
When did the Sassanid Empire start and end?
The Sassanid Empire or Sassanian Dynasty is the name used for the Persian dynasty which lasted from 224 to 651 AD. Cameo of Shapur I humiliating Emperor Valerian.
What was the Sassanid Empire known for?
Sassanid emperors consciously sought to resuscitate Persian traditions and to obliterate Greek cultural influence. The active army of the Sassanid Empire originated from Ardashir I, the first shahanshah of the empire.
Where did the Sasanian Empire extend to?
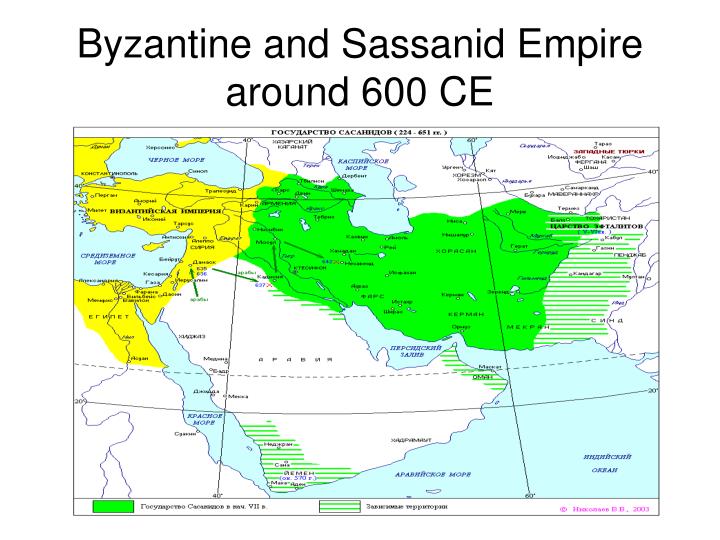
At its greatest extent, the Sasanian Empire encompassed all of present-day Iran and Iraq and stretched from the eastern Mediterranean (including Anatolia and Egypt) to Pakistan, and from parts of southern Arabia to the Caucasus and Central Asia. According to legend, the vexilloid of the Empire was the Derafsh Kaviani.
Who established the Sassanian Empire in Estakhr?
The Sassanian Empire was established in Estakhr by Ardashir I . Ardashir's father, Papak, was originally the ruler of a region called Khir. However, by the year 200, Papak had managed to overthrow Gochihr and appoint himself the new ruler of the Bazrangids.

When did the Sasanian Empire start and end?
Sasanian dynasty, Sasanian also spelled Sassanian, also called Sasanid, ancient Iranian dynasty that ruled an empire (224–651 ce), rising through Ardashīr I's conquests in 208–224 ce and destroyed by the Arabs during the years 637–651. The dynasty was named after Sāsān, an ancestor of Ardashīr.
How did the Sassanid Empire begin?
The empire was founded by Ardashir I, an Iranian ruler who rose to power as Parthia weakened from internal strife and wars with the Romans.
When did the Sassanid Empire end?
651 CEThe Sasanian Empire (224-651 CE, also given as Sassanian, Sasanid or Sassanid) was the last pre-Islamic Persian empire, established in 224 CE by Ardeshir I, son of Papak, descendant of Sasan. The Empire lasted until 651 CE when it was overthrown by the Arab Rashidun Caliphate.
When did the Sasanian Empire exist?
The Sasanian Empire (224–651 A.D.)
Who defeated the Sassanids?
In 642, Umar ibn al-Khattab, then-Caliph of the Muslims, ordered a full-scale invasion of Persia by the Rashidun army, which led to the complete conquest of the Sassanid Empire by 651.
Who founded the Sassanid Empire?
Ardashir IThe Sasanian dynasty was the house that founded the Sasanian Empire, ruling this empire from 224 to 651 in Persia (modern-day Iran). It began with Ardashir I, who named the dynasty as Sasanian in honour of his grandfather (or father), Sasan, and after the name of his tribe.
Are Persians Arabs?
Arab people, or Arabs, are those people who inhabit the Arab world. “Arab world” is considered to be located in North Africa and Western Asia; Persians are those people who inhabit the Iranian Cultural Continent which includes the Iranian Plateau to the Indus River of Pakistan in the east to Turkey in the West.
What was the last Persian Empire called?
the Achaemenid EmpireAt its greatest territorial extent, the Achaemenid Empire stretched from the Balkans and Eastern Europe in the west to the Indus Valley in the east. The empire was larger than any previous empire in history, spanning a total of 5.5 million square kilometres (2.1 million square miles).
Who conquered Persia?
