
Full Answer
Why were the Barbary States declaring war?
The principle cause of the war was that those states harbored and supported the actions of pirates against American shipping vessels in the Mediterranean Sea. Subsequently, question is, how was conflict between the Barbary states and the United States resolved?
How many people died in the Barbary Wars?
The Barbary Wars were a series of conflicts culminating in two main wars fought between the United States, Sweden, and the Barbary states (Ottoman Empire, including Tunis, Algiers, and Tripoli) of North Africa in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. Barbary Wars United States: 45 killed 94 wounded 853 dead Popular
When was War landed on Britain?
The military history of the United Kingdom in World War II covers the Second World War against the Axis powers, starting on 3 September 1939 with the declaration of war by the United Kingdom and France, followed by the UK's Dominions and Crown colonies, on Nazi Germany in response to the invasion of Poland by Germany. There was little, however, the Anglo-French alliance could do or did do to ...
When did the First Boer War end?
The First Boer War (Afrikaans: Eerste Vryheidsoorlog, literally "First Freedom War"), 1880–1881, also known as the First Anglo-Boer War, the Transvaal War or the Transvaal Rebellion, was a war fought from 16 December 1880 until 23 March 1881 between the United Kingdom and Boers of the Transvaal (as the South African Republic was known while under British administration).
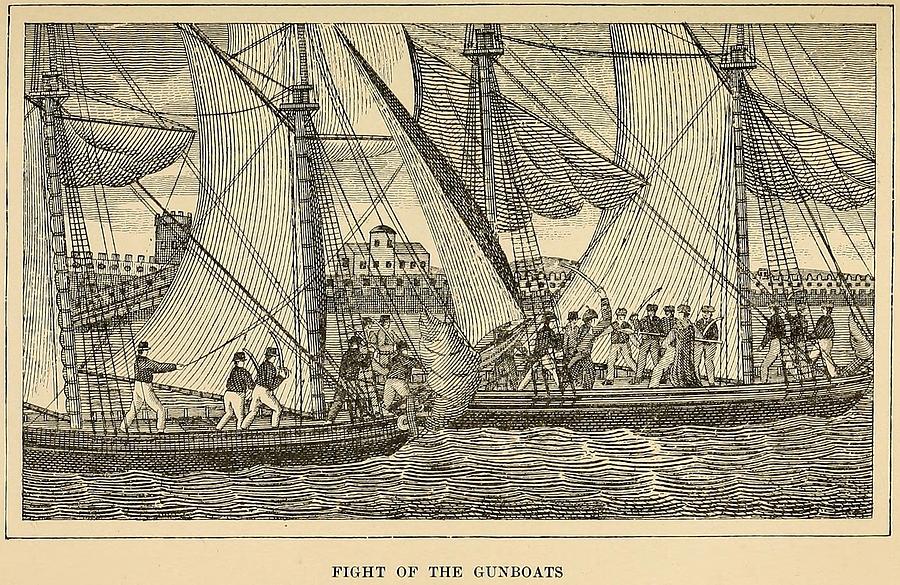
How did Thomas Jefferson end the Barbary War?
The combination of a strong American naval blockade and an overland expedition from Egypt finally brought the war to a close, with a treaty of peace (June 4, 1805) favourable to the United States. The other Barbary rulers, though considerably chastened, continued to receive some tribute until 1816.
What was the Barbary War and why did it occur?
The Barbary States were a collection of North African states, many of which practiced state-supported piracy in order to exact tribute from weaker Atlantic powers. Morocco was an independent kingdom, Algiers, Tunis, and Tripoli owed a loose allegiance to the Ottoman Empire.
Did the US win the Barbary Wars?
The Barbary Wars were a series of two wars fought by the United States, Sweden, and the Kingdom of Sicily against the Barbary states (including Tunis, Algiers, and Tripoli) of North Africa in the early 19th century....Barbary Wars.DateMay 10, 1801 – June 10, 1805 & June 17–19, 1815LocationBarbary CoastResultUnited States victory
Where was the Barbary War fought?
