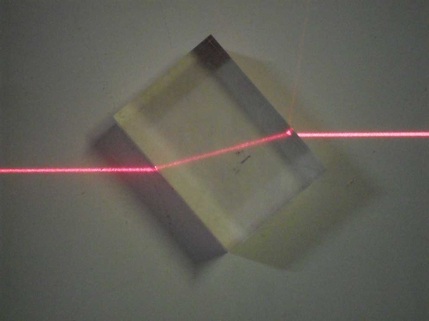
...
Part A: Multiple Choice.
| a. passing through a boundary | b. bouncing off a boundary |
|---|---|
| c. changing speed at a boundary | d. changing direction when crossing a boundary |
When light travels from air to glass at an angle?
When light travels from air to glass at an angle of incidence greater than 0 o, it bends toward the normal.
What happens to a ray when it travels along a normal?
1) A ray directed along a normal does not refract as it moves from one medium another; refraction will occur if the ray is travelling on an angle different from that of the normal through two different mediums. 2) When light travels from air to glass at an angle of incidence greater than 0o, it bends toward the normal.
Which side of the boundary line is the ray of refraction?
In this diagram, the incident ray is on the left side and consequently, ray of refraction is on the right side on the opposite side of the boundary line. When light travels from air to glass at an angle of incidence greater than 0 o, it bends toward the normal.
What is the ratio of angle of incidence to angle of refraction?
The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant. 7) If light were to travel from glass to air, it would bend farther away from the normal.
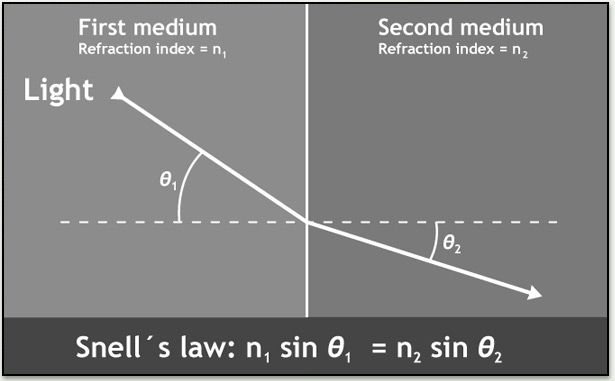
When a ray of light passes from glass into air is the angle of refraction greater than or less than the angle of incidence?
When a ray of light passes from a denser material (eg water or glass) into a less dense material (eg air) it is bent towards the surface between the two materials. This means that in this situation the angle of refraction is always greater than the angle of incidence.
What happens when light passes from air into glass?
As light passes through air and into another clear material (such as glass), it changes speed, and light is both reflected and refracted by the glass. This results in us seeing the glass because it reflects and refracts light differently than the air around it does.
What is the refraction angle?
Definition of angle of refraction : the angle between a refracted ray and the normal drawn at the point of incidence to the interface at which refraction occurs.
Does air or glass have a higher index of refraction?
The refractive index of air is 1.00029, while the glass is 1.52 so if you just want the air refractive index as glass is under pressure and temperature variations, you would have to increase therefore the pressure in the room to get the density cm2 is equivalent to the density of the glass.
Why does a ray not refract?
1) A ray directed along a normal does not refract as it moves from one medium another; refraction will occur if the ray is travelling on an angle different from that of the normal through two different mediums.
Why does light travel farther away from the normal?
This is because as the light reaches the less dense medium and it encounters a lower number of molecules collisions and assuming the kinetic energy from the light remains constant the light particles collisions decrease resulting in the light speeding up.
Related Doubts
A ray of light passes from glass into air. The angle of refraction will be: (a) equal to the angle of incidence (b) greater than the angle of incidence (c) smaller than the angle of incidence (d) 45° Asked on 23rd Apr, 2021
Referral Program
Distribute the referral code to your friends and ask them to register with Tutorix using this referral code.