Alexander the GreatThe Persian Empire began to decline under the reign of Darius's son, Xerxes. Xerxes depleted the royal treasury with an unsuccessful campaign to invade Greece and continued with irresponsible spending upon returning home. Persia was eventually conquered by Alexander the Great in 334 B.C.E.
Are Kurds sassanids?
The vast majority of eastern and western historians, regard the Sassanids as Persians, while reliable historical sources unequivocally confirm that the Sassanids belong to the Kurdish people.
Where did the Persians defeat the Romans in 613 CE?
Antioch, TurkeyThe Battle of Antioch took place in 613 outside Antioch, Turkey between a Byzantine army led by Emperor Heraclius and a Persian Sassanid army under Generals (spahbed) Shahin and Shahrbaraz as part of the Byzantine–Sassanid War of 602–628.
What countries did the Sassanid Empire control?
The Sassanid Empire's traditional territory included all of today's Iran, Iraq, Armenia, Afghanistan, eastern parts of Turkey, and parts of Syria, Pakistan, Caucasia, Central Asia and Arabia .
How were the Sassanids united?
They were united by Islam. Years of warfare had exhausted both the Byzantines and the Persians. The Sassanids were further weakened by economic decline, heavy taxation, religious unrest, rigid social stratification, the increasing power of the provincial landholders, and a rapid turnover of rulers.
What was the name of the Iranian dynasty?
The Sassanid Empire or Sassanian Dynasty is the name used for the Iranian dynasty which lasted from 224 to 651 AD.
Where was Yazdegerd III killed?
651: Last Sassanid ruler Yazdegerd III murdered at Merv, present-day Turkmenistan, ending the dynasty. His son Pirooz and many others went into exile in China .
What is the name of the council that declared the Eastern Church independent of Constantinople?
424: Council of Dad-Ishu declares the Eastern Church independent of Constantinople.
What was Armenia divided into?
387: Armenia partitioned into Roman and Persian zones.
Which empire ceded much of Armenia and Iberia to Constantinople?
572-591: War with Constantinople. Persia cedes much of Armenia and Iberia to Constantinople.
Where was the Sassanid Empire located?
The Sassanid Empire was centered in the fertile lowlands of Mesopotamia, now southeastern Iraq, and on the Iranian plateau on the other side of the Zagros Mountains. At its peak, the empire stretched from beyond the Oxus River (modern-day Amu Dar’ya) in Central Asia, south to the Indus River in India, and west through present-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Iraq, to the Tigris River, where it bordered and contested with the Roman Empire.
Who was the first Sassanid king?
The first Sassanid monarch, Ardashīr I (third century) defeated his predecessor, the Parthian king Artabanus V (third century), in 224. Ardashīr I was from the Persian heartland of Fārs. (Persia was the name used in Western languages for Iran from ancient times into the twentieth century; from the time of the Sassanids, the natives have called it Iran. The local language is called either Persian or Farsi.) Borrowing from the courtly rule and customs of the Achaemenid ancestors he claimed, he sought to revive the Iranian traditions and set his sights on reestablishing the borders held by the Achaemenid Empire before its conquest by the Macedonian Alexander the Great (356–323 BC) between 330 and 327 BC. Ardashīr is thought to have observed the benefit Roman emperors drew from allowing the existence of small semiautonomous kingdoms on their borders. While he promoted a strongly centralized government, Ardashīr allowed for these sorts of buffer states in outlying territories.
What was the Sassanid model of government?
The Sassanid model of imperial rule began with the shahenshah, whose royal authority was declared by the powerful Zoroastrian priests to be of divine origin. The shahenshah was seen as the earthly incarnation of the supreme god, though not identical with it.
What was the most powerful factor uniting citizens of the new Sassanid Empire?
One of the most powerful factors uniting citizens of the new Sassanid Empire was their shared Zoroastrian religion. The world’s first monotheistic religion, Zoroastrianism was founded by the Persian prophet Zoroaster (c. 628–c. 551 BC) in the seventh century BC. His teachings described existence as a struggle between the forces of good and evil.
What were the Mobads?
The mobads (Zoroastrian priests) concerned themselves primarily with legal affairs and were active both at court and in the outlying districts. They were judges, as well as advocates for the poor, and some were spiritual counselors to the Sassanid queens.
What was the last great empire in Iran?
The last great Iranian empire before the Muslim invasion of Iran in the seventh century, the Sassanid Empire united diverse holdings under a shahenshah (king of kings), who was considered to be of divine origin. The king was advised by a council comprising four regional kings and a variety of other officials. The empire was strongly centralized and was administered by a highly structured bureaucracy that included priests of the state religion, Zoroastrianism.
What were the factors that weakened Sassanid rule?
