Moche civilization have?
They had a hierarchical government and social structure. At the top were the royal family and warrior priests, who made most of the government decisions and controlled the Moche religion, which relied on human sacrifice.
What type of government did the Moche civilization have?
They had a hierarchical government and social structure. At the top were the royal family and warrior priests, who made most of the government decisions and controlled the Moche religion, which relied on human sacrifice.
What did Moche trade?
So, what trade the Moche did engage in was largely to exchange works of art, weapons, and other goods. The Moche were master craftsmen and created elaborate ceramic sculpture and other artwork. They had large quantities of gold and silver and Moche artisans worked well in these mediums.
Who were the Moche?
The Moche were contemporary with the Nazca civilization (200 BCE - 600 CE) further down the coast but, thanks to their conquest of surrounding territories, they were able to accumulate the wealth and power necessary to establish themselves as one of the most unique and important early-Andean cultures.
Why are Moche artifacts expensive?
While this issue is the subject of some debate, many scholars contend that the Moche were not politically organized as a monolithic empire or state. Rather, they were likely a group of autonomous polities that shared a common culture, as seen in the rich iconography and monumental architecture that survives today.
What is the Moche culture?
AD 100-750) was a South American society, with cities, temples, canals, and farmsteads located along the arid coast in a narrow strip between the Pacific Ocean and the Andes mountains of Peru. The Moche or Mochica are perhaps best known for their ceramic art: their pots include life-sized portrait heads ...
Where was the capital of Moche?
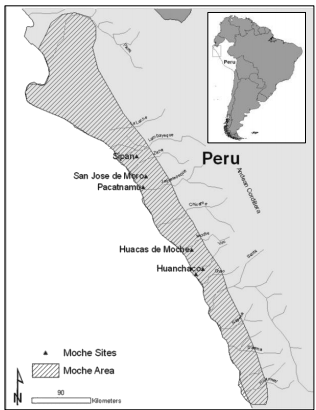
The Northern Moche capital was at Sipan; the southern at the Huacas de Moche, where the Huaca de la Luna and Huaca del Sol are the anchor pyramids.
What were the structures of Moche society?
In addition to the canals and aqueducts, architectural elements of Moche society included large monumental pyramid-shaped architecture called huacas which were apparently partly temples, palaces, administrative centers, and ritual meeting places . The huacas were large platform mounds, built of thousands of adobe bricks, and some of them towered hundreds of feet above the valley floor. On top of the tallest platforms were large patios, rooms and corridors, and a high bench for the seat of the ruler.
How many Huacas were there in Moche?
Most of the Moche centers had two huacas, one larger than the other. Between the two huacas could be found the Moche cities, including cemeteries, residential compounds, storage facilities and craft workshops.
What was the Moche economy?
Moche Politics and Economy. The Moche were a stratified society with a powerful elite and an elaborate, well-codified ritual process. The political economy was based on the presence of large civic-ceremonial centers that produced a wide range of goods which were marketed to rural agrarian villages.
Why are Moche so famous?
While the Moche did not leave a written record (they may have used the quipu recording technique that we have yet to decipher), the Moche ritual contexts and their daily lives are known because of excavations and detailed study of their ceramic, sculptural and mural art.
What is Moche art?
The Moche or Mochica are perhaps best known for their ceramic art: their pots include life-sized portrait heads of individuals and three-dimensional representations of animals and people.
Where did the Moche civilization live?
e. The Moche civilization ( Spanish pronunciation: [ˈmotʃe]; alternatively, the Mochica culture or the Early, Pre- or Proto- Chimú) flourished in northern Peru with its capital near present-day Moche, Trujillo, Peru from about 100 to 700 AD during the Regional Development Epoch.
When did Moche culture begin?
Moche history may be broadly divided into three periods – the emergence of the Moche culture in Early Moche (100–300 AD), its expansion and florescence during Middle Moche (300–600 AD), and the urban nucleation and subsequent collapse in Late Moche (500–750 AD).
What did the Moche people use to weave?
The Moche wove textiles, mostly using wool from vicuña and alpaca. Although there are few surviving examples of this, descendants of the Moche people have strong weaving traditions.
What color is Moche pottery?
