
When there is demand there is supply? There is an inverse relationship between the supply and prices of goods and services when demand is unchanged. If there is an increase in supply for goods and services while demand remains the same, prices tend to fall to a lower equilibrium price and a higher equilibrium quantity of goods and services.
What are the basic principles of supply and demand?
When there is demand there is supply? There is an inverse relationship between the supply and prices of goods and services when demand is unchanged. If there is an increase in supply for goods and services while demand remains the same, prices tend to fall to a lower equilibrium price and a higher equilibrium quantity of goods and services.
What are some examples of supply and demand?
· The supply and demand theory states that the price of a product depends on its availability and buyers' demand. If the product has a high price, the sellers will supply more of it to the market. However, keeping the price high can have a negative effect on the way buyers think about the product. If customers don't think the product is worth the high price, they may begin …
What is the difference between supply and demand?
3 Supply and Demand 3.1 Demand. From Openstax Principles of Microeconomics (Chapter 3) Economists use the term demand to refer to the amount of some good or service consumers are willing and able to purchase at each price. Demand is fundamentally based on needs and wants—if you have no need or want for something, you won’t buy it.
What is the equation for supply and demand?
· Demand refers to the amount of goods that will be used at any given price level and along with supply determines the price. Now look at the figures below: In Fig 1 above, we …

Where there is demand there will be supply?
The law of demand says that at higher prices, buyers will demand less of an economic good. The law of supply says that at higher prices, sellers will supply more of an economic good. These two laws interact to determine the actual market prices and volume of goods that are traded on a market.
How can supply affect demand?
The relationship between supply and demand is indirect, meaning that when supply increases, prices decrease and demand increases. When supply reduces, prices rise and demand goes down.
What comes first demand or supply?
Demand comes first and it's followed by the corresponding supplies.
What causes supply in demand?
The market forces and behavior of people in regards to price cause movements along the supply and demand curve. As people demand more of a product, they will bid up prices to get what they desire. This entices suppliers and sellers to offer more of the product.
When supply and demand are balanced it is called?
The tendency to move toward the equilibrium price is known as the market mechanism, and the resulting balance between supply and demand is called a market equilibrium.
Does a decrease in supply increase demand?
Decrease in supply decreases the quantity. Figure 4.14(b) shows the effects of a decrease in demand and an increase in supply. A decrease in demand shifts the demand curve leftward, and an increase in supply shifts the supply curve rightward.
What is relation between demand and supply?
It's a fundamental economic principle that when supply exceeds demand for a good or service, prices fall. When demand exceeds supply, prices tend to rise. There is an inverse relationship between the supply and prices of goods and services when demand is unchanged.
IS IT demand and supply or supply and demand?
supply and demand, in economics, relationship between the quantity of a commodity that producers wish to sell at various prices and the quantity that consumers wish to buy.
What does demand mean in supply and demand?
The term supply refers to how much of a certain product, item, commodity, or service suppliers are willing to make available at a particular price. Demand refers to how much of that product, item, commodity, or service consumers are willing and able to purchase at a particular price.
What factors change supply?
Factors that can shift the supply curve for goods and services, causing a different quantity to be supplied at any given price, include input prices, natural conditions, changes in technology, and government taxes, regulations, or subsidies.
When supply is higher than demand prices will?
When Supply Is Greater Than Demand A Exists? When the demand for a product exceeds the supply, a shortage occurs. When the quantity supplied exceeds the amount demanded, a surplus occurs. If, for example, $2 is the price, then it would be $2.
What is decrease in supply?
A decrease in supply means that producers plan to sell less of the good at each possible price. 2. Other factors affecting supply include technology, the prices of inputs, and the prices of alternative goods that could be produced.
What happens when supply increases?
There is an inverse relationship between the supply and prices of goods and services when demand is unchanged. If there is an increase in supply for goods and services while demand remains the same, prices tend to fall to a lower equilibrium price and a higher equilibrium quantity of goods and services.
What factors affect demand?
Market Factors Affecting Demand. The demand for a good increases or decreases depending on several factors. This includes the product's price, perceived quality, advertising spend, consumer income, consumer confidence, and changes in taste and fashion.
What are the three 3 factors that may influence the demand and supply of construction?
Myers (2008) concluded that demand for construction is affected by the construction price, price of other goods or services related to construc- tion, income, government policy, consumer's expec- tation and other influencing factors.
What factors affect supply?
Supply refers to the quantity of a good that the producer plans to sell in the market. Supply will be determined by factors such as price, the number of suppliers, the state of technology, government subsidies, weather conditions and the availability of workers to produce the good.