A weak economic infrastructure was one of the factors to irreversibly weaken Sassanid rule.
What is the Sasanian Dynasty?
Full Article. Sasanian dynasty, Sasanian also spelled Sassanian, also called Sasanid, ancient Iranian dynasty that ruled an empire (224–651 ce ), rising through Ardashīr I ’s conquests in 208–224 ce and destroyed by the Arabs during the years 637–651.
What was the art style of the Sasanians?
Under the Sasanians Iranian art experienced a general renaissance. Architecture often took on grandiose proportions, such as the palaces at Ctesiphon, Fīrūzābād, and Sarvestan.
What was the name of the empire that was in existence for 400 years?
ancient Iran: The Sāsānian period. At the beginning of the 3rd century ad, the Arsacid empire had been in existence for some 400 years. Its strength had been... A revival of Iranian nationalism took place under Sasanian rule. Zoroastrianism became the state religion, and at various times followers of other faiths suffered official persecution.
Where was the surrender of the emperor Valerian?
The surrender of the emperor Valerian to the Persian king Shāpūr I, rock relief, 260 ce; in the province of Fārs, Iran.
Who was the last king of the Sassanian Empire?
Belisarius defeats the Persians to the east of the Byzantine Empire and the Vandals of Africa . East Rome defeats Sasanian Persia . Reign of Yazdegerd III , the last king of the Sasanian Empire .
Which empire invaded Armenia?
The Sasanid Empire invades the Kingdom of Armenia .
Who was the king of Persis?
Ardashir, king (malakh) of Persis, revolts against the Parthians and founds the Sasanian Empire .
What was the name of the battle between Armenia and Persia?
Battle of Avarayr between Armenian forces and those of the Sasanian Empire . The Treaty of Nvarsak is signed between Persia and Armenia giving the latter a greater political autonomy and freedom of religious thought. Kavad, king of the Sasanian Empire, unsuccessfully besieges Edessa .
What was the Sassanid ruler's title?
Sassanid rulers adopted the title of shahanshah (king of kings), as sovereigns over numerous petty rulers, known as shahrdars.
What were the factors that weakened the Sassanids?
The later Sassanids were further weakened by economic decline, heavy taxation, religious unrest, rigid social stratification, the increasing power of the provincial landholders, and a rapid turnover of rulers. These factors facilitated the Arab invasion in the seventh century. It was the beginning of the end.
What was the reign of Khosro II?
The reign of Khosro II (591-628 CE) was characterized by the wasteful splendor and lavishness of the court. Toward the end of his reign Khosro II's power declined. In renewed fighting with the Byzantines, he enjoyed initial successes, captured Damascus, and seized the Holy Cross in Jerusalem.
What was the history of Iran?
History of Iran. T he Sassanids established an empire roughly within the frontiers achieved by the Achaemenids, with the capital at Ctesiphon. The Sassanids consciously sought to resuscitate Iranian traditions and to obliterate Greek cultural influence. Their rule was characterized by considerable centralization, ambitious urban planning, ...
When did Yezdegerd ascend the throne?
In the spring of 633 CE a grandson of Khosro called Yezdegerd ascended the throne, and in that same year the first Arab squadrons made their first raids into Persian territory. Years of warfare exhausted both the Byzantines and the Iranians.
Who was Shahpur I?
Shahpur I (240-272 CE), son and successor of Ardeshir, waged successful campaigns against the Romans and in 260 CE even took the emperor Valerian prisoner. Between 260 and 263 CE he had lost his conquest to Odenathus, and ally of Rome.
Who was the head of the priestly class?
The head of the priestly class, the mobadan mobad, along with the military commander, the eran spahbod, and the head of the bureaucracy, were among the great men of the state. Rome, with its capital at Constantinople, had replaced Greece as Iran's principal Western enemy, and hostilities between the two empires were frequent.
What is the Sassanid Empire?
Sasanian Empire timeline including important events and territorial evolution. The Sassanid Empire or Sassanian Dynasty is the name used for the Persian dynasty which lasted from 224 to 651 AD. Cameo of Shapur I humiliating Emperor Valerian.
Who was the leader of Zoroastrianism in c. 224-240?
c. 224-240 – Zoroastrianism belief experiences an era of recovery under the reign of Ardashir I.
What happened in 363?
363 - War between Julian and Persian troops follows his back off and demise; the surrendered territories and Nisibis are brought back to Persia.
What treaty gave Armenians the right to profess Christianity?
484 - Coronation of Balash. The Nvarsak Treaty grants the Armenians the right to profess Christianity freely.
Which country was the first to accept Christianity as its state religion?
c. 301 - The realm of Armenia is the first nation to accept Christianity as the state religion.
