
What happens when an ideal gas molecule collides with its container walls? As the temperature of a gas rises, the average velocity of the molecules will increase; a doubling of the temperature will increase this velocity by a factor of four.
Do ideal gas molecules attract or repel each other?
Ideal gas molecules do not attract or repel each other. The only interaction between ideal gas molecules would be an elastic collision upon impact with each other or an elastic collision with the walls of the container.
Can an ideal gas molecule collide with the walls?
An ideal gas molecule has zero volume hence they cannot collide. They can collide with the walls elastically [KE and Momentum conserved].
Why are particles in an ideal gas in constant motion?
Particles in an ideal gas are in constant motion, colliding against each other and the walls of the container they're stored in. However, these collisions are perfectly elastic (ie. Momentum and kinetic energy conserved).
Do gases collide with each other in a pressure sensor?
Answer Wiki. Yes. The atoms/ molecules of all gases that are confined do collide with the each other and with the atoms in the walls and pressure sensors. On the sensors, that impact force / area exposed is the pressure of the gas in that container.
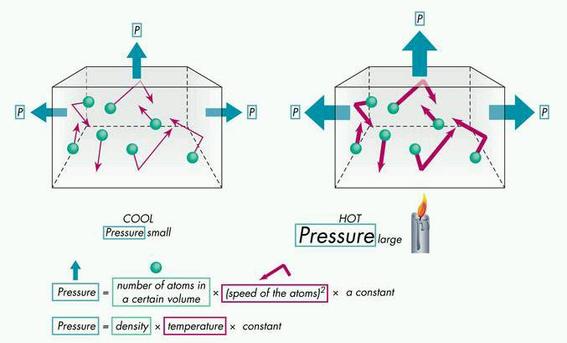
What happens when ideal gas molecules collide?
The only interaction between ideal gas molecules would be an elastic collision upon impact with each other or an elastic collision with the walls of the container. What is an elastic collision? Ideal gas molecules themselves take up no volume.
What is caused when gas particles hit the walls of a container?
Gas pressure is caused when gas particles hit the walls of their container. The more often the particles hit the walls and the faster they are moving when they do this the higher the pressure.
When particles of a gas collide with a wall of a container the wall experiences a pressure What is the cause of this pressure?
When a molecule collides with the wall of the container, a change of momentum occurs. The molecule exerts an equal but opposite force on the wall (Newton's third law). The pressure exerted by the gas is due to the sum of all these collision forces.
When gas molecules collide with each other there is a change in?
Collisions are perfectly elastic; when two molecules collide, they change their directions and kinetic energies, but the total kinetic energy is conserved. Collisions are not “sticky". The average kinetic energy of the gas molecules is directly proportional to the absolute temperature.
What property of gas is described when gases hit the walls of its container?
Gas particles are constantly colliding with each other and the walls of their container. These collisions are elastic; that is, there is no net loss of energy from the collisions. Gas particles are small and the total volume occupied by gas molecules is negligible relative to the total volume of their container.
What causes air pressure in a container?
Molecules of gas in a sealed glass container move rapidly in random directions, and some strike the walls of the container. The force imparted by these collisions is pressure. The more collisions there are, the more pressure is exerted on the walls of the container.
Why does gas exert pressure on the walls of a container?
According to the kinetic theory of gases, gases exert pressure on the walls of the container because of the collisions between the molecule and the wall. These collisions are perfectly elastic.
What properties of gas that force of gas particles striking the walls of a container?
Answer and Explanation: (a) pressure. This is the correct response.