The coloration of Moche pottery is often simple, with yellowish cream and rich red used almost exclusively on elite pieces. White and black are rarely used. The Moche are known for their portraiture pottery. The pottery portraits created by the Moche appear to represent actual individuals. Many of the portraits are of individuals with physical disfigurements or genetic defects.
What was Moche society?
Moche society was agriculturally based, with a significant level of investment in the construction of a network of irrigation canals for the diversion of river water to supply their crops. Their culture was sophisticated; and their artifacts express their lives, with detailed scenes of hunting, fishing, fighting, sacrifice, ...
Why is Moche important?
Because irrigation was the source of wealth and foundation of the empire, the Moche culture emphasized the importance of circulation and flow. Expanding upon this, Moche artwork frequently depicted the passage of fluids, particularly life fluids through vulnerable human orifices.
What are the two regions of Moche?
Two distinct regions of the Moche civilization have been identified, Southern and Northern Moche, with each area probably corresponding to a different political entity.
Where did the Moche people get their name?
The name is taken from the great site of Moche, in the river valley of the same name, which appears to have been the capital or chief city of the Moche peoples. Their settlements extended along the hot, arid coast of northern Peru from the Lambayeque River valley south for more than 215 miles (350 km) to the Nepeña River valley. ...
What did the Moche do?
Painted scenes on some vessels have yielded an understanding of ceremonial and everyday life in the Moche culture, including the sacrifice of prisoners-of-war and the ritual consumption of their blood. The Moche also were skilled metalworkers who in their jewelry used chemical means to electroplate gold and silver.
Where is the Moche burial chamber?
Moche: burial chamber. Moche burial chamber at Huaca Cao Viejo in El Brujo archaeological complex, near Trujillo, Peru.
Where is the tomb of a Moche warrior?
In 1987 archaeologists excavated a site called Huaca Rajada, near the village of Sipán in the Lambayeque valley, and uncovered the elaborate, jewelry-filled tomb of a Moche warrior-priest. Several more burial chambers containing the remains of Moche royalty were soon excavated, all dating from about 300 ce.
Why did the Moche civilization die?
The reasons for the demise of the Moche are unknown, but the civilization may have succumbed to earthquakes, prolonged drought, catastrophic flooding arising from the El Niño climatic anomaly , the encroachment of sand dunes on populated areas, or less-tangible social and cultural factors.
What were the pre-Columbian civilizations?
pre-Columbian civilizations: The northern coast. …valleys of Pacasmayo, Chicama, and Moche on the northern Peruvian coast. A large proportion of this area has been grouped by archaeologists into a Moche culture, although some of the territory encompassed by these valleys was not part of the polity called Moche.
Where is the Moche water bottle?
Moche (Mochica) stirrup-spouted water bottle, c. 250–500 ce; in the Museum of the American Indian, Heye Foundation, New York City.
Moche Civilization Location
The Moche civilization was located in the northern coastal region of Peru. Its capital city, Moche, was located near modern-day Trujillo. Dominating the Chicama and Trujillo Valleys, the Moche civilization ultimately expanded up to the Piura Valley and down to the Huarmey Valley.
History of the Moche
The Moche thrived from approximately 100-800 CE. During their several hundred year reign, they made quite a mark on the history of Peru. While there is no written record of the Moche civilization, scientists have determined much about this culture through their artifacts and archaeological research.
The Moche Culture
This culture is best known for their intricately decorated ceramics, goldwork, and monumental constructions known as huacas.
Moche Economy
The Moche irrigation system was extremely efficient. As the economy relied heavily on agriculture and internal trading relationships, the irrigation system ensured their entire region had water for their crops. As a result, this prevented internal conflict over resources.
Moche Political Structure
Although this is a topic of much debate, most scholars believe that the Moche were not a monolithic state or empire. Instead, researchers believe that they were a group that shared a common elite culture, depicted in the iconography and architecture that still survives today.
Women in Moche Society
Recent excavations and discoveries have shown that women held an elite role in ruling the Moche civilization. The idea that men exclusively ruled the culture has been discounted after several prominent female skeletons were exhumed from opulent burial chambers.