Who was assassinated in 590?
590 - Hormizd IV is assassinated; Coronation of Khosrow II. 590 - Uprising of Bahrām Chobin and his seizure of the Persian throne. 591 - Overwhelming of Bahrām Chobin; he escapes to the Turks in Central Asia but is killed after a year. Khosrow II regains the throne with the help of the Byzantine Emperor Maurice.
Who defeated his rivals and triumphed to the Persian throne?
293 - Narseh overwhelms his competitors and triumphs to the Persian throne.
Overview
Name
Officially, the Empire was known as the Empire of Iranians (Middle Persian: ērānšahr, Parthian: aryānšahr); the term is first attested in the Great Inscription of Shapur I, where the king says "I am the ruler of Empire of Iranians" (Middle Persian: ērānšahr xwadāy hēm, Parthian: aryānšahr xwadāy ahēm).
More commonly, due to the fact that the ruling dynasty was named after Sasan, the Empire is kno…
History
Conflicting accounts shroud the details of the fall of the Parthian Empire and subsequent rise of the Sassanian Empire in mystery. The Sassanian Empire was established in Estakhr by Ardashir I.
Ardashir's father, Papak, was originally the ruler of a region called Khir. However, by 200, Papak had managed to overthrow Gochihr and appoint himself the new …
Government
The Sassanids established an empire roughly within the frontiers achieved by the Parthian Arsacids, with the capital at Ctesiphon in the Asoristan province. In administering this empire, Sassanid rulers took the title of shahanshah (King of Kings), becoming the central overlords and also assumed guardianship of the sacred fire, the symbol of the national religion. This symbol is explicit on Sass…
Relations with neighboring regimes
The Sassanids, like the Parthians, were in constant hostilities with the Roman Empire. The Sassanids, who succeeded the Parthians, were recognized as one of the leading world powers alongside its neighboring rival the Byzantine Empire, or Eastern Roman Empire, for a period of more than 400 years. Following the division of the Roman Empire in 395, the Byzantine Empire, with its capital at Constantinople, continued as Persia's principal western enemy, and main enem…
Society
In contrast to Parthian society, the Sassanids renewed emphasis on a charismatic and centralized government. In Sassanid theory, the ideal society could maintain stability and justice, and the necessary instrument for this was a strong monarch. Thus, the Sasanians aimed to be an urban empire, at which they were quite successful. During the late Sasanian period, Mesopotamia had the l…
Culture
There was a major school, called the Grand School, in the capital. In the beginning, only 50 students were allowed to study at the Grand School. In less than 100 years, enrollment at the Grand School was over 30,000 students.
On a lower level, Sasanian society was divided into Azatan (freemen). The Azatan formed a large low-aristocracy of low-level administrators, mostly livin…
Economy
Due to the majority of the inhabitants being of peasant stock, the Sasanian economy relied on farming and agriculture, Khuzestan and Iraq being the most important provinces for it. The Nahravan Canal is one of the greatest examples of Sasanian irrigation systems, and many of these things can still be found in Iran. The mountains of the Sasanian state were used for lumbering by the nom…
King of Kings
Decline
- In the spring of 632, a grandson of Khosrau I, Yazdegerd III who had lived in hiding, ascended the throne. In that same year, the first raiders from the Arab tribes made their raids into Persian territory. They were united by Islam. Years of warfare had exhausted both the Byzantines and the Persians. The Sassanids were further weakened by economic decline, heavy taxation, religious u…
Sassanid Empire Chronology
- 226–241: Reign of Ardashir I: 1. 224–226: Overthrow of Parthian Empire. 2. 229–232: War with Rome. 3. Zoroastrianismis revived as official religion. 4. The collection of texts known as the Zend Avestais assembled. 241–271: Reign of Shapur I: 1. 241–244: War with Rome. 2. 252–261: War with Rome. Capture of Roman emperor Valerian. 3. 215–271: Mani, founder of Manichaeism. 27…
References
- Iranologie History of Iran Chapter V: Sasanians Archived 2009-07-15 at the Wayback Machine
- Iran Chamber Society (History of Iran) Archived 2006-11-10 at the Wayback Machine
- Livius articles on ancient Persia Archived 2011-05-13 at the Wayback Machine
- Richard Frye "The History of Ancient Iran"
Other Websites
- Sasanian rock reliefs, Photos from Iran, Livius Archived 2016-11-10 at the Wayback Machine.
- Sasanian Dynasty entry in the Encyclopædia Iranica
- ECAI.org The Near East in Late Antiquity: The Sasanian Empire Archived 2006-12-14 at the Wayback Machine
- The Art of Sassanians