Mediterran... SeaTripoliDernaNorthwest AfricaFirst Barbary War/Locations
What race are Barbary pirates?
The Barbary pirates were mostly Berbers, Arabs, and other Muslims, but some came from Christian Europe. The pirates used small, fast-moving vessels to capture trading ships and their cargoes. They held the crews and passengers for ransom or sold them as slaves. Each of the four Barbary States had its own ruler.
Do the Barbary pirates still exist?
Do Barbary pirates still exist? The Barbary pirates who hailed from the northern African countries of Morocco, Algeria, Tunis, and Tripoli operated throughout the Mediterranean from medieval times until the 19th century. The Barbary pirates ceased to exist in 1830, when France secured control of Algeria.
How many slaves did the Barbary pirates take?
According to Robert Davis, between 1 million and 1.25 million Europeans were captured by Barbary pirates and sold as slaves in North Africa and The Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 19th centuries.
Who stopped the Barbary pirates?
FrenchFollowing the Napoleonic Wars and the Congress of Vienna in 1814–15, European powers agreed upon the need to suppress the Barbary corsairs entirely. The threat was finally subdued by the French conquest of Algeria in 1830 and subsequent pacification by the French during the mid-to-late 19th century.
Why did Jefferson fight the Barbary pirates?
The participation of the United States was due to pirates from the Barbary States seizing American merchant ships and holding the crews for ransom, demanding that the United States pay tribute to the Barbary rulers. United States President Thomas Jefferson refused to pay this tribute.
Who Won the First Barbary War?
the United StatesThe First Barbary War (1801-1805) was the first overseas war conducted by the United States. The nations on the Barbary Coast of Morocco involved were Algiers, Tunis and Tripoli. The war ended in victory for the United States, with peace treaties between the three Barbary States and Morocco.
What is the meaning of Barbary?
noun. : a tailless monkey (Macaca sylvanus) of northern Africa and Gibraltar. See the full definition.
What did the Barbary Wars prove?
The war, which lasted from 1801 to 1805, did not completely end the acts of piracy against American vessels, but it did prove that the United States was capable of waging war, if necessary, in places far from its own shores.
Why was the First Barbary War important?
The First Barbary War was important for several reasons: It was the first foreign war conducted by the United States and was fought entirely overseas on land and water. Prior to the war, the United States ended the practice of paying tribute to the Barbary States.
What are the effects of the Barbary Wars?
The main long-term outcome of the wars was the establishment of the US as a global player and a naval/military force. In particular, in the US it established the precedent of utilizing the Navy to accomplish diplomatic goals but also established many smaller traditions and more abstract concepts.
What is the meaning of Barbary?
noun. : a tailless monkey (Macaca sylvanus) of northern Africa and Gibraltar. See the full definition.
What was the name of the war between the United States and Libya?
Alternative Title: Tripolitan War. First Barbary War, also called Tripolitan War, (1801–05), conflict between the United States and Tripoli (now in Libya), incited by American refusal to continue payment of tribute to the piratical rulers of the North African Barbary States of Algiers, Tunis, Morocco, and Tripoli.
What brought the war to a close?
The combination of a strong American naval blockade and an overland expedition from Egypt finally brought the war to a close, with a treaty of peace (June 4, 1805) favourable to the United States. The other Barbary rulers, though considerably chastened, continued to receive some tribute until 1816.
What frigate was seized by Tripolitan gunboats?
The U.S. frigate Philadelphia being seized by Tripolitan gunboats in Tripoli's harbour during the Tripolitan War, undated engraving. Library of Congress, Washington, D.C. A demand from the pasha of Tripoli for greater tribute and his dramatic declaration of war on the United States (May 14, 1801) coincided with a decision by U.S. Pres.
Who was the commander of the Mediterranean squadron in 1803?