What are the factors that affect supply?
In thinking about the factors that affect supply, remember what motivates firms: profits , which are the difference between revenues and costs. A firm produces goods and services using combinations of labor, materials, and machinery, or what we call inputs or factors of production. If a firm faces lower costs of production, while the prices for the good or service the firm produces remain unchanged, a firm’s profits go up. When a firm’s profits increase, it is more motivated to produce output, since the more it produces the more profit it will earn. When costs of production fall, a firm will tend to supply a larger quantity at any given price for its output. We can show this by the supply curve shifting to the right.
What is individual supply curve?
Individual supply shows some firm’s preferences about the quantity they are willing to produce at different prices. For example, if there are four different firms producing the same product, then there are four individual supply curves. On the other hand, market supply is the aggregation (sum) of all individual supply curves. We generally use market supply (unless otherwise specified.) The table below shows the individual supply for three firms for hamburgers sold per week in addition to the market supply (comprised of the three individuals) for hamburgers sold per week.
What does quantity supplied mean?
When economists talk about quantity supplied, they mean only a certain point on the supply curve, or one quantity on the supply schedule. In short, supply refers to the curve and quantity supplied refers to the (specific) point on the curve.
Is supply the same as quantity supplied?
In economic terminology, supply is not the same as quantity supplied. When economists talk about supply, they mean the relationship between a range of prices and the quantities supplied at those prices, as illustrated by a supply curve or a supply schedule. When economists talk about quantity supplied, they mean only a certain point on the supply curve, or one quantity on the supply schedule. In short, supply refers to the curve and quantity supplied refers to the (specific) point on the curve.
What is supply curve?
Nearly all supply curves share the fundamental similarity that they slope up from left to right. Supply curves embody the law of supply: As the price increases, the quantity supplied increases, and conversely, as the price decreases, the quantity supplied decreases.
What is the relationship between price and quantity supplied?
Economists call this positive relationship between price and quantity supplied—that a higher price leads to a higher quantity supplied and a lower price leads to a lower quantity supplied —the law of supply. The law of supply assumes that all other variables that affect supply are held constant.
How do income taxes affect demand?
Income taxes will affect demand in the same way as changes in income did because they are essentially the same thing. For instance, an increase in income tax means that people now have less disposable income. Therefore, an increase in income taxes will cause a decrease in the demand for normal goods and an increase in the demand for inferior goods.
What is ELM in finance?
Elearnmarkets (ELM) is a complete financial market portal where the market experts have taken the onus to spread financial education. ELM constantly experiments with new education methodologies and technologies to make financial education effective, affordable and accessible to all.
What does increase in consumption mean?
Increase in consumption will mean a rightward shift in the supply curve a rightward shift in supply is a bearish development.
Did the quantity demanded change in any of the two years?
Well the quantity demanded did not change in any of the two year’s, what changed was the supply. The year 2017 was the excess supply year and in the year 2016, the supply of mangoes was limited
What does consumption reflects?
In the figure above, consumption reflects supply and not by the quantity demanded. For example, consumption of ripe mangoes during peak harvest season.
What does the demand curve shift to the right?
In Fig 2 above, you can see an increase in quantity demanded, wherein the demand curve shifts to the right and at a given price level, there is higher consumption due to increase in quantity demanded.
What is the difference between consumption and demand?
Let us understand the following difference: Consumption is the amount of goods used and is determined by the price which in turn is determined by the demand and supply factors. Demand refers to the amount of goods that will be used at any given price level and along with supply determines the price.
How to determine quantity demanded?
The only way to determine quantity demanded is through inference of demand curves through a detailed study of the historical consumption pattern and the price data. It is an easy process when the quantity demanded is stable in nature. On the other hand, frequent changes in the pattern of quantity demanded, makes this methodology almost impossible. This difficulty in the quantification of demand can be circumvented by considering consumption figures as a proxy to carry on with the workable analysis of projecting prices. This assumption is wrong, but in order to get a workable figure, we need to know the conceptual mistakes involved in this.
Why does the demand curve slope downward?
For all time periods, the demand curve slopes downward because of the law of diminishing marginal utility. The first unit of a good that any buyer demands will always be put to that buyer's highest valued use. For each additional unit, the buyer will use it (or plan to use it) for a successively lower-valued use.
Is the supply curve always downward sloping?
In other words, the supply curve, in this case, is a vertical line, while the demand curve is always downward sloping due to the law of diminishing marginal utility. Sellers can charge no more than the market will bear based on consumer demand at that point in time.
Why is time important in supply and demand?
