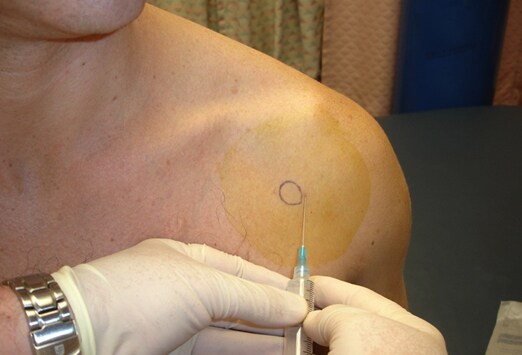
How do you use a needle decompression?
A needle decompression should only be performed if the patient has a tension pneumothorax. When inserting the needle, it should be inserted at a 90-degree angle to the chest wall. This is a critical point as this will position the needle straight into the pleural space.
When should needle decompression of the chest not be performed?
Needle decompression shouldn't be performed unless tracheal deviation is present. The patient who requires needle decompression of the chest is often in extremis. Pulsus Paradoxus is best defined as a decrease in the:
Which patient is often in extremis during needle decompression?
The patient who requires needle decompression of the chest is often in extremis. b.) Needle decompression is performed on the side where breath sounds are heard. c.) Patients who need chest decompression may require sedation before proceeding. d.)
What is needle decompression for pneumothorax?
This involves using a needle catheter to release the trapped air in the pleural space. If the patient has either a closed or open tension pneumothorax, then the need for a needle decompression is required to save the patient. A needle decompression involves inserting a large bore needle in the second intercostal space, at the midclavicular line.
When do you use needle decompression vs chest tube?
Needle thoracostomy is indicated for emergent decompression of suspected tension pneumothorax. Tube thoracotomy is indicated after needle thoracostomy, for simple pneumothorax, traumatic hemothorax, or large pleural effusions with evidence of respiratory compromise.
What is the purpose of needle decompression?
Needle decompression is a procedure used to treat patients who have a tension pneumothorax. Tension pneumothorax is when air from the lungs escapes into the pleural space – which is in between the lungs and the chest.
Where should needle decompression be placed?
Both the 2nd intercostal space in the midclavicular line (ICS2-MCL) and the 4th/5th intercostal space in the anterior axillary line (ICS 4/5-AAL) have been proposed as preferred locations for needle decompression (ND) of a TP.
Where do you decompress a tension pneumothorax?
Abstract. Background: A tension pneumothorax requires immediate decompression using a needle thoracostomy. According to advanced trauma life support guidelines this procedure is performed in the second intercostal space (ICS) in the midclavicular line (MCL), using a 4.5-cm (2-inch) catheter (5-cm needle).
Can a nurse perform needle decompression?
It is within the scope of practice of the appropriately prepared and competent registered nurse to perform needle decompression for a tension pneumothorax under the direction of an authorized health care practitioner, following clinical practice standards.
What are the signs of tension pneumothorax?
Tension PneumothoraxSymptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, rapid breathing, and a racing heart, followed by shock.Doctors can usually diagnose tension pneumothorax based on the person's history, symptoms, and examination results.Doctors immediately insert a large needle into the chest to remove the air.
Is needle decompression the same as thoracentesis?
Thoracentesis /ˌθɔːrəsɪnˈtiːsɪs/, also known as thoracocentesis (from Greek θώραξ thōrax 'chest, thorax'—GEN thōrakos—and κέντησις kentēsis 'pricking, puncture'), pleural tap, needle thoracostomy, or needle decompression (often used term), is an invasive medical procedure to remove fluid or air from the pleural space ...
What size needle is used for needle decompression?
14-gaugeObjective: Needle thoracostomy is a life-saving procedure. Advanced Trauma Life Support guidelines recommend insertion of a 5 cm, 14-gauge needle for pneumothorax decompression. High-risk complications can arise if utilizing an inappropriate needle size.
What is difference between pneumothorax and tension pneumothorax?
Pneumothorax is when air collects in between the parietal and viscera pleurae resulting in lung collapse. It can happen secondary to trauma (traumatic pneumothorax). When mediastinal shifts accompany it, it is called a tension pneumothorax. This is a life-threatening emergency that needs urgent management.
What is the treatment for tension pneumothorax?
Treatment of tension pneumothorax is immediate needle decompression by inserting a large-bore (eg, 14- or 16-gauge) needle into the 2nd intercostal space in the midclavicular line. Air will usually gush out.
Is a tension pneumothorax a collapsed lung?
A pneumothorax (noo-moe-THOR-aks) is a collapsed lung. A pneumothorax occurs when air leaks into the space between your lung and chest wall. This air pushes on the outside of your lung and makes it collapse. A pneumothorax can be a complete lung collapse or a collapse of only a portion of the lung.
What is the purpose of thoracentesis?