During the following years, American warships fought in the waters around Tripoli, and, in 1803, when Commodore Edward Preblebecame commander of the Mediterranean squadron, greater successes ensued. The intrepidPreble sailed into Tangiers to rescue a number of American prisoners, and, on February 16, 1804, he ordered his young lieutenant, Stephen Decatur, to undertake the spectacular raid in which the captured U.S. frigate Philadelphiawas destroyed in the harbour of Tripoli.
Who was the lieutenant of the Preble?
The intrepid Preble sailed into Tangiers to rescue a number of American prisoners, and, on February 16, 1804, he ordered his young lieutenant, Stephen Decatur, to undertake the spectacular raid in which the captured U.S. frigate Philadelphia was destroyed in the harbour of Tripoli.
Where did the Barbary Corsairs live?
Labelled as such for their shared homeland on the North African (Barbary) coast, particularly the ports of Tunis, Algiers and Tripoli, these seafarers never really operated as a single organized group.
What happened to the Bey of Algiers?
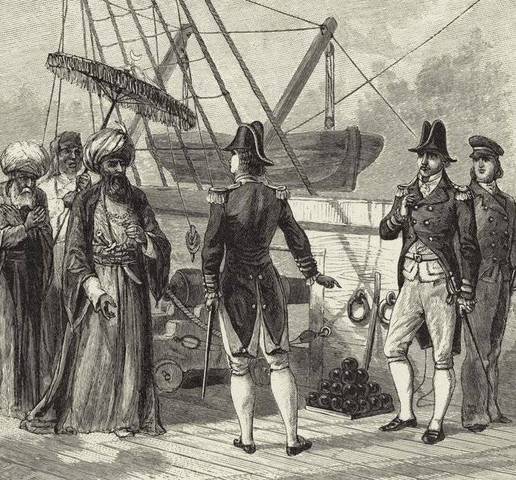
The Bey of Algiers, now facing pressure from both Britain and the Netherlands as well as the United States, surrendered to Decatur. North African piracy proved to be a difficult problem until 1830, when French conquest and colonization of the region put an end to the issue for good.
What happened in 1804?
On a late February morning in 1804, Lord Horatio Nelson, busy besieging the French Mediterranean port of Toulon, heard some news about a conflict to the south between the Barbary pirates of Tripoli and a group of American seamen. The way he heard it, the pirates had managed to get their hands on an American frigate, the USS Philadelphia, ...
Who was the most famous naval officer in history?
Upon hearing this news, Lord Nelson, perhaps the most famous naval military figure in history, simply declared the American’s feat “the most bold and daring act of the Age.”. He was not the only figure to heap praise upon the American Navy.
What were the Barbary States?
The Barbary States were a collection of North African states, many of which practiced state-supported piracy in order to exact tribute from weaker Atlantic powers. Morocco was an independent kingdom, Algiers, Tunis, and Tripoli owed a loose allegiance to the Ottoman Empire. The United States fought two separate wars with Tripoli (1801–1805) and Algiers (1815–1816), although at other times it preferred to pay tribute to obtain the release of captives held in the Barbary States.
Which two European powers encouraged the Barbary States' policy and paid tribute to them?
The two major European powers, Great Britain and France, found it expedient to encourage the Barbary States’ policy and pay tribute to them, as it allowed their merchant shipping an increased share of the Mediterranean trade, and Barbary leaders chose not to challenge the superior British or French navies.
What was the name of the treaty that Decatur signed with the Barbary States?
In Tripoli, Decatur also secured from Pasha Qaramanli the release of all European captives. The U.S. Senate ratified Decatur’s Algerian treaty on December 5, 1815.
How many wars did the United States fight?
The United States fought two separate wars with Tripoli (1801–1805) and Algiers (1815–1816), although at other times it preferred to pay tribute to obtain the release of captives held in the Barbary States. The Barbary Wars. The practice of state-supported piracy and ransoming of captives was not wholly unusual for its time.
What was the practice of state-supported piracy and ransoming of captives?
The practice of state-supported piracy and ransoming of captives was not wholly unusual for its time. Many European states commissioned privateers to attack each others’ shipping and also participated in the transatlantic slave trade.
How many sailors were freed by the Treaty of Algiers?