It is important for both supply and demand to understand that time is always a dimension on these charts. The quantity demanded or supplied, found along the horizontal axis, is always measured in units of the good over a given time interval. Longer or shorter time intervals can influence the shapes of both the supply and demand curves.
What is the quantity demanded or supplied?
The quantity demanded or supplied, found along the horizontal axis, is always measured in units of the good over a given time interval. Longer or shorter time intervals can influence the shapes of both the supply and demand curves.
Why do producers supply more at a higher price?
Producers supply more at a higher price because the higher selling price justifies the higher opportunity cost of each additional unit sold. For both supply and demand, it is important to understand that time is always a dimension on these charts.
What is supply relationship?
But unlike the law of demand, the supply relationship shows an upward slope. This means that the higher the price, the higher the quantity supplied. From the seller's perspective, the opportunity cost of each additional unit ...
Why is the amount of a good that buyers purchase at a higher price less?
The amount of a good that buyers purchase at a higher price is less because as the price of a good goes up, so does the opportunity cost of buying that good. As a result, people will naturally avoid buying a product that will force them to forgo the consumption of something else they value more.
What could reduce the supply of coffee?
Possible supply shifters that could reduce supply include an increase in the prices of inputs used in the production of coffee, an increase in the returns available from alternative uses of these inputs, a decline in production because of problems in technology (perhaps caused by a restriction on pesticides used to protect coffee beans), a reduction in the number of coffee-producing firms, or a natural event, such as excessive rain.
What causes a shift in demand?
Demand shifters that could cause an increase in demand include a shift in preferences that leads to greater coffee consumption; a lower price for a complement to coffee, such as doughnuts; a higher price for a substitute for coffee, such as tea; an increase in income; and an increase in population . A change in buyer expectations, perhaps due to predictions of bad weather lowering expected yields on coffee plants and increasing future coffee prices, could also increase current demand.
How does an increase in demand for coffee affect the demand curve?
An increase in demand for coffee shifts the demand curve to the right, as shown in Panel (a) of Figure 3.17 “Changes in Demand and Supply”. The equilibrium price rises to $7 per pound. As the price rises to the new equilibrium level, the quantity supplied increases to 30 million pounds of coffee per month. Notice that the supply curve does not shift; rather, there is a movement along the supply curve.
What happens when the demand and supply curves change?
A shift in a demand or supply curve changes the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity for a good or service. Figure 3.17 “Changes in Demand and Supply” combines the information about changes in the demand and supply of coffee presented in Figure 3.2 “An Increase in Demand” Figure 3.3 “A Reduction in Demand” Figure 3.9 “An Increase in Supply” and Figure 3.10 “A Reduction in Supply” In each case, the original equilibrium price is $6 per pound, and the corresponding equilibrium quantity is 25 million pounds of coffee per month. Figure 3.17 “Changes in Demand and Supply” shows what happens with an increase in demand, a reduction in demand, an increase in supply, and a reduction in supply. We then look at what happens if both curves shift simultaneously. Each of these possibilities is discussed in turn below.
What does change in demand mean in equilibrium?
A change in demand or in supply changes the equilibrium solution in the model. Panels (a) and (b) show an increase and a decrease in demand, respectively; Panels (c) and (d) show an increase and a decrease in supply, respectively.
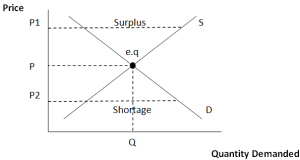
What happens to the price of a product when there is a shortage?
In the face of a shortage, sellers are likely to begin to raise their prices. As the price rises, there will be an increase in the quantity supplied (but not a change in supply) and a reduction in the quantity demanded (but not a change in demand) until the equilibrium price is achieved.
What happens when a price is above equilibrium?
Just as a price above the equilibrium price will cause a surplus, a price below equilibrium will cause a shortage. A shortage is the amount by which the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied at the current price.
What is supply in manufacturing?
Supply refers to the quantity of a commodity or service that is offered by the manufacturer at various prices to the customers during a given point of time.
What is demand in a market?
Demand is when a customer desires for a particular commodity at the given price in which they are ready to buy in one market at different prices during a certain period of time .
What does point E represent?
In the above graph, point E represents the intersection of both supply and demand, resulting in an equilibrium point.
What is equilibrium point?
The equilibrium point is a situation wherein the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of a commodity intersect. This represents the equilibrium price. It is the point at which both the buyers and the sellers are satisfied. Equilibrium is also called the market-clearing price or market equilibrium.
What is the difference between the vertical and horizontal axis of a supply curve?