Moche Archaeological Sites
While studies and excavations continue at several archaeological sites, the following are top Moche sites to see in Peru.
What was the Moche civilization?
The Moche Civilization were a highly advanced warrior civilization who controlled parts of Peru along the Cerro Blanco Mountains in South America. They were organized into two tribes who spoke different languages called Muchic and Quingan.
Where did the Moche tribes live?
Original Moche lands stretched across the Chicama and Trujillo Valleys. Through warfare the Moche were able to expand their mighty empire further north to the Piura Valley and further south to the Huarmey Valley.
What is the Moche platform called?
In Pampa Grande the Moche built a 180 ft. platform called Huaca Fortaleza they used for rituals.
What were the Moche's headdresses made of?
Headdresses have also been excavated at Moche sites like Pampa Grande and Sipán made of gold and turquoise. Tumi knives and copper bowls have also been discovered which show how skilled the Moche were at metallurgy, and how rich their lands were with minerals. Tombs and pyramids of the Moche display artwork so detailed that they can often be compared to similar antiquities found among early Greek ruins.
What happened to the Moche in 550 CE?
However, in 550 CE natural disasters like flooding and high winds began to erode their canals and sully their fields necessitating their relocation to the northern Moche cities of Pampa Grande and Sipán. By this point in Moche history they also faced incursions from other hostile factions like the Huari who descended upon them from the mountains of central Peru.
What did the Moche do?
Moche structures had features like split levels, access ramps for convenience, and angled roofing to accommodate heavy rains.
What language did the Moche speak?
The Moche were organized into two distinct tribes located in the north of their empire who spoke a language called Muchic, and another tribe in the southern part of their domain who spoke a language called Quingan . They had an advancement culture with a capital city located in the valley of the Cerro Blanco Mountains that contained a varied infrastructure of homes, market places, warehouses for grain, and places of worship.
What was the Moche civilization based on?
Everything about the Moche Civilization was based on conquest, and building super structures really showed it. Their massive empire ranged from the Chicama and Trujillo Valleys, but after conquering other tribes also included the northern Piura Valley through the southern Huarmey Valley.
What did the Moche make?
The Moche had vast stores of gold, silver and copper and they used them to create beautiful masks like the golden masks that were found in the tomb of the warrior priest. They also made bracelets, headdresses, and necklaces made of gold, silver, and turquoise that have been found in the other pyramids.
What was the Moche economy?
Moche Economy. The Moche economy was a well-oiled machine. The Moche presided over an empire that was extremely rich in natural resources. Their artisan class thrived due to the mineral wealth the civilization enjoyed, and these artisans created works of art that rival any of the native tribes of South America.
What was the Moche government?
The Moche Government and Social Structure. The Moche government and social structure were hierarchical and very organized. It was split between the northern and southern regions of their lands.
Why were the Moche priests so successful?
As the empire expanded and other tribes were defeated, the Moche warrior priests were given high praise and veneration for their military success. They could advance through Moche government to places of high power and influence, and could also join the royal family.
How were Conquest and Moche religion connected?
Conquest and the Moche religion were connected to each other in other ways as well. Their religion relied on human or blood sacrifice, and those taken in battle were often used for this purpose. Those at the bottom of Moche society were used for this purpose as well.
Why did the Moche need a developed and organized economy?
In order to fight wars of conquest, build huge cities, and erect massive monuments, the Moche needed a developed and organized economy, government, and social structure. Let's discuss their organization and see how they were able to become one of the most important native cultures of the Americas.
What emerged from the Moche?
What emerged was a vision of the Moche as politically independent groups who shared a common ideology, mythical and religious beliefs and practices, as well as a common iconography for their artwork.
Where did the Moche culture live?
The Moche culture thrived on Peru’s northern coast between approximately 200 and 900 C.E. Rising and falling long before the Inka, the culture left no written records, and the early Spanish colonists who chronicled the cultures of Peru found the Chimú people in what had earlier been Moche territory. The Moche are a prime example of how archaeologists and art historians use scientific methods of data collection and evaluation in understanding ancient, non-literate cultures.
What is a Moche vessel?