Thoracentesis is a procedure to remove fluid or air from around the lungs. A needle is put through the chest wall into the pleural space. The pleural space is the thin gap between the pleura of the lung and of the inner chest wall.
Can Emts do needle decompression?
If an EMS provider suspects a tension pneumothorax, they should perform immediate needle decompression in the second intercostal space to restore cardiac output. The definitive treatment for pneumothorax is chest tube placement in the emergency department.
What size needle is used for needle decompression?
14-gaugeObjective: Needle thoracostomy is a life-saving procedure. Advanced Trauma Life Support guidelines recommend insertion of a 5 cm, 14-gauge needle for pneumothorax decompression. High-risk complications can arise if utilizing an inappropriate needle size.
What is Ars needle decompression?
2:077:05ARS® For Needle Decompression - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipColor recognition and inhibits fine motor skills the ARS needle decompression kit is intended forMoreColor recognition and inhibits fine motor skills the ARS needle decompression kit is intended for use in the management of casualties. Who present with signs and symptoms of a tension pneumothorax.
What happens after needle decompression?
For example, a tension pneumothorax and a needle decompression may cause bleeding into the pleural space , a condition known as a hemothorax. It should be noted that most patients who suffer a tension pneumothorax will eventually require the insertion of a thoracostomy tube (chest tube) to help drain excess fluid and air from the pleural space.
What is the purpose of a thoracostomy tube after needle decompression?
After needle decompression, it is important to constantly monitor the patient's breathing and pulse as well as check for possible complications, such as a hemothorax (bleeding into the pleural space). Also, most patients who suffer a tension pneumothorax will eventually require the insertion of a thoracostomy tube (chest tube) to help drain excess fluid and air from the pleural space.
How long should a 14 g catheter be?
You also need to keep in mind that the first rib lies under the clavicle. Use a large bore, 10 G to 14 G catheter at least 3.25 inches (ca. 8 cm) long to decompress the chest. Clean the site with alcohol swipes, insert the needle using the third rib as a backboard.
How long to wait to remove catheter from pleural cavity?
Once in the pleural cavity, advance the needle down to the hub, wait 10 seconds, then remove the needle while leaving the catheter in the body. Check the patient for signs and symptoms of relief.
Why is the decrease in cardiac output something we need to be cognizant of?
But the decrease in cardiac output is something we need to be cognizant of because it produces his causes respiratory difficulties, shock and death.
Can you insert a catheter through a chest seal?
Do not insert the catheter through a chest seal covering the site you’ve chosen for the NCD. Instead, slightly roll the edge of the chest seal enough to make room for the NCD. If you’re unsure whether you can make it work at that particular location, chose a different site.
Can you perform chest decompression multiple times?
Conclusion. In some instances, it will be necessary to perform needle chest decompression multiple times on the same casualty, as time allows. Multiple attempts become necessary when the catheter kinks, becomes obstructed by a clot, or in some other way fails to serve its intended purpose.
When to use needle decompression?
A needle decompression should only be performed if the patient has a tension pneumothorax. When inserting the needle, it should be inserted at a 90-degree angle to the chest wall. This is a critical point as this will position the needle straight into the pleural space. If any other angle is used, there may be a chance of hitting other structures in the area such as major blood vessels or even the heart.
How long does a 14 gauge needle last?
Studies have determined that chest decompression with a 14 gauge needle is as successful as a chest tube in relieving a tension pneumothorax and therapeutic benefits can continue for as long a four hours. If using a needle catheter with a flash chamber, you should ensure that the chamber is removed.
What happens when a patient cannot compensate for a pneumothorax?
A tension pneumothorax occurs when the patient cannot compensate, and several events begin to occur that can lead to death. As air fills the pleural space on inspiration through the opening with an open pneumothorax, the wound can act as a one-way valve and not allow the air to exit.
What to do if tension pneumothorax is not improving?
If there is no improvement, the procedure will need to be repeated with another needle placed adjacent to the first needle. Monitor, then reassess the patient. A tension pneumothorax is a life-threatening situation.
How to treat an open pneumothorax?
For an open pneumothorax, treatment requires sealing the open wound with an occlusive dressing. This is often taught by using Vaseline gauze and securing the gauze to the patient's chest with tape. However, this can be a difficult process in the field depending on the size of the wound, the patient's condition, and the area the dressing is applied.
Do needle catheters have flash chambers?
If using a needle catheter with a flash chamber, you should ensure that the chamber is removed. There are specially manufactured needles designed just for a tension pneumothorax. These are prepackaged 3.25-inch 14 gauge needles that do not have flash chambers.
Can you lift a dressing from an open chest wound?
When the patient's condition is deteriorating, some paramedic programs teach that it may be possible to lift the dressing from the wound allowing trapped air to escape, or even gently spread the wound to help air escape. The wound is then resealed after such a procedure.