The treaty with Algiers freed 83 American sailors. The adoption of the Constitution in 1789 gave the U.S. Government the power to levy taxes and to raise and maintain armed forces, powers which had been lacking under the Articles of Confederation.
Who declared war on the United States?
In 1785, Dey Muhammad of Algiers declared war on the United States and captured several American ships. The financially troubled Confederation Government of the United States was unable to raise a navy or the tribute that would protect U.S. ships. In contrast to the dispute with Algiers, U.S. negotiations with Morocco went well.
What was the first barbary war?
The First Barbary War (1801–1805), also known as the Tripolitan War and the Barbary Coast War, was the first of two Barbary Wars, in which the United States and Sweden fought against the four North African states known collectively as the " Barbary States ". Three of these were autonomous, but nominally provinces of the Ottoman Empire: Tripoli, ...
Why was the Barbary War important?
The First Barbary War was beneficial to the reputation of the United States' military command and war mechanism, which had been up to that time relatively untested. The First Barbary War showed that America could execute a war far from home, and that American forces had the cohesion to fight together as Americans rather than separately as Georgians, New Yorkers, etc. The United States Navy and Marines became a permanent part of the American government and American history, and Decatur returned to the U.S. as its first post-revolutionary war hero.
What was the cause of the U.S. participation in the Barbary War?
The fourth was the independent Sultanate of Morocco. The cause of the U.S. participation was pirates from the Barbary States seizing American merchant ships and holding the crews for ransom, demanding the U.S. pay tribute to the Barbary rulers. United States President Thomas Jefferson refused to pay this tribute.
How much money did the Barbary Coast States demand?
All four Barbary Coast states demanded $660,000 each. However, the envoys were given only an allocated budget of $40,000 to achieve peace. Diplomatic talks to reach a reasonable sum for tribute or for the ransom of the captured sailors struggled to make any headway.
Why did the Barbary Corsairs attack the US?
Barbary corsairs led attacks upon American merchant shipping in an attempt to extort ransom for the lives of captured sailors, and ultimately tribute from the United States to avoid further attacks, as they did with the various European states. Before the Treaty of Paris, which formalized the United States' independence from Great Britain, U.S. shipping was protected by France during the revolutionary years under the Treaty of Alliance (1778–83). Although the treaty does not mention the Barbary States in name, it refers to common enemies between both the U.S. and France. As such, piracy against U.S. shipping only began to occur after the end of the American Revolution, when the U.S. government lost its protection under the Treaty of Alliance.
Where did the Barbary Corsairs and crews come from?
Barbary corsairs and crews from the quasi-independent North African Ottoman provinces of Algiers, Tunis, Tripoli, and the independent Sultanate of Morocco under the Alaouite dynasty (the Barbary Coast) were the scourge of the Mediterranean.
Who won the Barbary War?
was unable to respond to the provocation until 1815, with the Second Barbary War, in which naval victories by Commodores William Bainbridge and Stephen Decatur led to treaties ending all tribute payments by the U.S.
What was the Barbary War?
The Barbary wars were a series of conflicts that led to two wars fought on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea during the late 18th and early 19th centuries. The wars involved the Barbary states of North Africa and the United States, ...
Where were the Barbary Wars fought?
The Conflict. The Barbary Wars were fought in the waters off the coast of Algiers, Algeria and other North African cities. The pirates caused the United States of America’s navy to engage them in a series of battles in the areas where piracy was rampant in a bid to end the escalating menace.
What was the cause of the Barber Pirates?
The cause of the conflicts was the prevalence of Barber pirates in the Mediterranean demanding trading fees from ships and ransoms for releasing captured crewmen. These wars were fought more than once in the cities of Tripoli, Algiers, and present-day Morocco during the rule of the Ottoman Empire in North Africa.
What was the significance of the Barbary War?
The Barbary wars gave the newly formed United States of America an opportunity to present itself as a strong nation capable of standing for itself defensively against its enemies. The wars created a new relationship between the United States of America and the Northern African nations.