Early Moche vessels are very sculptural, depicting humans, supernatural figures, animals, and plants in a great variety. Later Moche ceramics feature complex line drawings of similar subject matter (called fineline style). The Moche often used a distinctive spout on their vessels, called a stirrup spout. It is composed of a hollow tube of clay bent into an upside-down U shape, with another tube piercing it at the apex of the curve (see images below). This spout form has ancient origins in the Andes, and it seems possible that the Moche deliberately chose this form to echo its use in during the earlier Cupisnique (1500-500 B.C.E.) and Chavín (900-200 B.C.E.) cultures. Fine ceramics would have been used as gifts from the highest elites to the lower elites and middle classes, helping to cement the social bonds that supported the power that the elites held. Fine ceramics have been found in households, and the pieces in graves show evidence that they had been used.
What were Moche ceramics made of?
Many Moche ceramics were made using molds , and so we have many duplicate pieces. The ability to control imagery through the use of molds seems to have been important to the political elites of the Moche. Ceramic artist Walter Acosta showing a replica Moche mold. Ceramic artist Walter Acosta showing a replica Moche mold.
What were the Moche known for?
The Northern Moche are celebrated for their metalwork, especially the exquisite pieces found in the tombs of Sipán in the Lambayeque valley. Working in gold and silver, Moche artists were adept at hammering, soldering, and setting stones, as well as developing a process to make a copper-gold alloy appear to be solid gold—a technique known as depletion gilding. Gold, silver, semiprecious stones and Spondylus shell were used to make the elaborate regalia of the highest elites. Massive necklaces and bracelets, ear spools, headdresses, nose ornaments, and more were made by Moche artists for the great lords. While there certainly were skilled ceramicists in the north and able metalsmiths in the south, the general division of materials between these two areas helps define some of their differences. Both areas also would have had weavers producing fine textiles, but few examples have survived.
How did independent areas of Moche culture differ from other areas?
Independent areas (sometimes as large as a pair of river valleys, sometimes as small as one section of a single valley) would signal that they belonged to Moche culture by using Moche themes in their artwork, while at the same time asserting differences—in architecture, in iconographic style, and in which figures from the mythology were deemed important. In this way, separate Moche polities could express both their political independence as well as their sense of belonging to a larger cultural system. The biggest separation of Moche style and iconography splits them into northern and southern areas (see map above), which can then be subdivided into smaller, politically independent areas.
What colors did the Moche use?
Moche artists used only three colors—cream, red-brown or red-orange, and black to decorate their ceramics. Many Moche ceramics were made using molds, and so we have many duplicate pieces. The ability to control imagery through the use of molds seems to have been important to the political elites of the Moche.
Where did the Inca Empire flourish?
The Inca Empire flourishes in South America.
Where did the Hellenistic civilization live?
Hellenistic civilization in Greece, the Mediterranean and Asia.
Where did the Gandhara civilization flourish?
The Gandhara Civilization flourishes in what is today the northern portion of Pakistan and Afghanistan.
Where was the Sumerian civilization located?
Sumerian civilization in the Tigris-Euphrates valley.

Moche Chronology
Moche Politics and Economy
Moche Architecture
Moche Burials
Moche Violence
History of Moche Archaeology
- The Moche were first recognized as a distinct cultural phenomenon by archaeologist Max Uhle, who studied the site of Moche in the early decades of the 20th century. The Moche civilization is also associated with Rafael Larco Hoyle, the "father of Moche archaeology" who proposed the first relative chronology based on ceramics.
Sources
Overview
Material culture
Moche pottery is some of the most varied in the world. The use of mold technology is evident, which would have enabled the mass production of certain forms. But Moche ceramics vary widely in shape and theme, with most important social activities documented in pottery, including war, metalwork, weaving, and erotica.
Background
Southern and Northern Moche
Religion
Social stratification
Collapse
Links with other cultures
Moche Civilization Location
History of The Moche
- The Moche thrived from approximately 100-800 CE. During their several hundred year reign, they made quite a mark on the history of Peru. While there is no written record of the Moche civilization, scientists have determined much about this culture through their artifacts and archaeological research. Historians generally divide the history of the Mo...
The Moche Culture
Moche Economy
Moche Political Structure
Women in Moche Society
Moche Archaeological Sites
Discover The Moche Civilization