In the above graph, the vertical axis represents the price of the commodity , while the horizontal axis is the quantity supplied. The Supply curve implies a direct relationship between the quantity supplied and price of the commodity.
When the price of a commodity rises, what happens to the demand for the commodity?
When there is a rise in the price of a commodity, the customer demands less quantity. Whereas, when the prices of the commodity fall, the demand for the commodity will rise.
What is the ability to pay?
Ability to pay: Customer’s purchasing power to pay the price for the desired commodity
What is the cost of a product?
The cost of a product, that is, the price at which the product will be purchased.
What factors affect supply?
There are certain factors that directly affect supply and determines whether there will be high or low supply. The capacity of a producer or company, the costs of producing specific items including cost of materials, labor, and equipment can affect supply. Other factors include the presence of competitors in the market. Also, if the production of an item is determined by weather, for instance, a company that manufactures sweaters, the supply of products will the determined by weather. The supply chain is another factor that affects supply.
What is the law of supply and demand?
The law of supply and demand is an economic theory that explains how demand and supply are connected and how these two concepts strive to find market balance or equilibrium price. Usually, when there is excess supply in the market and a low demand for the supplied products, there is a decrease in the price of goods. There are many factors that influence demand and supply. Supply and demand can rise for multiple reasons, so also can they decline. The law of supply and demand is connected to almost all economic principles, although there are exceptions.
Do the magnitudes of the two curves move in opposite directions?
In this case, although the two curves move in opposite directions, the magnitudes of their shifts is effectively the same. As a result, the equilibrium quantity remains the same but the equilibrium price falls.
Which direction does the demand curve shift?
This condition translates to the fact that the demand curve shifts leftwards whereas the supply curve shifts rightwards. As they move in opposite directions, the final market conditions are deduced by pointing out the magnitude of their shifts. Here, three cases further arise which are as follows:
When the increase is demand is less than the increase in supply, the right shift of the demand curve is less than the
When the increase is demand is less than the increase in supply, the right shift of the demand curve is less than the right shift of supply curve. In this case, the equilibrium price falls whereas the equilibrium quantity rises.
Which shift of the demand curve is more relative to the supply curve?
In such a case, the right shift of the demand curve is more relative to that of the supply curve. Effectively, both equilibrium price and quantity tend to increase.
What happens when the equilibrium price is the same?
If the increase in both demand and supply is exactly equal, there occurs a proportionate shift in the demand and supply curve. Consequently, the equilibrium price remains the same. However, the equilibrium quantity rises. The increase in demand > increase in supply.
What happens when the decrease in demand is greater than the decrease in supply?
When the decrease in demand is greater than the decrease in supply, the demand curve shifts more towards left relative to the supply curve. Effectively, there is a fall in both equilibrium quantity and price. The decrease in demand < decrease in supply.
How to determine final market conditions?
The final market conditions can be determined only by a deduction of the magnitude of the decrease in both demand and supply. In fact, both the demand and supply curve shift towards the left. Essentially, there is a need to compare their magnitudes. Such conditions are better analyzed by dividing this case further into three:
What Is The Law of Supply and Demand?
Understanding The Law of Supply and Demand
- The law of supply and demand, one of the most basic economic laws, ties into almost all economic principles somehow. In practice, people's willingness to supply and demand a good determines the market equilibrium price or the price where the quantity of the good that people are willing to supply equals the quantity that people demand. However, multiple factors can affe…
Shifts vs. Movement
- For economics, the "movements" and "shifts" in relation to the supply and demand curves represent very different market phenomena. A movement refers to a change along a curve. On the demand curve, a movement denotes a change in both price and quantity demanded from one point to another on the curve. The movement implies that the demand relationship remains cons…
Equilibrium Price
- Also called a market-clearing price, the equilibriumprice is the price at which the producer can sell all the units he wants to produce, and the buyer can buy all the units he wants. With an upward-sloping supply curve and a downward-sloping demand curve, it is easy to visualize that the two will intersect at some point. At this point, the market price is sufficient to induce suppliers to bri…
Factors Affecting Supply
- Supply is largely a function of production costs, including:
- Labor and materials (which reflect their opportunity costs of alternative uses to supply consumers with other goods)
- The physical technology available to combine inputs
- The number of sellers and their total productive capacity over the given time frame
Factors Affecting Demand
- Consumer preferences among different goods are the most important determinant of demand. The existence and prices of other consumer goods that are substitutes or complementary products can modify demand. Changes in conditions that influence consumer preferences can also be significant, such as seasonal changes or the effects of advertising. Changes in incomes …