What happened to the British Empire in the 1780s?
During the 1780s, just after the United States of America became an independent state, the British Empire ceased to protect American ships using the route. When the Barbary pirates learnt of this new development, they jumped on the opportunity by robbing and hijacking the ships.
What happened after the war ended?
After the war ended, the pirates retreated and allowed fair passage to the ships. It was not long before the pirates struck again and started making it difficult for the ships to ply that route. President James Madison, Jefferson's successor, directed the US military to engage the pirates in the second war in 1815.
What cities were pirates in before the war?
Prior to the wars, pirates in the Barber cities of Tripoli, Algiers, and Tunis would demand a levy from trade ships plying these routes. Ships that refused to pay the demanded fee were hijacked and had their goods stolen.
When did Madison declare the Barbary War over?
December 15th — Madison declares the Barbary War over; American squadrons still patrol the Mediterranean
How much money did Congress raise to purchase peace with the Barbary States?
Congress raises one million dollars to purchase peace with the Barbary States and begins to construct a small naval force
What was the act passed by Congress on February 6th?
February 6th — Congress passes the Act for Protection of Commerce and Seamen of the United States Against the Tripolitian Corsairs, essentially a declaration of war
What was the name of the treaty between the United States and Great Britain that ended the War of 1812?
December 24th — United States and Great Britain sign the Treaty of Ghent, ending the War of 1812
What happened on September 3rd?
September 3rd — Signing of the Treaty of Paris ends the American war for independence; American ships are no longer protected under British treaties.
When did William Bainbridge surrender?
October 31st — William Bainbridge and his warship the Philadelphia surrender to Tripoli after running aground in Tripoli harbor
Who attacked Derna?
April 27th — After a two month march across the Libyan desert, William Eaton, former Tripoli Pasha Hamet Karamanli, and a group of mercenaries attack Derna by land, meanwhile three US warships under Captain Isaac Hull strike Derna by sea; together they take the fort
When was the Barbary War?
Barbary Warfare. Treaties with The Barbary Powers: 1786–1836. Text of the treaty signed in Algiers 30 June And 3 July 1815. The Barbary Wars at the Clements Library: An online exhibit on the Barbary Wars with images and transcriptions of primary documents from the period.
What war led to the Barbary War?
See also: Barbary slave trade. The First Barbary War (1801–05) had led to an uneasy truce between the US and the Barbary states, but American attention turned to Britain and the War of 1812.
What did Pellew warn the Dey of?
Pellew warned that if the terms were not accepted, he would continue the action. The Dey accepted the terms, but Pellew had been bluffing since his fleet had already spent all its ammunition. A treaty was signed on 24 September 1816.
What countries were colonized by France after the Second Barbary War?
However, in the years immediately following the Second Barbary War, there was no general European war, which allowed the Europeans to build up their resources and challenge Barbary power in the Mediterranean without distraction. Algiers and Tunis were seized and colonized by France in 1830 and 1881, respectively.
How many slaves were freed in the First Barbary War?
The British Consul and 1,083 other Christian slaves were freed, and the U.S. ransom money repaid. After the First Barbary War, the European nations had been engaged in warfare with one another and the U.S. with the British.
What did the British do to help the Deys?
In early 1816, Britain undertook a diplomatic mission, backed by a small squadron of ships of the line, to Tunis, Tripoli, and Algiers to convince the Deys to stop their piracy and free enslaved European Christians. The Beys of Tunis and Tripoli agreed without any resistance, but the Dey of Algiers was less cooperative, and the negotiations were stormy. The leader of the diplomatic mission, Edward Pellew, believed that he had negotiated a treaty to stop the slavery of Christians and returned to England. However, just after the treaty was signed, Algerian troops massacred 200 Corsican, Sicilian and Sardinian fishermen who had been under British protection thanks to the negotiation. This caused outrage in Britain and Europe, and Pellew's negotiations were seen as a failure.
What happened on August 27th 1816?
On 27 August 1816, following a round of failed negotiations, the fleet delivered a punishing nine-hour bombardment of Algiers. The attack immobilized many of the Dey's corsairs and shore batteries, forcing him to accept a peace offer of the same terms that he had rejected the day before.
What was the practice of state supported piracy and ransoming of captives?
The practice of state-supported piracy and ransoming of captives was not wholly unusual for its time. Many European states commissioned privateers to attack each others' shipping and also participated in the transatlantic slave trade. The two major European powers, Great Britain and France, found it expedient to encourage the Barbary States' policy and pay tribute to them, as it allowed their merchant shipping an increased share of the Mediterranean trade, and Barbary leaders chose not to challenge the superior British or French navies.
What was the purpose of the Treaty of 1793?
In 1793 a brief Portuguese-Algerian truce exposed American merchant ships to capture, forcing the United States, which had thus far only managed to conclude a treaty with Morocco, to engage in negotiations with the other Barbary States. In 1795, The U.S. Government dispatched diplomats Joel Barlow, Joseph Donaldson, and Richard O'Brien to North Africa and successfully concluded treaties with the states of Algiers, Tunis, and Tripoli. Under the terms of these treaties, the United States agreed to pay tribute to these states. The treaty with Algiers freed 83 American sailors.

Overview
The First Barbary War (1801–1805), also known as the Tripolitan War and the Barbary Coast War, was the first of two Barbary Wars, in which the United States and Sweden fought against the four North African states known collectively as the "Barbary States".
The participation of the United States was due to pirates from the Barbary Stat…
Background and overview
Barbary corsairs and crews from the quasi-independent North African Ottoman provinces of Algiers, Tunis, Tripoli, and the independent Sultanate of Morocco under the Alaouite dynasty (the Barbary Coast) were the scourge of the Mediterranean. Capturing merchant ships and enslaving or ransoming their crews provided the rulers of these nations with wealth and naval power. The Tr…
Declaration of war and naval blockade
Just before Jefferson's inauguration in 1801, Congress passed naval legislation that, among other things, provided for six frigates that "shall be officered and manned as the President of the United States may direct." In the event of a declaration of war on the United States by the Barbary powers, these ships were to "protect our commerce and chastise their insolence—by sinking, burning or …
Battles
In October 1803, Tripoli's fleet captured USS Philadelphia intact after the frigate ran aground on a reef while patrolling Tripoli harbor. Efforts by the Americans to float the ship while under fire from shore batteries and Tripolitan Naval units failed. The ship, her captain, William Bainbridge, and all officers and crew were taken ashore and held as hostages. Philadelphia was turned against the Ameri…
Peace treaty and legacy
Wearied of the blockade and raids, and now under threat of a continued advance on Tripoli proper and a scheme to restore his deposed older brother Hamet Karamanli as ruler, Yusuf Karamanli signed a treaty ending hostilities on 10 June 1805. Article 2 of the treaty reads:
The Bashaw of Tripoli shall deliver up to the American squadron now off Tripoli, all the Americans in his possession; and all the subjects of the Bashaw of Tripoli now in the power of the United St…
Monument
The Tripoli Monument, the oldest military monument in the United States, honors the American heroes of the First Barbary War: Master Commandant Richard Somers, Lieutenant James Caldwell, James Decatur (brother of Stephen Decatur), Henry Wadsworth, Joseph Israel and John Dorsey. Originally known as the Naval Monument, it was carved of Carrara marble in Italy in 1806 and brought to the United States on board Constitution ("Old Ironsides"). From its original location in t…
See also
• Barbary slave trade
• Barbary treaties
• Islamic views on slavery
• Military history of the United States
• Second Barbary War
Bibliography
• Farber, Hannah (2014), "Millions for Credit: Peace with Algiers and the Establishment of America's Commercial Reputation Overseas, 1795–96.", Journal of the Early Republic, 34 (2): 187–217, doi:10.1353/jer.2014.0028, S2CID 154186346
• Keynes, Edward (2004), Undeclared War, Penn State Press, ISBN 978-0-271-02607-7